Dissent involves a strong expression of opposition often based on principles or beliefs, while disagreement is a broader term indicating a difference in opinion or perspective. Dissent can lead to constructive dialogue by challenging prevailing ideas, whereas disagreement may simply reflect varying preferences or interpretations. Understanding the nuances between the two helps foster respectful and meaningful conversations.
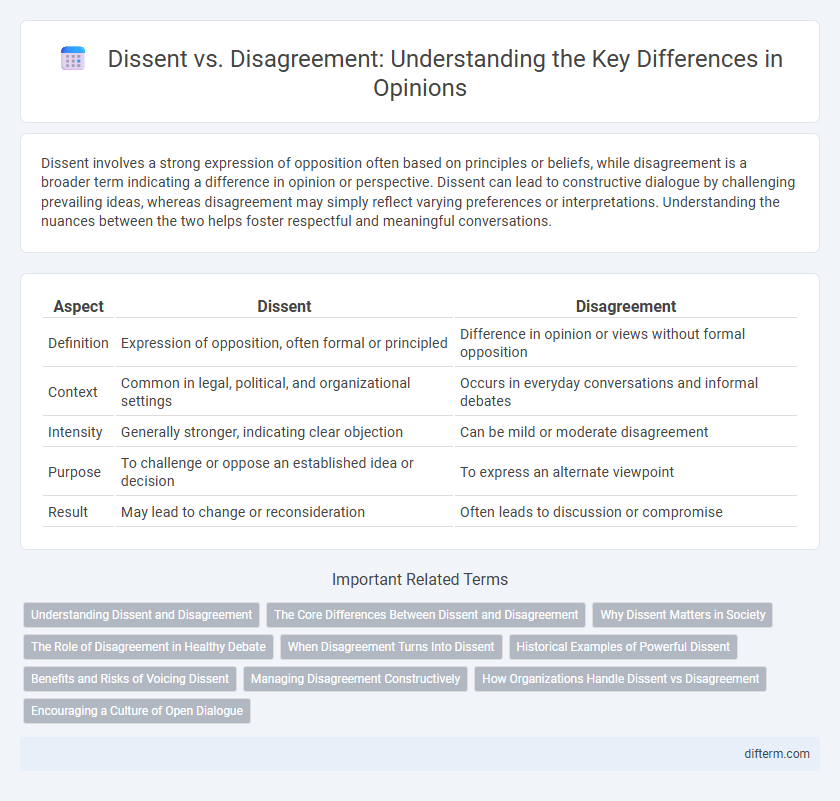
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dissent | Disagreement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expression of opposition, often formal or principled | Difference in opinion or views without formal opposition |
| Context | Common in legal, political, and organizational settings | Occurs in everyday conversations and informal debates |
| Intensity | Generally stronger, indicating clear objection | Can be mild or moderate disagreement |
| Purpose | To challenge or oppose an established idea or decision | To express an alternate viewpoint |
| Result | May lead to change or reconsideration | Often leads to discussion or compromise |
Understanding Dissent and Disagreement
Dissent involves a principled opposition rooted in deeply held beliefs, often challenging foundational ideas or policies, while disagreement tends to reflect a difference in opinion without necessarily questioning underlying values. Understanding dissent requires recognizing its role in promoting democratic dialogue and institutional change, whereas disagreement may simply indicate varying perspectives on specific issues. Both play critical roles in fostering critical thinking and diversity of thought within societies and organizations.
The Core Differences Between Dissent and Disagreement
Dissent involves a principled opposition to an idea or policy, often rooted in values or beliefs, while disagreement typically reflects a difference in opinion or perspective without necessarily challenging underlying principles. Dissent is more likely to provoke change or critical reevaluation, as it questions the status quo, whereas disagreement may simply indicate varying viewpoints within an accepted framework. Understanding these core differences is essential for fostering constructive dialogue and effective conflict resolution in any setting.
Why Dissent Matters in Society
Dissent plays a crucial role in a healthy society by fostering diverse perspectives that challenge prevailing norms and prevent stagnation. It encourages critical thinking and innovation, enabling progress in political, social, and cultural spheres. The presence of dissent safeguards democratic values by holding authorities accountable and empowering marginalized voices.
The Role of Disagreement in Healthy Debate
Disagreement fosters critical thinking by challenging assumptions and encouraging diverse perspectives, which is essential for robust decision-making. It acts as a catalyst for constructive dialogue, preventing groupthink and promoting intellectual growth within any debate. Embracing disagreement enables participants to refine arguments and reach well-informed conclusions, enhancing the overall quality of discussions.
When Disagreement Turns Into Dissent
Disagreement occurs when individuals hold differing views but remain within acceptable boundaries of dialogue, while dissent arises when opposition challenges the core principles or authority of a group or institution. When disagreement turns into dissent, it signifies a deeper conflict where the dissenting party actively resists or undermines the established consensus, often risking social or professional repercussions. This transformation highlights the complex dynamics between personal conviction and collective cohesion in organizational or political contexts.
Historical Examples of Powerful Dissent
Powerful dissent has shaped history through moments like the Civil Rights Movement, where figures such as Martin Luther King Jr. challenged systemic racism with nonviolent protests. The suffragette movement demonstrated how dissent against gender inequality spurred women's voting rights in early 20th-century Britain and the United States. Instances of dissent, unlike mere disagreement, involve organized resistance that demands societal change rather than simple conflicting opinions.
Benefits and Risks of Voicing Dissent
Voicing dissent promotes innovation and critical thinking by challenging prevailing ideas, leading to better decision-making and inclusivity. However, expressing dissent carries risks such as social ostracism, professional retaliation, and psychological stress, which can discourage individuals from sharing valuable perspectives. Balancing these benefits and risks is essential for fostering a culture where diverse opinions contribute to organizational and societal growth.
Managing Disagreement Constructively
Managing disagreement constructively requires recognizing that dissent involves expressing opposing viewpoints to challenge ideas, while disagreement often reflects a difference in opinion without necessarily questioning underlying beliefs. Encouraging open dialogue and active listening fosters a culture where diverse perspectives contribute to problem-solving rather than conflict. Emphasizing respect and clarity in communication helps transform disagreements into opportunities for growth and innovation.
How Organizations Handle Dissent vs Disagreement
Organizations handle dissent by creating structured platforms for open dialogue that encourage diverse viewpoints, whereas disagreement is often managed through conflict resolution mechanisms aiming for consensus. Effective dissent management can foster innovation and critical thinking, while disagreement resolution emphasizes maintaining team cohesion and productivity. Balancing both requires clear communication policies and leadership trained to navigate complex interpersonal dynamics.
Encouraging a Culture of Open Dialogue
Promoting a culture of open dialogue requires distinguishing dissent from mere disagreement by valuing diverse perspectives as opportunities for growth rather than conflict. Encouraging thoughtful dissent fosters innovation and critical thinking by challenging prevailing assumptions without undermining respect or collaboration. Organizations and communities thrive when open dialogue is prioritized, creating an environment where constructive dissent leads to better decision-making and collective progress.
dissent vs disagreement Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com