Political decentralization transfers decision-making power to elected local authorities, enhancing democratic participation and accountability at the grassroots level. Administrative decentralization distributes managerial responsibilities within the central government's bureaucracy to improve efficiency and service delivery without shifting political authority. Balancing these types of decentralization is crucial for promoting local autonomy while maintaining cohesive national governance.
Table of Comparison
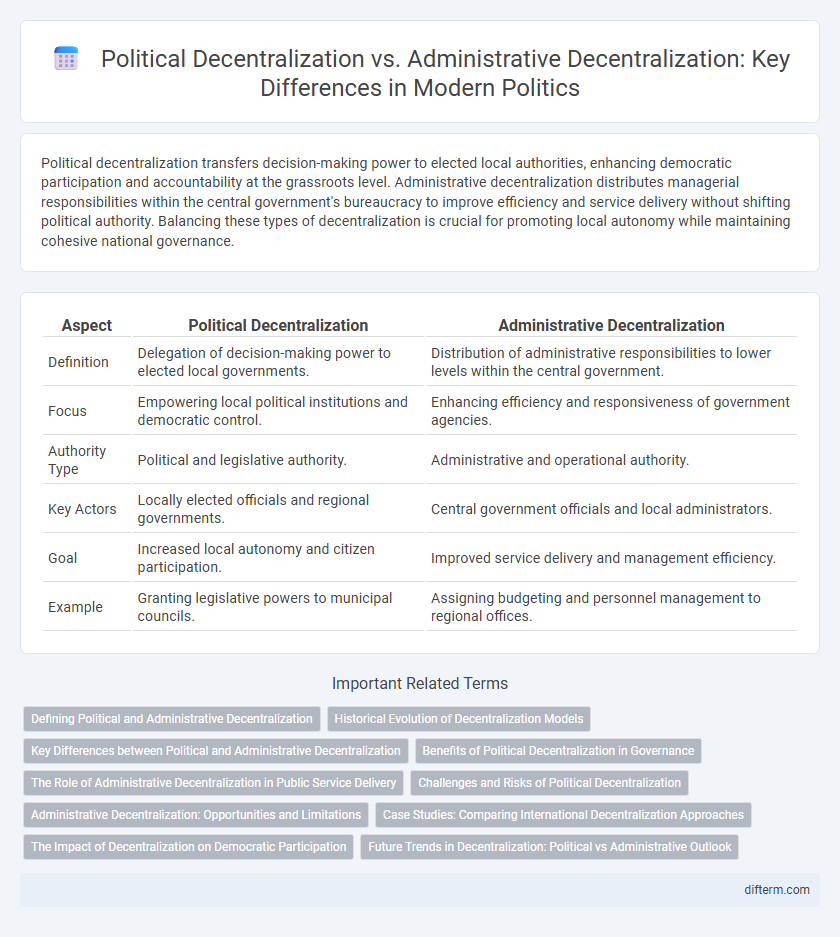
| Aspect | Political Decentralization | Administrative Decentralization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delegation of decision-making power to elected local governments. | Distribution of administrative responsibilities to lower levels within the central government. |
| Focus | Empowering local political institutions and democratic control. | Enhancing efficiency and responsiveness of government agencies. |
| Authority Type | Political and legislative authority. | Administrative and operational authority. |
| Key Actors | Locally elected officials and regional governments. | Central government officials and local administrators. |
| Goal | Increased local autonomy and citizen participation. | Improved service delivery and management efficiency. |
| Example | Granting legislative powers to municipal councils. | Assigning budgeting and personnel management to regional offices. |
Defining Political and Administrative Decentralization
Political decentralization involves transferring authority and decision-making power from central government to elected local governments, enhancing local political autonomy and accountability. Administrative decentralization redistributes planning, financing, and management responsibilities to lower levels of government or semi-autonomous agencies, aiming to improve efficiency and service delivery without necessarily altering political control. Understanding these definitions clarifies the distinction between empowering local elected bodies in political decentralization and delegating bureaucratic functions in administrative decentralization.
