Vote buying undermines democratic integrity by coercing voters with money or gifts to influence their choice, whereas electoral fraud involves illegal manipulation of the voting process, such as tampering with ballots or miscounting votes. Both practices distort election outcomes and erode public trust in political systems, but vote buying directly targets voter behavior while electoral fraud attacks the procedural fairness of elections. Addressing these issues requires robust legal frameworks, transparent electoral monitoring, and voter education to safeguard democracy.
Table of Comparison
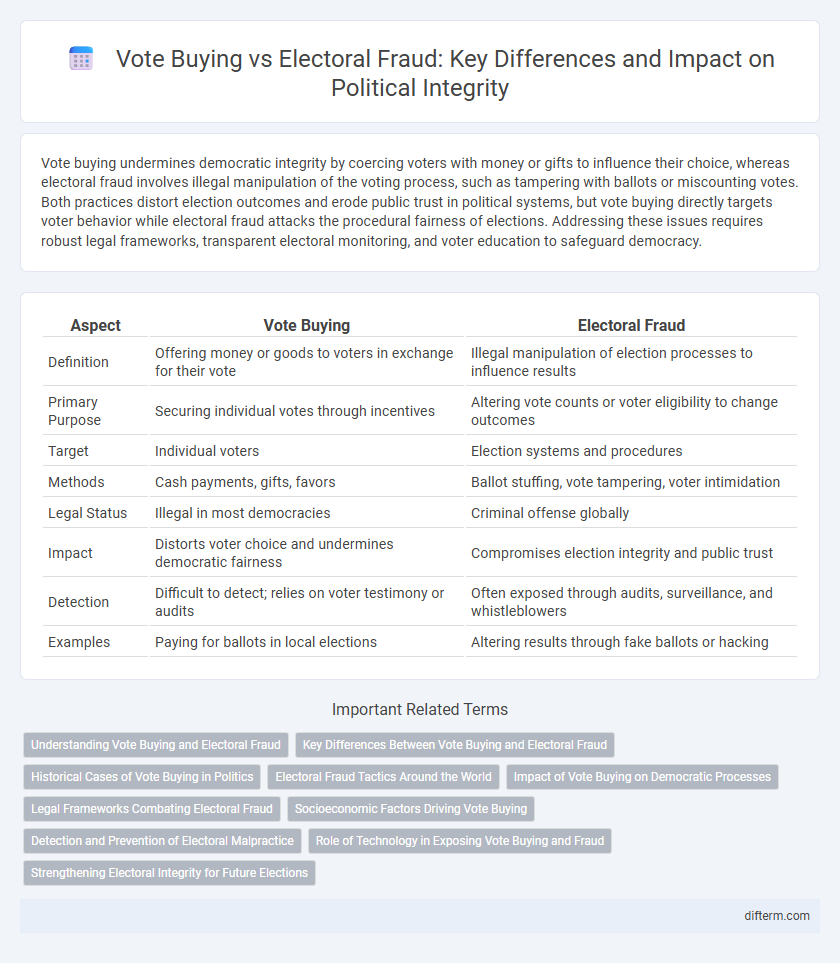
| Aspect | Vote Buying | Electoral Fraud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Offering money or goods to voters in exchange for their vote | Illegal manipulation of election processes to influence results |
| Primary Purpose | Securing individual votes through incentives | Altering vote counts or voter eligibility to change outcomes |
| Target | Individual voters | Election systems and procedures |
| Methods | Cash payments, gifts, favors | Ballot stuffing, vote tampering, voter intimidation |
| Legal Status | Illegal in most democracies | Criminal offense globally |
| Impact | Distorts voter choice and undermines democratic fairness | Compromises election integrity and public trust |
| Detection | Difficult to detect; relies on voter testimony or audits | Often exposed through audits, surveillance, and whistleblowers |
| Examples | Paying for ballots in local elections | Altering results through fake ballots or hacking |
Understanding Vote Buying and Electoral Fraud
Vote buying involves the direct exchange of money or goods for votes, undermining the democratic principle of free choice by coercing voters. Electoral fraud encompasses a broader range of illegal activities such as ballot stuffing, voter intimidation, and tampering with election results that distort the integrity of the electoral process. Understanding these practices is critical for implementing effective electoral reforms and safeguarding democratic institutions globally.
