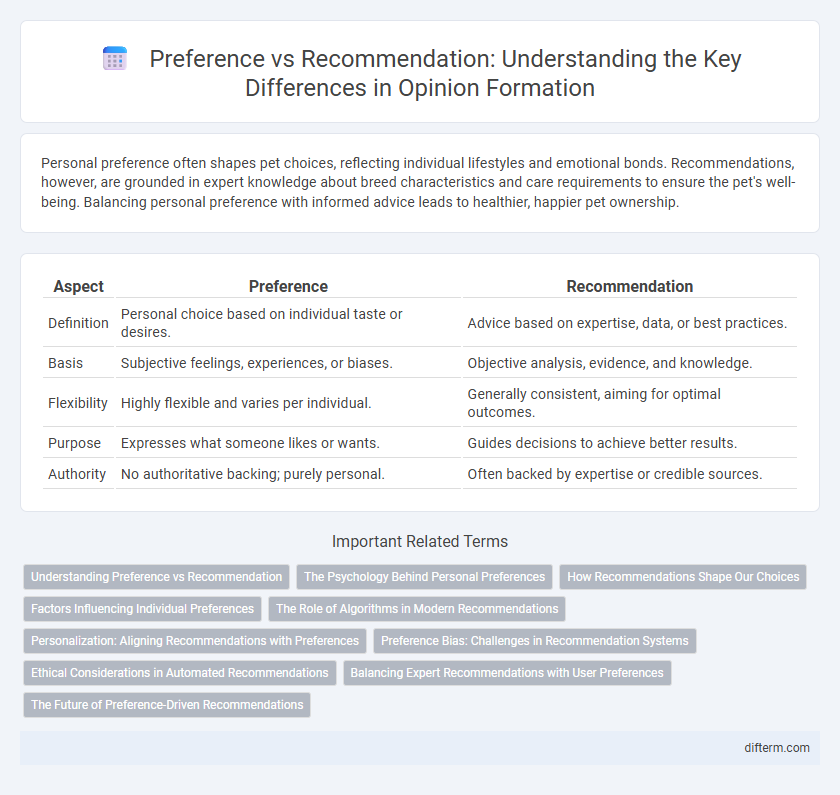
Personal preference often shapes pet choices, reflecting individual lifestyles and emotional bonds. Recommendations, however, are grounded in expert knowledge about breed characteristics and care requirements to ensure the pet's well-being. Balancing personal preference with informed advice leads to healthier, happier pet ownership.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Preference | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Personal choice based on individual taste or desires. | Advice based on expertise, data, or best practices. |
| Basis | Subjective feelings, experiences, or biases. | Objective analysis, evidence, and knowledge. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and varies per individual. | Generally consistent, aiming for optimal outcomes. |
| Purpose | Expresses what someone likes or wants. | Guides decisions to achieve better results. |
| Authority | No authoritative backing; purely personal. | Often backed by expertise or credible sources. |
Understanding Preference vs Recommendation
Preference reflects an individual's personal choices based on subjective tastes and experiences, while recommendation stems from an informed suggestion aimed at guiding others toward beneficial options. Recognizing this distinction is crucial for effective decision-making, as preferences highlight unique individual needs, whereas recommendations often rely on broader criteria or expertise. Understanding both concepts allows for a balanced approach that respects personal desires while considering expert insights.
The Psychology Behind Personal Preferences
Personal preferences stem from individual psychological factors such as past experiences, values, and emotional associations, making them deeply subjective and unique to each person. In contrast, recommendations often rely on objective criteria and collective data to guide decision-making. Understanding the psychology behind preferences highlights why people resist changing their choices despite evidence, emphasizing the role of cognitive biases and emotional attachment in shaping personal tastes.
How Recommendations Shape Our Choices
Recommendations significantly influence consumer decisions by leveraging trust and perceived expertise, often overriding personal preferences. Social proof and tailored suggestions increase the likelihood of adopting recommended products or services, highlighting the powerful role of curated advice in shaping behavior. This dynamic underscores the psychological impact of endorsements in guiding choices beyond individual inclinations.
Factors Influencing Individual Preferences
Individual preferences are shaped by a complex interplay of cultural background, personal experiences, and psychological traits, which influence how people perceive value and satisfaction. Emotional attachment and cognitive biases often skew preferences away from objective criteria, leading to subjective choices that reflect identity more than logic. Environmental factors such as social influences and contextual settings further modify preferences, making them dynamic rather than fixed.
The Role of Algorithms in Modern Recommendations
Algorithms have transformed modern recommendations by analyzing vast amounts of user data to predict preferences with high accuracy. These systems optimize content delivery, enhancing personalized experiences across platforms like streaming services and e-commerce sites. However, algorithms often prioritize engagement metrics over genuine user interests, blurring the line between true preference and algorithm-driven suggestion.
Personalization: Aligning Recommendations with Preferences
Personalization enhances user engagement by aligning recommendations with individual preferences, increasing relevance and satisfaction. Leveraging data analytics and machine learning models allows systems to predict user preferences accurately, tailoring content or products to specific tastes. This focused approach surpasses generic recommendations by creating a customized experience that resonates with personal interests and behavior patterns.
Preference Bias: Challenges in Recommendation Systems
Preference bias in recommendation systems arises when user choices disproportionately influence algorithmic suggestions, leading to a narrow range of recommendations that fail to capture diverse interests. This bias challenges the effectiveness of recommendation engines by reinforcing existing preferences and limiting exposure to novel or serendipitous content. Addressing preference bias requires integrating multi-faceted user data and implementing diversity-promoting algorithms to enhance recommendation accuracy and user satisfaction.
Ethical Considerations in Automated Recommendations
Automated recommendations raise ethical concerns regarding user autonomy and informed consent, as preference-based systems may manipulate choices without transparent reasoning. Prioritizing recommendations that align strictly with user preferences risks reinforcing biases and limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. Ethical frameworks must be integrated to ensure recommendations promote fairness, transparency, and respect for individual decision-making rights.
Balancing Expert Recommendations with User Preferences
Balancing expert recommendations with user preferences enhances personalized decision-making while maintaining reliability and relevance. Expert insights provide data-driven guidance grounded in industry standards, whereas user preferences capture individual needs and contextual nuances. Integrating both elements optimizes outcomes by ensuring choices reflect authoritative advice and personal values.
The Future of Preference-Driven Recommendations
Preference-driven recommendations are reshaping the future of personalized experiences by leveraging real-time user data and advanced machine learning algorithms. This approach enhances accuracy and relevance by dynamically adapting to evolving consumer tastes and contextual factors. Emerging technologies like AI-powered sentiment analysis and behavioral tracking will further refine preference models, enabling highly intuitive and customized recommendations across industries.
preference vs recommendation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com