Historical Evolution of Decentralization Models
Political decentralization historically emphasizes transferring decision-making authority to elected local governments, fostering democratic participation and local accountability. Administrative decentralization dates back to colonial administrations restructuring governance by delegating administrative functions to regional offices to improve efficiency. Over time, hybrid models emerged, combining political autonomy with administrative delegation to balance local empowerment and centralized oversight.
Key Differences between Political and Administrative Decentralization
Political decentralization involves transferring decision-making power to elected local governments, enhancing political accountability and citizen participation. Administrative decentralization redistributes authority within the public sector, focusing on the delegation or deconcentration of tasks to lower-level officials without altering political control. The key difference lies in political decentralization emphasizing local autonomy and representative governance, whereas administrative decentralization prioritizes efficiency and improved service delivery through organizational restructuring.
Benefits of Political Decentralization in Governance
Political decentralization enhances governance by empowering local authorities to make decisions tailored to the specific needs and preferences of their communities, leading to increased responsiveness and accountability. It promotes citizen participation in the political process, fostering greater legitimacy and trust in government institutions. Furthermore, political decentralization can reduce the concentration of power, mitigating risks of authoritarianism and encouraging more balanced resource distribution.
The Role of Administrative Decentralization in Public Service Delivery
Administrative decentralization enhances public service delivery by delegating decision-making authority to lower levels of government, enabling more responsive and tailored services for local populations. This structure improves efficiency by reducing bureaucratic delays and encourages accountability through closer oversight by local officials. Effective administrative decentralization aligns resources with community needs, improving healthcare, education, and infrastructure outcomes.
Challenges and Risks of Political Decentralization
Political decentralization often faces challenges such as the risk of local elite capture, which can undermine democratic governance and exacerbate inequality. The fragmentation of authority may lead to inconsistent policy implementation and reduced national cohesion. Moreover, varying administrative capacities at the local level can hinder effective service delivery and accountability mechanisms.
Administrative Decentralization: Opportunities and Limitations
Administrative decentralization involves redistributing authority, responsibility, and resources from central governments to lower levels, such as regional or local agencies, enhancing efficiency and public service delivery. Opportunities include improved responsiveness to local needs, increased citizen participation, and greater accountability in governance structures. Limitations arise from potential coordination challenges, uneven resource distribution, and risks of local elite capture or bureaucratic inefficiency.
Case Studies: Comparing International Decentralization Approaches
Political decentralization redistributes decision-making authority to elected local governments, enhancing democratic participation in countries like Brazil and India, where regional autonomy fosters policy responsiveness. Administrative decentralization transfers managerial responsibilities to lower-level agencies or local offices, as seen in France and Kenya, which improves efficiency but maintains central government control. Comparative case studies reveal that political decentralization strengthens local governance legitimacy, whereas administrative decentralization primarily enhances service delivery without altering power dynamics.
The Impact of Decentralization on Democratic Participation
Political decentralization empowers local governments with decision-making authority, increasing citizen engagement and strengthening democratic participation by reducing the distance between government and the governed. Administrative decentralization reallocates bureaucratic responsibilities to subnational agencies, improving service delivery but often maintaining central political control, which may limit direct citizen influence. Studies show that political decentralization more effectively boosts democratic participation as it fosters accountability and responsiveness, essential for vibrant local democracies.
Future Trends in Decentralization: Political vs Administrative Outlook
Future trends in decentralization highlight a growing emphasis on political decentralization, empowering local governments with legislative and fiscal autonomy to enhance democratic participation and accountability. Administrative decentralization will increasingly focus on streamlining service delivery and improving efficiency through delegated authorities and capacity building at regional levels. The balance between political decentralization and administrative decentralization will shape governance reforms aimed at fostering responsive, transparent, and locally accountable institutions worldwide.
political decentralization vs administrative decentralization Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com