An opinion can stem from personal inclination, reflecting subjective preferences shaped by individual experiences and emotions. In contrast, opinions grounded in principle are based on objective values or ethical standards that guide consistent judgment beyond personal bias. Understanding the distinction between inclination and principle helps clarify the foundation and reliability of one's viewpoints.
Table of Comparison
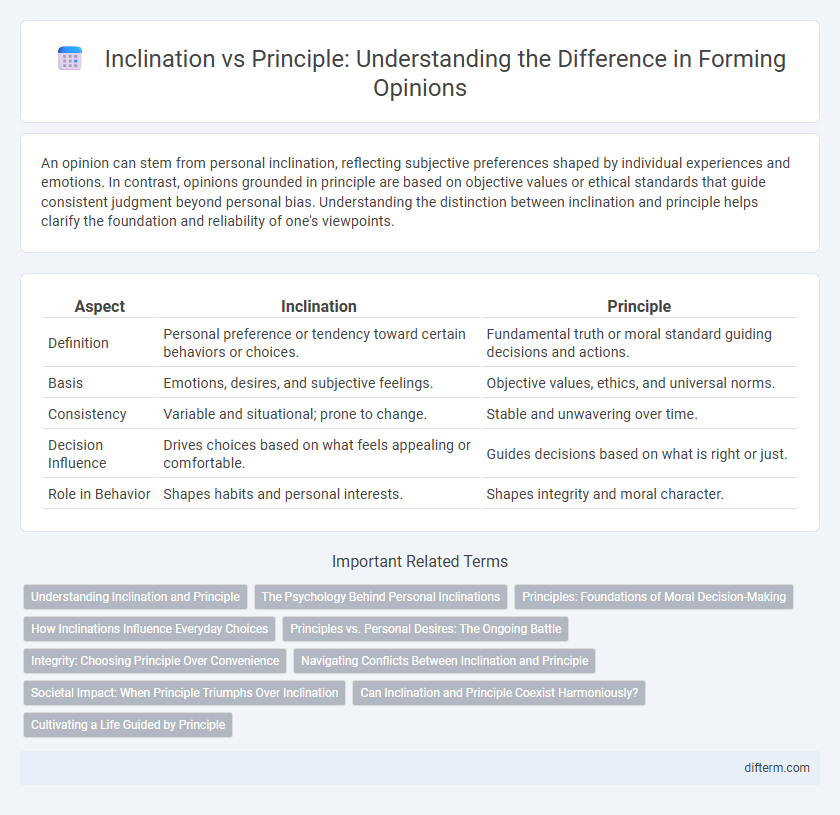
| Aspect | Inclination | Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Personal preference or tendency toward certain behaviors or choices. | Fundamental truth or moral standard guiding decisions and actions. |
| Basis | Emotions, desires, and subjective feelings. | Objective values, ethics, and universal norms. |
| Consistency | Variable and situational; prone to change. | Stable and unwavering over time. |
| Decision Influence | Drives choices based on what feels appealing or comfortable. | Guides decisions based on what is right or just. |
| Role in Behavior | Shapes habits and personal interests. | Shapes integrity and moral character. |
Understanding Inclination and Principle
Inclination reflects a person's natural tendencies or preferences, often shaped by emotions and experiences, while principle represents a consistent ethical or moral standard guiding decisions. Understanding inclination involves recognizing how personal desires influence actions, whereas grasping principle requires adherence to objective values regardless of circumstance. Balancing inclination with principle fosters authentic integrity and mindful choice-making.
The Psychology Behind Personal Inclinations
Personal inclinations often stem from innate psychological patterns shaped by past experiences and emotional associations, influencing decision-making more than abstract principles. The brain's reward system reinforces behaviors linked to pleasure, making inclinations powerful motivators that can override rational principles in real-time choices. Understanding these subconscious drivers offers insight into why individuals may prioritize feelings over ethical standards despite recognizing the importance of principles.
Principles: Foundations of Moral Decision-Making
Principles serve as the foundational framework for moral decision-making, guiding actions based on consistent ethical standards rather than fluctuating personal inclinations. Unlike subjective preferences, principles provide objective criteria that uphold integrity and fairness across diverse situations. Emphasizing principles ensures decisions are rooted in universal values, fostering accountability and trust in moral judgments.
How Inclinations Influence Everyday Choices
Inclinations shape everyday decisions by guiding preferences and immediate reactions, often driven by emotions and personal experiences rather than fixed principles. These natural tendencies influence choices from simple habits to social interactions, subtly steering behavior without conscious deliberation. Understanding the role of inclinations highlights their impact on daily life, emphasizing how personal biases shape routine actions beyond rigid moral frameworks.
Principles vs. Personal Desires: The Ongoing Battle
Principles serve as steadfast guides rooted in ethical standards, while personal desires often fluctuate with emotions and external influences. This ongoing battle shapes decision-making, where prioritizing principles fosters integrity, whereas succumbing to desires may lead to short-term gratification but long-term conflict. Maintaining a balance requires conscious effort to uphold core values amidst evolving personal inclinations.
Integrity: Choosing Principle Over Convenience
Integrity demands unwavering adherence to core principles even when convenience tempts compromise. Choosing principle over convenience reinforces trustworthiness and fosters genuine respect in personal and professional relationships. This steadfast commitment to ethical values safeguards long-term character and credibility.
Navigating Conflicts Between Inclination and Principle
Navigating conflicts between inclination and principle challenges individuals to balance personal desires with core values, often requiring critical reflection and ethical reasoning. Decisions rooted in principle tend to foster long-term integrity, while those driven by inclination may address immediate emotional needs but risk compromising foundational beliefs. Effective navigation involves assessing potential consequences and prioritizing consistency to maintain moral coherence and personal authenticity.
Societal Impact: When Principle Triumphs Over Inclination
When principle triumphs over inclination, societal trust strengthens as individuals uphold ethical standards despite personal desires, fostering a culture of accountability and justice. This adherence to core values reduces corruption and bias, promoting equitable treatment across communities. The collective commitment to principled actions drives social progress by prioritizing common good over subjective preferences.
Can Inclination and Principle Coexist Harmoniously?
Inclination and principle can coexist harmoniously when personal desires align with ethical standards, fostering authentic decision-making that respects both self-interest and moral integrity. Tensions arise if inclinations challenge core principles, but mindful reflection enables balancing emotional impulses with steadfast values. This harmony cultivates consistent behavior while allowing flexibility in pursuing genuine aspirations within principled boundaries.
Cultivating a Life Guided by Principle
Cultivating a life guided by principle fosters consistency and integrity, enabling individuals to navigate challenges with unwavering moral clarity. While inclination may fluctuate with emotions and circumstances, principles provide a stable foundation for decision-making and long-term fulfillment. Embracing principled living encourages personal growth and a deeper alignment with enduring values.
inclination vs principle Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com