Libertarianism advocates for maximum individual freedom with minimal government intervention, emphasizing personal autonomy and free markets. Minarchism supports a limited government confined to protecting individual rights, typically focusing on defense, law enforcement, and judicial systems without extending into social or economic policies. Both ideologies prioritize liberty, but libertarianism often calls for even less government involvement than minarchism.
Table of Comparison
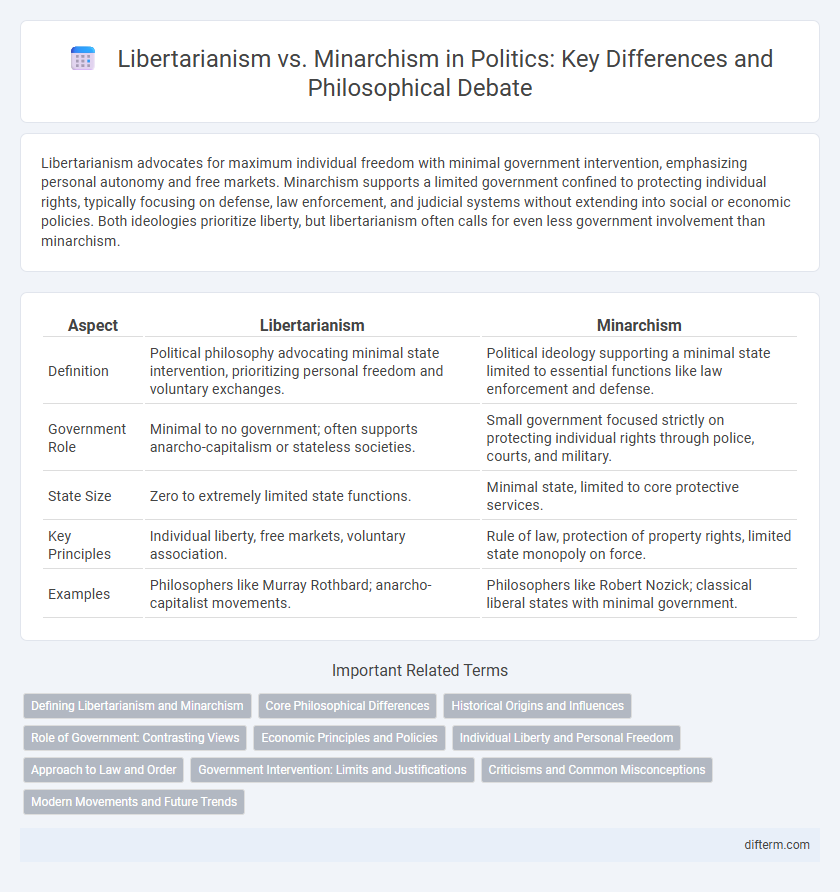
| Aspect | Libertarianism | Minarchism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political philosophy advocating minimal state intervention, prioritizing personal freedom and voluntary exchanges. | Political ideology supporting a minimal state limited to essential functions like law enforcement and defense. |
| Government Role | Minimal to no government; often supports anarcho-capitalism or stateless societies. | Small government focused strictly on protecting individual rights through police, courts, and military. |
| State Size | Zero to extremely limited state functions. | Minimal state, limited to core protective services. |
| Key Principles | Individual liberty, free markets, voluntary association. | Rule of law, protection of property rights, limited state monopoly on force. |
| Examples | Philosophers like Murray Rothbard; anarcho-capitalist movements. | Philosophers like Robert Nozick; classical liberal states with minimal government. |
Defining Libertarianism and Minarchism
Libertarianism advocates for maximizing individual freedom and minimizing state intervention, emphasizing personal autonomy and voluntary cooperation. Minarchism supports a minimal state limited to protecting individual rights through essential functions like law enforcement, defense, and judiciary. Both ideologies prioritize liberty but differ in the extent of government role, with libertarianism often favoring near-anarchistic principles while minarchism accepts a limited but necessary state apparatus.
