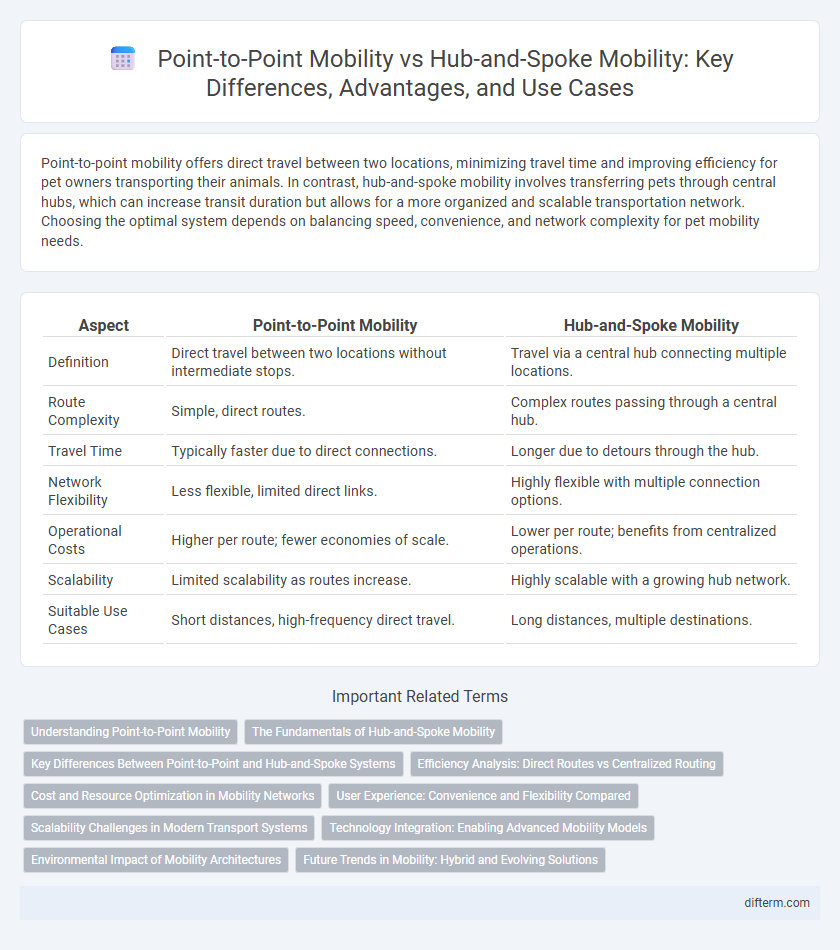
Point-to-point mobility offers direct travel between two locations, minimizing travel time and improving efficiency for pet owners transporting their animals. In contrast, hub-and-spoke mobility involves transferring pets through central hubs, which can increase transit duration but allows for a more organized and scalable transportation network. Choosing the optimal system depends on balancing speed, convenience, and network complexity for pet mobility needs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Point-to-Point Mobility | Hub-and-Spoke Mobility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct travel between two locations without intermediate stops. | Travel via a central hub connecting multiple locations. |
| Route Complexity | Simple, direct routes. | Complex routes passing through a central hub. |
| Travel Time | Typically faster due to direct connections. | Longer due to detours through the hub. |
| Network Flexibility | Less flexible, limited direct links. | Highly flexible with multiple connection options. |
| Operational Costs | Higher per route; fewer economies of scale. | Lower per route; benefits from centralized operations. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability as routes increase. | Highly scalable with a growing hub network. |
| Suitable Use Cases | Short distances, high-frequency direct travel. | Long distances, multiple destinations. |
Understanding Point-to-Point Mobility
Point-to-point mobility enables direct travel between two locations without transfers, significantly reducing travel time and improving passenger convenience. This model is often preferred in urban environments with high demand between specific origin-destination pairs, optimizing route efficiency and minimizing fuel consumption. In contrast to hub-and-spoke systems, point-to-point mobility decreases congestion at central hubs and enhances overall network flexibility.
