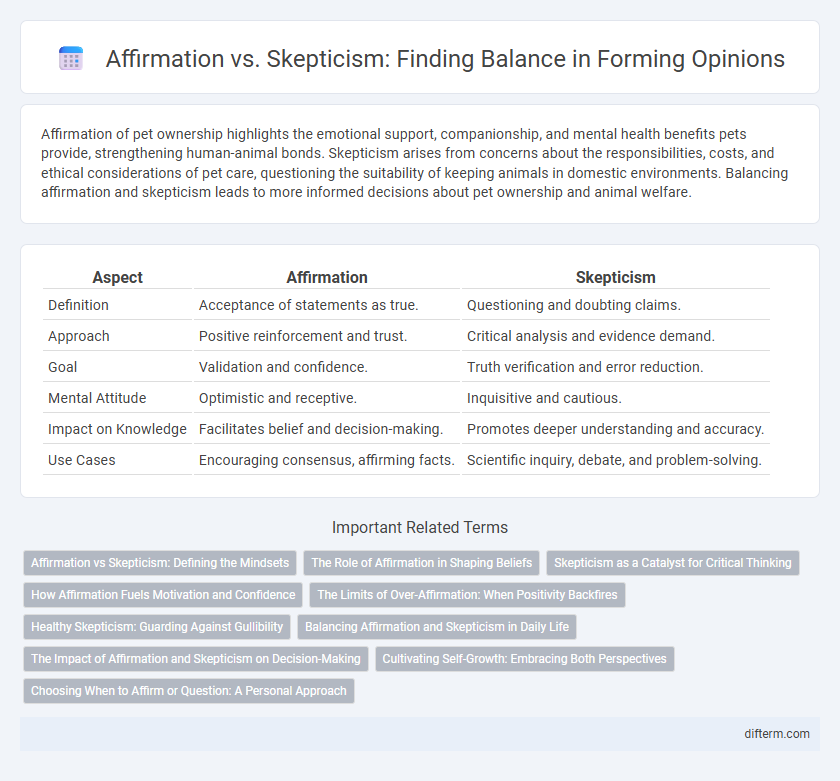
Affirmation of pet ownership highlights the emotional support, companionship, and mental health benefits pets provide, strengthening human-animal bonds. Skepticism arises from concerns about the responsibilities, costs, and ethical considerations of pet care, questioning the suitability of keeping animals in domestic environments. Balancing affirmation and skepticism leads to more informed decisions about pet ownership and animal welfare.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Affirmation | Skepticism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acceptance of statements as true. | Questioning and doubting claims. |
| Approach | Positive reinforcement and trust. | Critical analysis and evidence demand. |
| Goal | Validation and confidence. | Truth verification and error reduction. |
| Mental Attitude | Optimistic and receptive. | Inquisitive and cautious. |
| Impact on Knowledge | Facilitates belief and decision-making. | Promotes deeper understanding and accuracy. |
| Use Cases | Encouraging consensus, affirming facts. | Scientific inquiry, debate, and problem-solving. |
Affirmation vs Skepticism: Defining the Mindsets
Affirmation embraces certainty and confidence in beliefs, fostering proactive decision-making and a positive outlook on knowledge acquisition. Skepticism prioritizes questioning and critical analysis, promoting doubt as a tool to refine understanding and guard against misinformation. Both mindsets fundamentally shape cognitive approaches to truth, influencing how individuals engage with evidence and form opinions.
The Role of Affirmation in Shaping Beliefs
Affirmation plays a crucial role in shaping beliefs by reinforcing positive cognitive patterns and increasing confidence in one's perspectives. Through repeated affirmations, individuals are more likely to internalize and solidify their convictions, leading to stronger commitment to their beliefs. This process contrasts with skepticism, which challenges existing ideas but may also hinder the formation of stable belief systems.
Skepticism as a Catalyst for Critical Thinking
Skepticism serves as a powerful catalyst for critical thinking by encouraging individuals to question assumptions and evaluate evidence thoroughly before forming conclusions. It fosters intellectual humility and guards against cognitive biases, making decision-making more rigorous and informed. Embracing skepticism promotes a deeper understanding of complex issues through continuous inquiry and reflection.
How Affirmation Fuels Motivation and Confidence
Affirmation reinforces self-belief by highlighting strengths and past successes, which directly boosts motivation to pursue goals with greater determination. Positive affirmations stimulate the brain's reward system, increasing confidence and resilience against setbacks. This cognitive reinforcement creates an upward spiral of motivation, enabling individuals to overcome challenges more effectively than skepticism, which often undermines self-trust and hampers progress.
The Limits of Over-Affirmation: When Positivity Backfires
Excessive affirmation can undermine critical thinking by promoting a false sense of security and preventing individuals from recognizing genuine risks or flaws. Over-positivity often leads to complacency, where challenges are ignored rather than addressed, resulting in poor decision-making. Balancing affirmation with healthy skepticism encourages a more realistic perspective that fosters growth and resilience.
Healthy Skepticism: Guarding Against Gullibility
Healthy skepticism serves as a critical cognitive tool, enabling individuals to question information and avoid the pitfalls of gullibility. By prioritizing evidence-based reasoning and fostering inquisitive dialogue, skepticism promotes informed decision-making and resilience against misinformation. Embracing this mindset cultivates intellectual humility and sharpens analytical skills essential for navigating complex realities.
Balancing Affirmation and Skepticism in Daily Life
Balancing affirmation and skepticism in daily life enhances decision-making by fostering open-mindedness while critically evaluating information. Affirmation nurtures positive relationships and self-confidence, whereas skepticism guards against misinformation and biases. Integrating both approaches cultivates a pragmatic mindset that supports growth and resilience.
The Impact of Affirmation and Skepticism on Decision-Making
Affirmation enhances confidence and motivates decisive action by reinforcing positive beliefs, leading to faster and more committed decision-making. Skepticism encourages critical evaluation and cautious analysis, reducing the risk of errors but potentially slowing the decision process. Balancing affirmation with skepticism can optimize decision quality, combining confidence with thorough scrutiny to achieve more reliable outcomes.
Cultivating Self-Growth: Embracing Both Perspectives
Affirmation fosters confidence and motivation by reinforcing positive beliefs, while skepticism encourages critical thinking and self-awareness, essential for personal development. Balancing these perspectives cultivates resilience by enabling individuals to challenge assumptions without losing optimism. Embracing both affirmation and skepticism accelerates self-growth through a nuanced, adaptive mindset.
Choosing When to Affirm or Question: A Personal Approach
Choosing when to affirm or question depends on evaluating evidence, personal values, and context-specific factors. Affirmation strengthens convictions and builds confidence, while skepticism encourages critical thinking and guards against misinformation. Balancing both approaches fosters informed decisions and intellectual growth by recognizing when certainty is justified and when doubt is necessary.
affirmation vs skepticism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com