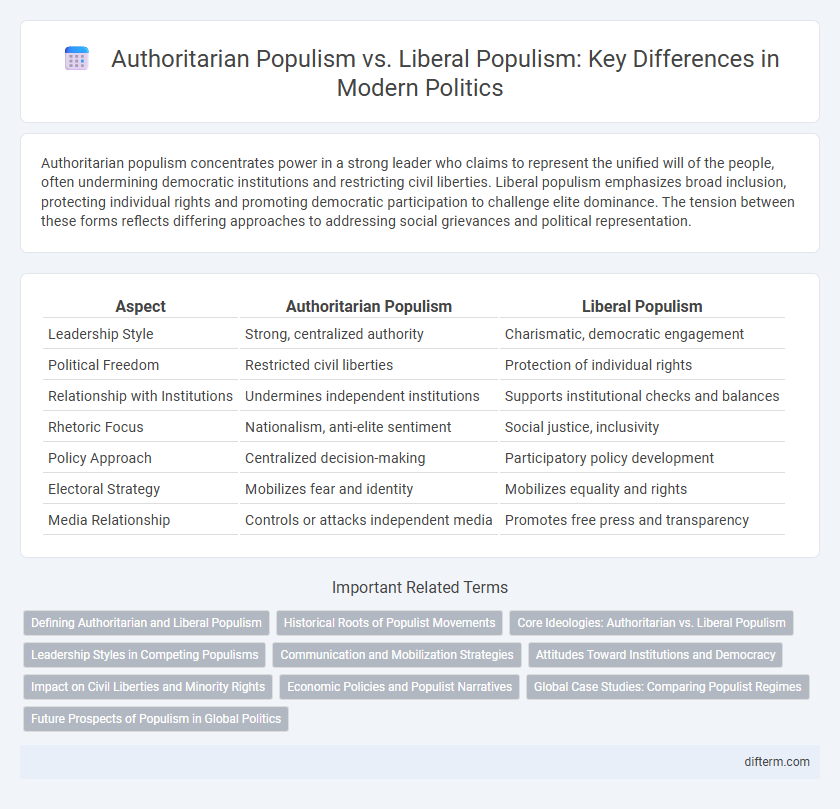
Authoritarian populism concentrates power in a strong leader who claims to represent the unified will of the people, often undermining democratic institutions and restricting civil liberties. Liberal populism emphasizes broad inclusion, protecting individual rights and promoting democratic participation to challenge elite dominance. The tension between these forms reflects differing approaches to addressing social grievances and political representation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Authoritarian Populism | Liberal Populism |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership Style | Strong, centralized authority | Charismatic, democratic engagement |
| Political Freedom | Restricted civil liberties | Protection of individual rights |
| Relationship with Institutions | Undermines independent institutions | Supports institutional checks and balances |
| Rhetoric Focus | Nationalism, anti-elite sentiment | Social justice, inclusivity |
| Policy Approach | Centralized decision-making | Participatory policy development |
| Electoral Strategy | Mobilizes fear and identity | Mobilizes equality and rights |
| Media Relationship | Controls or attacks independent media | Promotes free press and transparency |
Defining Authoritarian and Liberal Populism
Authoritarian populism centers on a strong, centralized leadership that claims to represent the "true people" against perceived enemies, often undermining democratic institutions and curbing civil liberties. Liberal populism emphasizes inclusive democracy, advocating for expanded political participation and protection of minority rights while challenging elite corruption and promoting social justice. These contrasting models reveal diverging approaches to power, governance, and the role of popular sovereignty in modern political systems.
Historical Roots of Populist Movements
Authoritarian populism traces its historical roots to early 20th-century movements that emphasized strong, centralized leadership and nationalist rhetoric, often emerging during periods of social unrest and economic instability. Liberal populism, in contrast, originated from 19th-century democratic reforms advocating for expanded political participation, social justice, and protection of individual rights against elite dominance. Both variants draw on populist traditions that challenge established power structures but diverge in governance philosophy and ideological goals.