Core Philosophical Differences
Libertarianism champions maximal individual freedom and minimal state intervention, advocating for voluntary associations and free markets without government coercion. Minarchism supports a limited government strictly confined to protecting individual rights through essential functions like law enforcement, defense, and judiciary. The core philosophical difference lies in libertarianism's skepticism of any state power versus minarchism's acceptance of a minimal state as necessary to prevent rights violations.
Historical Origins and Influences
Libertarianism and minarchism both emerged from classical liberalism and Enlightenment thought, emphasizing individual liberty and limited government. Key historical influences include John Locke's theories on natural rights and the social contract, which shaped early libertarian ideals advocating minimal state intervention. Minarchism evolved as a pragmatic offshoot, promoting the state's role in protecting individual rights through a minimal government, influenced by thinkers like Robert Nozick.
Role of Government: Contrasting Views
Libertarianism advocates for minimal government intervention, emphasizing individual freedom and free-market principles as the foundation of society. Minarchism supports a limited government role, restricted primarily to protecting citizens' rights through institutions like police, military, and courts. The core distinction lies in libertarianism's broader skepticism toward government functions, while minarchism accepts a minimal state presence to maintain law and order.
Economic Principles and Policies
Libertarianism advocates for minimal government intervention in markets to maximize individual economic freedom, emphasizing free trade, private property rights, and voluntary transactions. Minarchism supports a limited state primarily responsible for protecting property rights, enforcing contracts, and ensuring national defense, allowing markets to operate with minimal regulatory constraints. Both ideologies prioritize reducing taxation and deregulation but differ on the scope of government functions in economic affairs.
Individual Liberty and Personal Freedom
Libertarianism advocates for maximal individual liberty, emphasizing minimal government intervention to protect personal freedoms in all aspects of life. Minarchism supports a limited government focused solely on protecting individual rights, such as property and personal security, without extending control over economic or social decisions. Both philosophies prioritize personal freedom but differ in the extent of government presence, with libertarianism pushing for near-complete autonomy.
Approach to Law and Order
Libertarianism advocates for minimal state intervention, emphasizing individual freedom and voluntary associations to maintain law and order without extensive government control. Minarchism supports a limited government whose primary function is to enforce laws and protect property rights, relying on a legal system and policing to uphold societal order. Both philosophies prioritize personal liberty, but minarchism accepts state authority in law enforcement, whereas libertarianism often favors decentralized or privatized mechanisms.
Government Intervention: Limits and Justifications
Libertarianism advocates for minimal government intervention, emphasizing individual freedom and free markets as primary drivers of social order. Minarchism supports a limited government focused on essential functions like protecting property rights, enforcing contracts, and ensuring national defense, justifying intervention only to prevent coercion and uphold basic justice. Both philosophies reject expansive state control but differ in the scope of accepted government roles, with minarchism allowing narrowly defined, constitutionally legitimate powers to prevent anarchy.
Criticisms and Common Misconceptions
Libertarianism often faces criticism for its perceived impracticality in addressing large-scale social issues due to minimal government intervention, while minarchism is criticized for its ambiguous boundaries on the extent of state power, risking either overreach or ineffectiveness. Common misconceptions about libertarianism include conflating it with anarchism or neglecting social welfare, whereas minarchism is frequently misunderstood as merely a weaker form of authoritarianism rather than a principled limitation of government functions. Both ideologies grapple with debates over protecting individual liberties versus maintaining public order, making clarity around their principles essential for informed political discourse.
Modern Movements and Future Trends
Modern libertarianism emphasizes individual freedom and minimal state interference, advocating for broad civil liberties and free markets, while minarchism supports a minimal state limited primarily to protecting property rights and enforcing contracts. Current movements show libertarianism increasingly influencing digital rights and privacy debates, whereas minarchism finds support in discussions about constitutional reform and decentralized governance. Future trends indicate a blending of these philosophies through technological advances like blockchain and AI, potentially redefining the scope and role of government in society.
libertarianism vs minarchism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com