Key Differences Between Vote Buying and Electoral Fraud
Vote buying involves offering money or goods to voters in exchange for their support, directly influencing individual voting choices, whereas electoral fraud encompasses a broader range of illegal activities, including tampering with ballots, miscounting votes, or manipulating election results. While vote buying targets voter behavior, electoral fraud undermines the integrity of the entire electoral process through systemic corruption. Understanding these distinctions is critical for implementing effective legal frameworks and safeguarding democratic elections.
Historical Cases of Vote Buying in Politics
Historical cases of vote buying in politics reveal systematic manipulation where candidates provided money or goods to voters to secure support, impacting election integrity. Notable examples include the Tammany Hall political machine in 19th-century New York and vote buying during the 2010 Philippine general elections. These instances demonstrate how vote buying undermines democratic processes and skews representation, often making it difficult to distinguish from broader electoral fraud tactics.
Electoral Fraud Tactics Around the World
Electoral fraud tactics around the world include ballot stuffing, voter intimidation, and tampering with electronic voting machines, severely undermining democratic processes. In countries like Venezuela, ballot box stuffing and manipulation of voter rolls are common, while in Russia, media censorship and proxy voting distort election outcomes. These fraudulent practices erode public trust and distort legitimate electoral competition, contrasting with vote buying, which involves direct bribery rather than systemic interference.
Impact of Vote Buying on Democratic Processes
Vote buying undermines democratic processes by distorting voter preferences and eroding electoral integrity, often leading to skewed election outcomes and weakened public trust. This practice diverts political accountability as candidates prioritize financial exchanges over policy commitments, diminishing genuine political competition. The pervasive influence of vote buying perpetuates inequality in representation and hinders the development of transparent and fair democratic institutions.
Legal Frameworks Combating Electoral Fraud
Legal frameworks combating electoral fraud establish strict regulations and penalties targeting vote buying, ballot tampering, and voter intimidation to safeguard electoral integrity. Election commissions worldwide enforce comprehensive measures such as voter education, transparent ballot handling, and robust monitoring systems to detect and prevent illicit activities. International conventions like the Inter-American Convention Against Corruption supplement national laws by promoting accountability and encouraging cross-border cooperation in prosecuting electoral offenses.
Socioeconomic Factors Driving Vote Buying
Socioeconomic factors such as poverty, low education levels, and limited access to public services significantly drive vote buying, as vulnerable populations may exchange votes for immediate financial or material benefits. This practice disproportionately affects marginalized communities where economic insecurity incentivizes voters to accept bribes, undermining genuine political representation. Compared to broader electoral fraud tactics that manipulate vote counts or polling processes, vote buying directly exploits socioeconomic inequalities to influence election outcomes.
Detection and Prevention of Electoral Malpractice
Detecting vote buying and electoral fraud requires robust monitoring systems, including independent election commissions, biometric voter verification, and real-time data analytics to identify irregularities. Preventive measures encompass stringent legal frameworks, voter education campaigns to discourage malpractice, and the deployment of transparent ballot handling procedures. Effective collaboration between civil society organizations, technology providers, and law enforcement enhances the integrity and credibility of the electoral process.
Role of Technology in Exposing Vote Buying and Fraud
Advanced data analytics and blockchain technology significantly enhance the detection of vote buying and electoral fraud by providing transparent and tamper-proof voting records. Machine learning algorithms analyze voting patterns and social media activity to identify suspicious behavior indicative of vote buying schemes. Digital platforms increase accountability by enabling real-time monitoring and reporting, thereby strengthening the integrity of electoral processes.
Strengthening Electoral Integrity for Future Elections
Vote buying undermines democratic legitimacy by coercing voter choice through financial incentives, while electoral fraud manipulates results through illicit means such as ballot tampering or voter suppression. Strengthening electoral integrity requires robust legal frameworks, transparent monitoring systems, and widespread voter education to prevent both practices effectively. Implementing biometric voter identification and independent election oversight commissions enhances accountability and public trust in future elections.
Vote buying vs Electoral fraud Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com