Core Ideologies: Authoritarian vs. Liberal Populism
Authoritarian populism centers on centralized power, strong leadership, and often promotes nationalism and anti-elitism through top-down control, emphasizing social cohesion over individual freedoms. Liberal populism prioritizes democracy, civil liberties, and political pluralism, advocating for citizen participation and protection of minority rights against elite domination. The core ideological divide lies in authoritarian populism's preference for order and uniformity versus liberal populism's emphasis on inclusivity and constitutional governance.
Leadership Styles in Competing Populisms
Authoritarian populism features centralized, charismatic leadership emphasizing strongman authority and top-down decision-making, often marginalizing opposition and dissent. Liberal populism promotes inclusive leadership that values democratic deliberation, pluralism, and the protection of individual rights while mobilizing popular participation to challenge elite domination. These contrasting leadership styles shape how each populist movement engages with governance, public discourse, and policy implementation.
Communication and Mobilization Strategies
Authoritarian populism employs fear-based rhetoric and centralized leadership to rapidly mobilize supporters through emotional appeals and direct communication channels, often bypassing traditional media. Liberal populism, by contrast, emphasizes inclusive dialogue and participatory engagement, using social media platforms to foster grassroots organizing and consensus-building. Both strategies leverage digital tools but differ in messaging tone and methods of activating political participation.
Attitudes Toward Institutions and Democracy
Authoritarian populism often distrusts traditional democratic institutions, favoring centralized power and charismatic leadership over checks and balances, which can erode democratic norms. Liberal populism, by contrast, advocates for greater inclusivity and participation within existing democratic frameworks, emphasizing transparency and accountability in institutions. These differing attitudes shape public trust and engagement, influencing how populist movements affect democratic stability.
Impact on Civil Liberties and Minority Rights
Authoritarian populism often restricts civil liberties and undermines minority rights by consolidating power and promoting majoritarian rule, leading to increased state control and suppression of dissent. Liberal populism tends to advocate for expanded civil liberties and protections for minority groups by emphasizing inclusive representation and participatory democracy. The contrasting impacts highlight authoritarian populism's tendency toward exclusion and repression, whereas liberal populism aims to enhance pluralism and safeguard individual freedoms.
Economic Policies and Populist Narratives
Authoritarian populism often emphasizes protectionist economic policies, promoting state control and nationalist rhetoric to consolidate power and appeal to a sense of economic insecurity. Liberal populism, by contrast, advocates for inclusive economic reforms aimed at reducing inequality and expanding social welfare, framing the elite as responsible for economic disparities. Both strains use populist narratives that pit "the people" against a corrupt establishment but differ significantly in their approaches to state intervention and market regulation.
Global Case Studies: Comparing Populist Regimes
Authoritarian populism often consolidates power through centralized control, restricting political freedoms and manipulating nationalist sentiments, exemplified by regimes in Russia under Vladimir Putin and Turkey under Recep Tayyip Erdogan. In contrast, liberal populism emphasizes democratic processes, social inclusion, and advocates for redistributive policies, as seen in countries like Canada with Justin Trudeau and Uruguay under Jose Mujica. Comparative analysis of these regimes reveals divergent impacts on governance quality, civil liberties, and institutional trust across global democratic and hybrid systems.
Future Prospects of Populism in Global Politics
Authoritarian populism, characterized by centralized power and nationalist rhetoric, is likely to gain traction in regions facing economic instability and social fragmentation, exploiting fears through exclusionary policies. Liberal populism, emphasizing inclusive governance and democratic reforms, may find stronger support in societies with robust civil institutions and increasing demands for transparency and accountability. The future trajectory of populism in global politics hinges on the interplay between these models, influenced by technological advancements, demographic shifts, and geopolitical tensions shaping public sentiment and political engagement.
authoritarian populism vs liberal populism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com