Autonomous vehicles leverage advanced sensors and AI to operate without human intervention, offering enhanced safety and efficiency in mobility pets. Connected vehicles, on the other hand, rely on real-time communication with other vehicles and infrastructure to improve navigation and traffic management. Combining autonomous capabilities with connectivity creates a robust mobility solution that optimizes pet transportation through seamless coordination and adaptive responses.
Table of Comparison
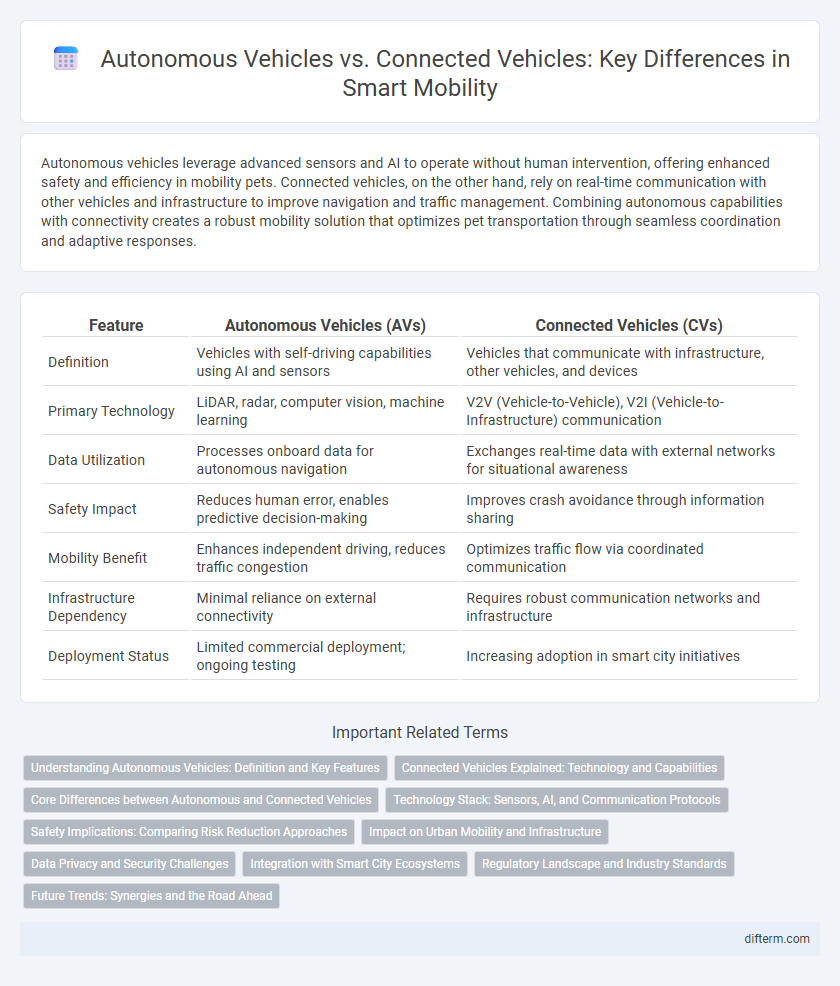
| Feature | Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) | Connected Vehicles (CVs) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Vehicles with self-driving capabilities using AI and sensors | Vehicles that communicate with infrastructure, other vehicles, and devices |
| Primary Technology | LiDAR, radar, computer vision, machine learning | V2V (Vehicle-to-Vehicle), V2I (Vehicle-to-Infrastructure) communication |
| Data Utilization | Processes onboard data for autonomous navigation | Exchanges real-time data with external networks for situational awareness |
| Safety Impact | Reduces human error, enables predictive decision-making | Improves crash avoidance through information sharing |
| Mobility Benefit | Enhances independent driving, reduces traffic congestion | Optimizes traffic flow via coordinated communication |
| Infrastructure Dependency | Minimal reliance on external connectivity | Requires robust communication networks and infrastructure |
| Deployment Status | Limited commercial deployment; ongoing testing | Increasing adoption in smart city initiatives |
Understanding Autonomous Vehicles: Definition and Key Features
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) operate using advanced sensors, machine learning algorithms, and real-time data processing to navigate without human input, distinguishing them from connected vehicles that primarily rely on vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication for data exchange. Key features of autonomous vehicles include environment perception through LiDAR, radar, and cameras, decision-making systems powered by artificial intelligence, and robust fail-safe mechanisms ensuring safety and reliability. Understanding these capabilities highlights the transformative impact of autonomous technology on mobility, urban planning, and transportation safety.
