Persuasion aims to influence attitudes or behaviors by appealing to emotions and values, while information focuses on delivering facts and objective data without bias. In opinion pet content, blending persuasive elements with accurate information can enhance engagement and credibility. Striking the right balance ensures the audience is both informed and motivated to consider different viewpoints.
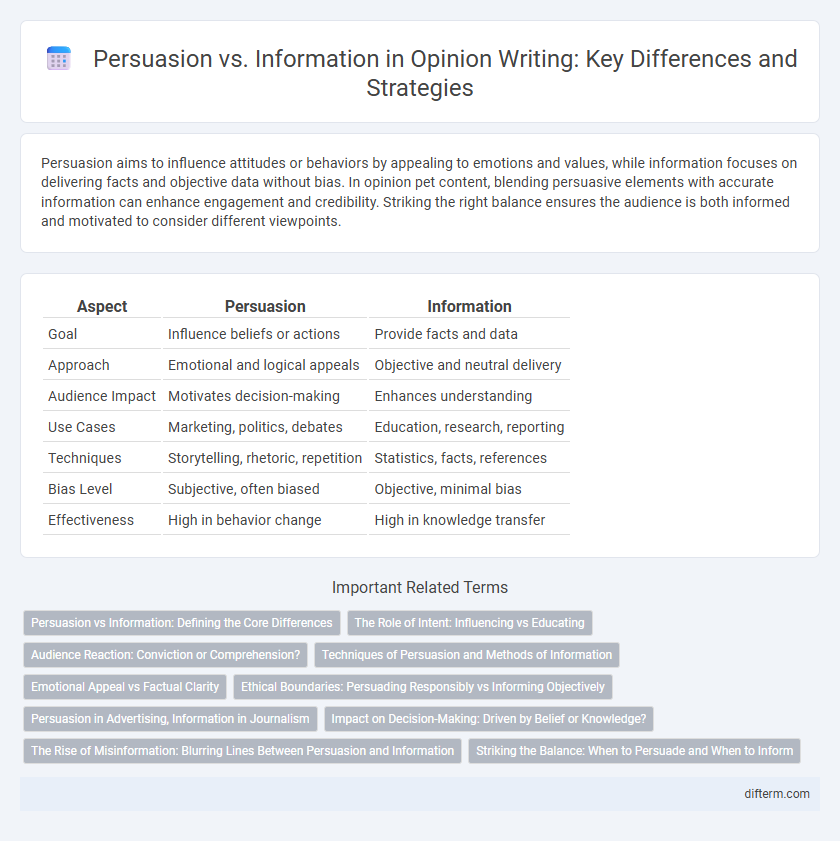
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Persuasion | Information |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Influence beliefs or actions | Provide facts and data |
| Approach | Emotional and logical appeals | Objective and neutral delivery |
| Audience Impact | Motivates decision-making | Enhances understanding |
| Use Cases | Marketing, politics, debates | Education, research, reporting |
| Techniques | Storytelling, rhetoric, repetition | Statistics, facts, references |
| Bias Level | Subjective, often biased | Objective, minimal bias |
| Effectiveness | High in behavior change | High in knowledge transfer |
Persuasion vs Information: Defining the Core Differences
Persuasion aims to influence attitudes or behaviors by appealing to emotions and values, while information prioritizes objective facts and clarity to enhance understanding. The core difference lies in persuasion's intent to motivate action, contrasting with information's goal to inform without bias. Recognizing this distinction is crucial for effective communication strategies in marketing, education, and media.
The Role of Intent: Influencing vs Educating
Persuasion often involves a deliberate intent to influence beliefs or behaviors, utilizing emotional appeals and selective information to guide decision-making. In contrast, education prioritizes the clear, unbiased presentation of facts to empower individuals with knowledge for independent judgment. Understanding these differing intents clarifies the ethical boundaries and effectiveness of communication strategies in shaping public opinion.
Audience Reaction: Conviction or Comprehension?
Persuasion aims to evoke conviction by appealing to emotions and values, often resulting in a stronger audience commitment to the message. Information prioritizes comprehension, providing clear, logical facts that enable the audience to understand and critically evaluate the content. Audience reaction varies significantly, with persuasion driving belief change and information fostering informed decision-making.
Techniques of Persuasion and Methods of Information
Techniques of persuasion leverage emotional appeal, social proof, and rhetorical strategies to influence attitudes and prompt action, often emphasizing subjective interpretation over factual accuracy. Methods of information prioritize clarity, evidence-based content, and logical structure to deliver unbiased knowledge and facilitate informed decision-making. Understanding the distinction between these approaches is crucial for evaluating communication effectiveness in various contexts.
Emotional Appeal vs Factual Clarity
Emotional appeal leverages feelings to persuade audiences, often creating strong connections that influence decisions more effectively than pure data. Factual clarity provides objective information, ensuring understanding and trust but may lack the compelling force needed for immediate action. Balancing emotional resonance with clear facts strengthens persuasive impact by engaging both the heart and mind.
Ethical Boundaries: Persuading Responsibly vs Informing Objectively
Ethical boundaries between persuasion and information hinge on transparency and respect for autonomy, ensuring messages do not manipulate or deceive. Persuasion must balance influencing attitudes with upholding honesty, avoiding coercion or emotional exploitation. Objective information delivery prioritizes factual accuracy and neutrality, empowering individuals to form independent judgments without bias.
Persuasion in Advertising, Information in Journalism
Persuasion in advertising aims to influence consumer behavior by appealing to emotions and desires through targeted messaging and creative visuals. Information in journalism prioritizes accuracy, neutrality, and factual reporting to inform the public without bias. Advertising leverages psychological triggers and persuasive techniques, while journalism upholds ethical standards to maintain credibility and trust.
Impact on Decision-Making: Driven by Belief or Knowledge?
Persuasion impacts decision-making by appealing to beliefs and emotions, often shaping choices through subjective influence rather than objective facts. Information provides a foundation rooted in knowledge and evidence, enabling decisions based on rational analysis and factual understanding. The balance between persuasion and information determines whether decisions are driven more by conviction or by informed reasoning.
The Rise of Misinformation: Blurring Lines Between Persuasion and Information
The rise of misinformation increasingly blurs the lines between persuasion and information by intertwining deceptive tactics with seemingly factual content, challenging the ability of audiences to discern truth. Social media platforms have amplified this phenomenon, enabling rapid spread of misleading narratives that exploit emotional triggers rather than rational analysis. This dynamic undermines informed decision-making, emphasizing the critical need for enhanced media literacy and transparent fact-checking mechanisms.
Striking the Balance: When to Persuade and When to Inform
Striking the balance between persuasion and information hinges on understanding audience needs and communication goals. Persuasion aims to influence beliefs or behaviors by appealing to emotions and values, while information focuses on delivering facts objectively for informed decision-making. Effective communicators tailor their approach, blending persuasive elements with clear, accurate information to foster trust and engagement.
persuasion vs information Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com