Social conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional values and cultural norms, often prioritizing family structures, religion, and moral standards in policy decisions. Fiscal conservatism focuses on limited government spending, reducing debt, and promoting free-market principles to ensure economic stability and growth. These two strands of conservatism can sometimes conflict when social policies require government intervention that challenges fiscal restraint.
Table of Comparison
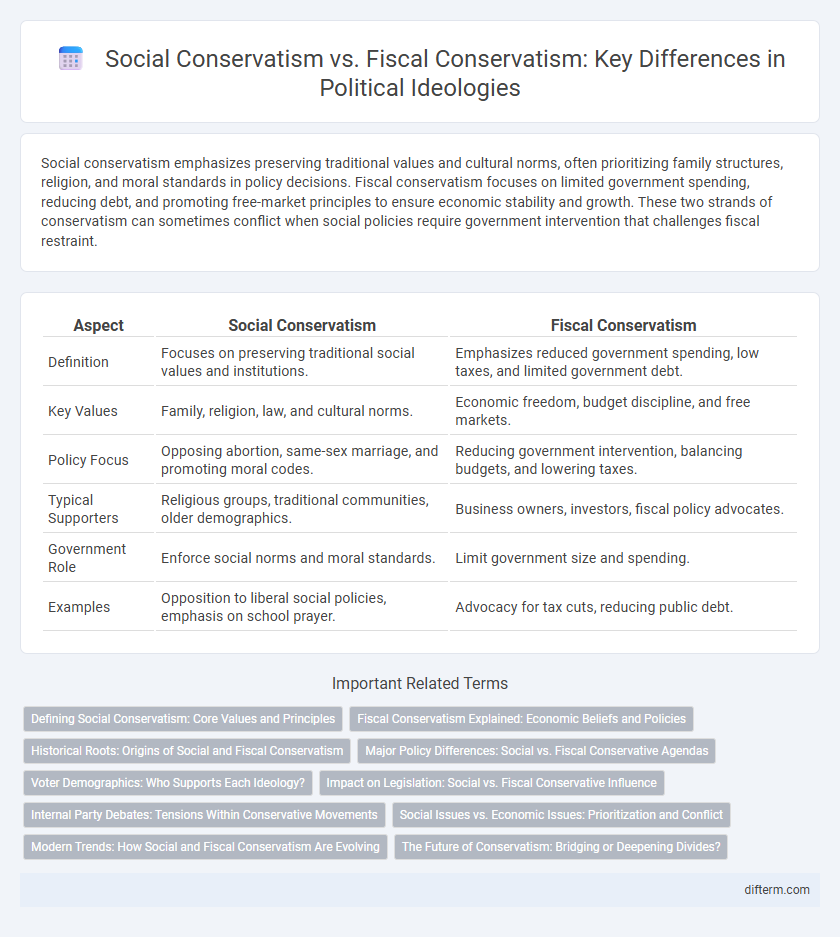
| Aspect | Social Conservatism | Fiscal Conservatism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on preserving traditional social values and institutions. | Emphasizes reduced government spending, low taxes, and limited government debt. |
| Key Values | Family, religion, law, and cultural norms. | Economic freedom, budget discipline, and free markets. |
| Policy Focus | Opposing abortion, same-sex marriage, and promoting moral codes. | Reducing government intervention, balancing budgets, and lowering taxes. |
| Typical Supporters | Religious groups, traditional communities, older demographics. | Business owners, investors, fiscal policy advocates. |
| Government Role | Enforce social norms and moral standards. | Limit government size and spending. |
| Examples | Opposition to liberal social policies, emphasis on school prayer. | Advocacy for tax cuts, reducing public debt. |
Defining Social Conservatism: Core Values and Principles
Social conservatism emphasizes the preservation of traditional values and institutions, advocating for policies that uphold family structures, religious beliefs, and social order. Core principles include moral objectivism, resistance to rapid cultural change, and support for laws reflecting community ethics. This ideology prioritizes societal cohesion and continuity over progressive reforms.
