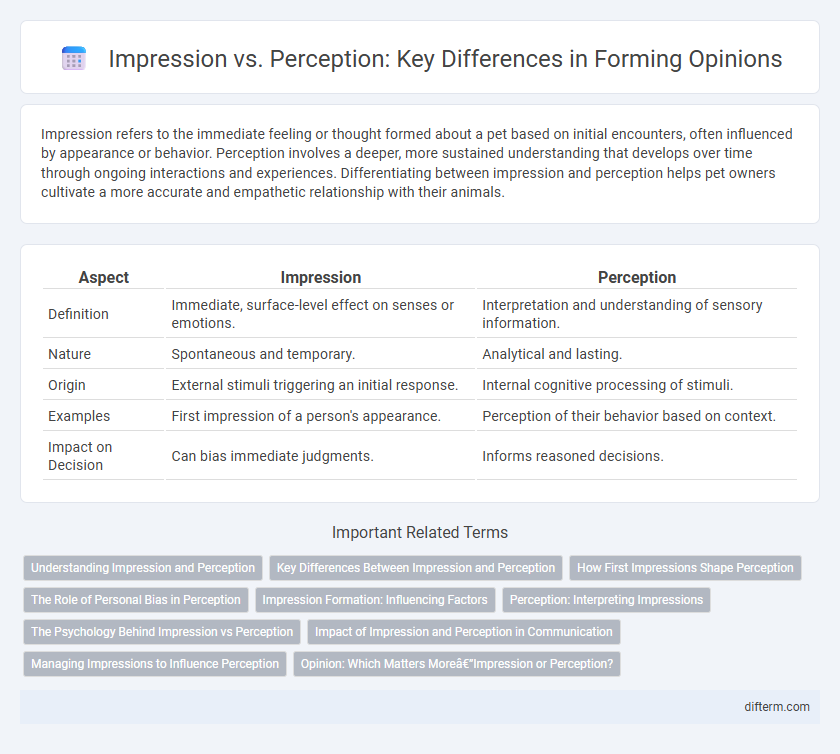
Impression refers to the immediate feeling or thought formed about a pet based on initial encounters, often influenced by appearance or behavior. Perception involves a deeper, more sustained understanding that develops over time through ongoing interactions and experiences. Differentiating between impression and perception helps pet owners cultivate a more accurate and empathetic relationship with their animals.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Impression | Perception |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Immediate, surface-level effect on senses or emotions. | Interpretation and understanding of sensory information. |
| Nature | Spontaneous and temporary. | Analytical and lasting. |
| Origin | External stimuli triggering an initial response. | Internal cognitive processing of stimuli. |
| Examples | First impression of a person's appearance. | Perception of their behavior based on context. |
| Impact on Decision | Can bias immediate judgments. | Informs reasoned decisions. |
Understanding Impression and Perception
Impression refers to the immediate, often subconscious, impact an object or experience has on an individual, while perception involves the active interpretation and organization of sensory information to form a coherent understanding. Understanding impression requires recognizing its transient and subjective nature, influenced by emotions and prior experiences. Perception, however, is a more deliberate cognitive process that shapes how we interpret and respond to impressions over time.
Key Differences Between Impression and Perception
Impression refers to the immediate, often superficial feeling or judgment formed about a person, object, or event, while perception involves the deeper cognitive process of interpreting and organizing sensory information to understand reality. Impressions are typically quick and may be influenced by biases or limited information, whereas perception is more analytical and shaped by experience, context, and prior knowledge. Understanding these key differences highlights how impressions can be misleading, whereas perception tends to provide a more accurate representation of the environment.
How First Impressions Shape Perception
First impressions significantly influence perception by creating a mental shortcut that guides how new information is interpreted. The initial encounter activates cognitive biases, causing individuals to filter subsequent experiences through the lens of those early judgments. This phenomenon underscores the importance of context and nonverbal cues in shaping lasting attitudes and beliefs.
The Role of Personal Bias in Perception
Personal bias significantly shapes perception by filtering experiences through individual beliefs, emotions, and past experiences, leading to subjective interpretations of reality. This selective filtering often causes discrepancies between impression and objective reality, as perception becomes a personalized construct rather than an accurate reflection. Understanding the impact of cognitive biases such as confirmation bias and stereotyping is crucial to recognizing how personal bias distorts perception and influences judgments.
Impression Formation: Influencing Factors
Impression formation is influenced by multiple factors including nonverbal cues, social context, and individual biases that shape how initial interactions are interpreted. Facial expressions and body language provide critical semantic signals that affect the perceived traits and intentions of others. Cognitive frameworks and prior experiences further modulate these impressions, leading to varied perception outcomes despite identical stimuli.
Perception: Interpreting Impressions
Perception involves actively interpreting and organizing sensory information to form a coherent understanding of an experience, going beyond mere impressions that are raw and fleeting. It relies on cognitive processes, memory, and context to assign meaning, shaping how individuals consciously comprehend their environment. This interpretative process makes perception a dynamic synthesis rather than a passive reception of impressions.
The Psychology Behind Impression vs Perception
Impression and perception differ fundamentally in psychological processes; impression involves the initial emotional response to stimuli, often shaped by subconscious biases, while perception entails the cognitive interpretation and organization of sensory input. Neural mechanisms in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex play crucial roles in forming impressions and refining perceptions based on past experiences and contextual cues. Understanding these distinctions enhances insight into how humans interpret social interactions and make judgment calls.
Impact of Impression and Perception in Communication
Impression shapes the initial emotional response and trust in communication, impacting how messages are received and interpreted. Perception filters these messages through personal experiences and biases, influencing understanding and reactions in ongoing interactions. Effective communication requires managing both impression and perception to align sender intent with receiver interpretation, enhancing clarity and engagement.
Managing Impressions to Influence Perception
Managing impressions effectively shapes how others perceive intentions, attitudes, and credibility in social and professional contexts. Strategic use of verbal and nonverbal cues, such as tone, body language, and appearance, enhances the alignment between desired image and audience interpretation. Understanding that perception is subjective emphasizes the importance of consistent impression management to influence judgments and build trust.
Opinion: Which Matters More—Impression or Perception?
Opinion often values perception over mere impression, as perception reflects deeper understanding formed through experience and context, making it more reliable for informed judgments. Impressions are immediate and surface-level responses that can be misleading or incomplete, whereas perception integrates sensory data and cognitive processes, offering a nuanced view. For meaningful opinions, perception holds greater weight because it aligns closer with reality and informed reasoning.
impression vs perception Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com