Public transportation offers affordable and eco-friendly mobility for pet owners, with many systems now accommodating pets through designated areas and policies. Private transportation provides greater flexibility and comfort, allowing pets to travel in familiar environments and reducing stress during transit. Choosing between the two depends on convenience, pet temperament, and specific travel requirements for a smooth and safe journey.
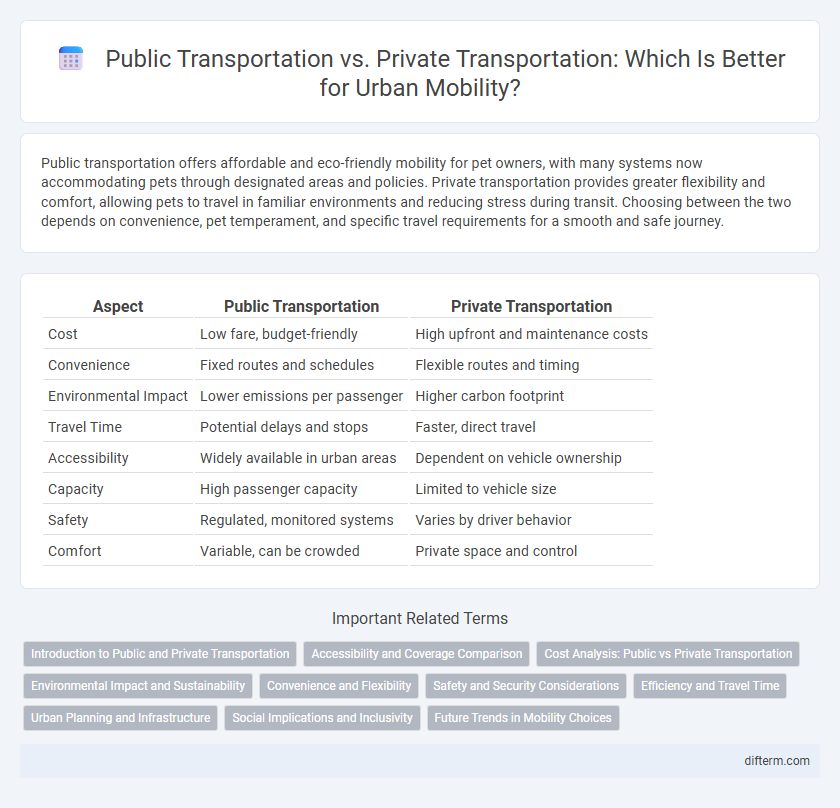
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Public Transportation | Private Transportation |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low fare, budget-friendly | High upfront and maintenance costs |
| Convenience | Fixed routes and schedules | Flexible routes and timing |
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions per passenger | Higher carbon footprint |
| Travel Time | Potential delays and stops | Faster, direct travel |
| Accessibility | Widely available in urban areas | Dependent on vehicle ownership |
| Capacity | High passenger capacity | Limited to vehicle size |
| Safety | Regulated, monitored systems | Varies by driver behavior |
| Comfort | Variable, can be crowded | Private space and control |
Introduction to Public and Private Transportation
Public transportation includes buses, trains, subways, and trams operated by government or private entities, providing cost-effective and environmentally friendly mobility options for urban and rural populations. Private transportation involves personally owned vehicles such as cars and motorcycles, offering greater flexibility and convenience but contributing to traffic congestion and higher carbon emissions. Understanding the differences between these modes is essential for developing sustainable transportation policies and improving urban mobility.
Accessibility and Coverage Comparison
Public transportation systems offer extensive coverage across urban and suburban areas, providing affordable and accessible options for diverse populations, including those without private vehicles. Private transportation offers flexibility and direct routes but often lacks comprehensive coverage, particularly in rural or underserved regions where public transit networks are limited. Accessibility in public transit is enhanced by features like low-floor buses and transit hubs, whereas private transport accessibility is constrained by vehicle ownership and driving ability.
Cost Analysis: Public vs Private Transportation
Public transportation generally offers lower cost per mile compared to private transportation due to shared infrastructure and economies of scale, reducing fuel, maintenance, and parking expenses for commuters. Private transportation involves higher fixed and variable costs, including vehicle purchase, insurance, depreciation, and toll fees, which significantly increase overall expenditure. Cost analysis favors public transit for urban commuters seeking affordable daily travel, while private transport may be cost-effective in low-density or rural areas with limited public options.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Public transportation reduces carbon emissions by carrying multiple passengers simultaneously, leading to lower per capita energy consumption compared to private vehicles. Electric buses and trains further enhance sustainability by utilizing renewable energy sources, decreasing air pollution in urban areas. In contrast, private transportation often results in higher greenhouse gas emissions and increased resource depletion due to single-occupancy travel and reliance on fossil fuels.
Convenience and Flexibility
Public transportation offers convenience through fixed routes and schedules that reduce the stress of parking and traffic navigation. Private transportation provides greater flexibility, allowing users to choose departure times and destinations without constraints. Balancing convenience and flexibility depends on individual needs, urban infrastructure, and travel habits.
Safety and Security Considerations
Public transportation systems often implement rigorous safety protocols, including surveillance cameras, emergency communication devices, and regular security patrols to ensure passenger safety. Private transportation, while offering greater control over travel conditions, presents variable security risks dependent on the driver's behavior and vehicle maintenance. Statistical data indicates that public transit environments experience lower rates of vehicular accidents per passenger mile compared to private cars, highlighting its relative safety advantage.
Efficiency and Travel Time
Public transportation systems typically offer greater efficiency by reducing road congestion and enabling faster travel times during peak hours through dedicated lanes and optimized routes. Private transportation, while offering flexibility, often results in longer travel durations due to traffic congestion and limited parking availability in urban areas. Efficient mass transit solutions such as buses and trains significantly lower average commute times and environmental impact compared to individual vehicle use.
Urban Planning and Infrastructure
Urban planning that prioritizes public transportation enhances infrastructure efficiency by reducing traffic congestion and lowering emissions in densely populated cities. Investments in dedicated bus lanes, metro systems, and bike-sharing networks promote sustainable mobility and optimize land use. In contrast, reliance on private transportation increases demand for extensive road networks and parking spaces, contributing to urban sprawl and environmental degradation.
Social Implications and Inclusivity
Public transportation fosters social inclusivity by providing affordable and accessible mobility options for diverse populations, including low-income communities, elderly individuals, and people with disabilities. Private transportation often exacerbates social inequalities due to higher costs and limited accessibility, leading to transportation deserts in underserved areas. Enhancing public transit infrastructure and services contributes to reducing socioeconomic disparities and promoting equitable urban mobility.
Future Trends in Mobility Choices
Future trends in mobility indicate a significant shift toward integrated public transportation systems enhanced by real-time data analytics and electric vehicle infrastructure, promoting sustainability and reducing urban congestion. Autonomous public transit options and shared mobility platforms are expected to complement traditional private transportation, offering cost-effective and eco-friendly alternatives. Advances in smart city technology will further optimize transit routes, enabling a seamless balance between private vehicle use and public transportation accessibility.
public transportation vs private transportation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com