Connected Vehicles Explained: Technology and Capabilities
Connected vehicles utilize wireless communication technologies such as Dedicated Short-Range Communication (DSRC) and 5G networks to exchange real-time data with other vehicles, infrastructure, and cloud services, enhancing situational awareness and traffic efficiency. These vehicles support Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication, enabling capabilities like collision avoidance, traffic signal coordination, and remote diagnostics. The integration of sensors, GPS, and advanced data processing allows connected vehicles to improve road safety and reduce congestion through synchronized information sharing.
Core Differences between Autonomous and Connected Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles operate independently by using sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence to navigate and make driving decisions without human intervention. Connected vehicles rely on communication technologies, such as Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) connectivity, to exchange data with other vehicles, infrastructure, and networks to enhance safety and traffic management. The core difference lies in autonomy emphasizing self-driving capabilities, whereas connected vehicles focus on data sharing to improve coordination and situational awareness.
Technology Stack: Sensors, AI, and Communication Protocols
Autonomous vehicles integrate advanced sensors such as LiDAR, radar, and cameras with AI algorithms to perceive and navigate environments independently. Connected vehicles rely on communication protocols like V2X (vehicle-to-everything) to exchange real-time data with other vehicles, infrastructure, and cloud platforms, enhancing situational awareness and traffic management. The synergy of sensor fusion in autonomous systems and robust connectivity in connected vehicles drives the evolution of intelligent mobility ecosystems.
Safety Implications: Comparing Risk Reduction Approaches
Autonomous vehicles rely on advanced sensors and AI algorithms to detect and respond to hazards independently, significantly reducing human error-related accidents. Connected vehicles enhance safety by communicating with each other and traffic infrastructure, enabling real-time hazard warnings and coordinated responses to prevent collisions. Integrating both technologies offers the most comprehensive risk reduction by combining AI-driven decision-making with networked situational awareness.
Impact on Urban Mobility and Infrastructure
Autonomous vehicles reduce human error and optimize traffic flow by utilizing advanced sensors and AI, leading to fewer accidents and more efficient road use in urban environments. Connected vehicles enhance real-time data exchange between vehicles and infrastructure, improving traffic management and enabling dynamic rerouting to alleviate congestion. Together, these technologies transform urban mobility by enabling smarter infrastructure investments and reducing the need for extensive parking spaces.
Data Privacy and Security Challenges
Autonomous vehicles generate and process vast amounts of sensor data requiring robust encryption and secure communication protocols to prevent hacking and unauthorized access. Connected vehicles rely on continuous data exchange with external networks, increasing exposure to cybersecurity threats such as data interception and spoofing attacks. Ensuring data privacy mandates stringent authentication methods and real-time monitoring systems to protect sensitive information from breaches and maintain user trust.
Integration with Smart City Ecosystems
Autonomous vehicles rely on advanced sensors and AI systems to navigate independently, while connected vehicles communicate with infrastructure and other devices through V2X technology. Integration with smart city ecosystems enhances traffic management by enabling real-time data exchange, reducing congestion, and improving safety through coordinated responses to environmental factors. Connected vehicles facilitate seamless interaction with smart traffic lights, road sensors, and public transportation networks, optimizing urban mobility efficiency.
Regulatory Landscape and Industry Standards
Regulatory frameworks for autonomous vehicles emphasize stringent safety validations and liability clarifications, with agencies like the NHTSA and UNECE setting detailed guidelines to ensure operational safety and ethical decision-making. Connected vehicles rely heavily on interoperability standards established by organizations such as IEEE and ETSI, focusing on secure data exchange and communication protocols like V2X to enhance traffic efficiency and prevent cyber threats. Industry standards for both vehicle types increasingly converge to address cybersecurity, data privacy, and compliance with regional regulations, creating a complex landscape that requires coordination between manufacturers, technology providers, and regulators.
Future Trends: Synergies and the Road Ahead
Autonomous vehicles leverage advanced AI to navigate independently, while connected vehicles rely on real-time data exchange through V2X communication to enhance situational awareness. Future trends emphasize the integration of these technologies, creating synergistic systems that improve safety, efficiency, and traffic management. The road ahead points to a unified mobility ecosystem where autonomous control and seamless connectivity drive smarter, more adaptive transportation networks.
autonomous vehicles vs connected vehicles Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com