Fiscal Conservatism Explained: Economic Beliefs and Policies
Fiscal conservatism emphasizes limited government spending, reduced public debt, and low taxation to promote economic growth and individual financial responsibility. Proponents advocate for balanced budgets, minimal government intervention in markets, and policies that encourage private sector efficiency. This ideology prioritizes sustainable fiscal policies to ensure long-term economic stability and national competitiveness.
Historical Roots: Origins of Social and Fiscal Conservatism
Social conservatism traces its origins to 19th-century movements emphasizing traditional values, religious influence, and social order, reacting against rapid industrialization and cultural change. Fiscal conservatism emerged from classical liberal economic theories advocating limited government spending, balanced budgets, and free-market principles rooted in Enlightenment thought. Both strands evolved as responses to distinct societal challenges, with social conservatism addressing cultural stability and fiscal conservatism focusing on economic prudence.
Major Policy Differences: Social vs. Fiscal Conservative Agendas
Social conservatives prioritize policies that uphold traditional values such as family structure, religious freedom, and moral norms, often advocating for restrictions on abortion, same-sex marriage, and sex education. Fiscal conservatives concentrate on reducing government spending, lowering taxes, and minimizing regulation to promote economic growth and individual financial responsibility. These differing priorities influence legislative agendas, where social conservatives push for laws reflecting cultural and ethical concerns, while fiscal conservatives emphasize budgetary discipline and free-market principles.
Voter Demographics: Who Supports Each Ideology?
Social conservatism primarily attracts older, religious voters who prioritize traditional values and cultural norms, often concentrated in rural and suburban areas. Fiscal conservatism resonates more with higher-income individuals and business owners who emphasize limited government spending and free-market principles, frequently found in urban and affluent regions. Both ideologies find support among different segments of the Republican Party, influencing policy priorities and electoral strategies.
Impact on Legislation: Social vs. Fiscal Conservative Influence
Social conservatism shapes legislation by emphasizing traditional values, influencing laws on marriage, education, and reproductive rights that reflect moral and cultural priorities. Fiscal conservatism drives policies centered on limited government spending, tax reduction, and deregulation to promote economic growth and budgetary restraint. The balance between these ideologies in lawmaking often determines the scope and focus of government intervention across social issues and economic management.
Internal Party Debates: Tensions Within Conservative Movements
Internal party debates reveal significant tensions within conservative movements, as social conservatism emphasizes traditional values and cultural preservation, while fiscal conservatism prioritizes limited government spending and economic freedom. These ideological divides often manifest in discussions over policy priorities, such as funding for social programs versus tax cuts, highlighting the challenge in uniting the party's platform. The clash between upholding moral stances and pursuing economic efficiency continues to shape legislative agendas and electoral strategies.
Social Issues vs. Economic Issues: Prioritization and Conflict
Social conservatism prioritizes traditional values, family structures, and cultural norms, often emphasizing issues like marriage, abortion, and religious freedoms. Fiscal conservatism centers on economic policies such as reduced government spending, low taxation, and free-market principles to promote financial stability and growth. Conflicts arise when social conservatives push for government intervention in cultural matters while fiscal conservatives advocate for limited government involvement, revealing tension between social regulation and economic freedom.
Modern Trends: How Social and Fiscal Conservatism Are Evolving
Modern trends reveal an increasing divergence between social conservatism, which emphasizes traditional values on issues like family and morality, and fiscal conservatism, prioritized by limited government spending and free-market policies. Political parties and policymakers are adapting to these evolving dynamics by tailoring campaigns and policy platforms to address these distinct voter bases. Data from recent elections indicate that younger conservatives tend to favor fiscal restraint while showing more openness to progressive social policies, reshaping the conservative landscape in the 21st century.
The Future of Conservatism: Bridging or Deepening Divides?
Social conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional cultural values and social norms, often prioritizing issues like family structures, religion, and moral policies. Fiscal conservatism advocates for limited government spending, reduced taxation, and free-market principles to ensure economic stability and growth. The future of conservatism hinges on whether these two branches can find common ground or if their differing priorities will deepen ideological divides within the movement.
social conservatism vs fiscal conservatism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com