The Fundamentals of Hub-and-Spoke Mobility
Hub-and-spoke mobility revolves around a central hub connecting multiple spokes or destinations, optimizing route efficiency and resource allocation. This model reduces direct routes between points, concentrating traffic flow through the hub to maximize capacity utilization and streamline scheduling. By contrast to point-to-point mobility, hub-and-spoke systems enhance scalability and cost-effectiveness in transportation networks, particularly in airline and public transit operations.
Key Differences Between Point-to-Point and Hub-and-Spoke Systems
Point-to-point mobility offers direct connections between two locations, minimizing travel time and reducing the risk of delays associated with transfers. Hub-and-spoke systems centralize routes through a main hub, optimizing operational efficiency and allowing for extensive network coverage despite longer travel times. The choice between these two models significantly impacts passenger convenience, network complexity, and overall service frequency.
Efficiency Analysis: Direct Routes vs Centralized Routing
Point-to-point mobility enhances efficiency by providing direct routes between locations, reducing travel time and minimizing transfers compared to hub-and-spoke systems that centralize routing through a single hub. Hub-and-spoke mobility often results in increased congestion and longer total journey durations due to the concentration of traffic at hub points. Evaluating operational costs, fuel consumption, and passenger convenience highlights point-to-point models as superior in optimizing route efficiency for high-demand, diverse origin-destination pairs.
Cost and Resource Optimization in Mobility Networks
Point-to-point mobility networks reduce transit times and fuel consumption by enabling direct routes between origins and destinations, leading to lower operational costs and enhanced resource utilization. Hub-and-spoke mobility models centralize resources and consolidate traffic through key nodes, optimizing fleet deployment and maintenance but often increasing transit delays and fuel costs. Choosing between these models depends on balancing the trade-offs between minimizing travel distances and maximizing logistical efficiencies in mobility network operations.
User Experience: Convenience and Flexibility Compared
Point-to-point mobility enhances user experience by offering direct routes that reduce travel time and eliminate the need for transfers, resulting in greater convenience and flexibility. Hub-and-spoke mobility often requires passengers to connect through central hubs, potentially increasing total travel time and limiting spontaneous route changes. Direct connections in point-to-point systems better accommodate individual schedules and optimize travel efficiency.
Scalability Challenges in Modern Transport Systems
Point-to-point mobility faces scalability challenges due to the exponential increase in direct routes required as network size grows, leading to higher operational complexity and costs. Hub-and-spoke mobility centralizes connections through key hubs, which simplifies route management but risks congestion and bottlenecks at these points. Modern transport systems must balance scalability by optimizing hub capacity and integrating flexible routing to accommodate fluctuating demand and maintain efficiency.
Technology Integration: Enabling Advanced Mobility Models
Technology integration drives the evolution from hub-and-spoke to point-to-point mobility models by enabling real-time data analytics, IoT connectivity, and AI-powered routing algorithms. These advancements facilitate direct, efficient travel paths and dynamic resource allocation, reducing congestion and wait times. Enhanced mobility platforms leverage cloud computing and edge devices to ensure seamless coordination and rapid adaptability across transportation networks.
Environmental Impact of Mobility Architectures
Point-to-point mobility systems, characterized by direct routes between origins and destinations, generally reduce total travel distance and emissions compared to hub-and-spoke models, which concentrate traffic through central hubs, often leading to increased congestion and higher carbon footprints. Hub-and-spoke architectures typically result in longer journey times and more fuel consumption due to indirect routing and transfer waits, amplifying environmental impacts in urban transportation networks. Emerging data suggest shifting towards decentralized, point-to-point mobility can significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions and improve overall energy efficiency in sustainable mobility planning.
Future Trends in Mobility: Hybrid and Evolving Solutions
Point-to-point mobility offers direct, personalized routes that reduce travel time and increase efficiency, while hub-and-spoke systems centralize transit for optimized resource management and scalability. Future trends emphasize hybrid models integrating both approaches, leveraging advanced data analytics and AI to dynamically adapt routes based on real-time demand and urban infrastructure. These evolving solutions aim to balance convenience, sustainability, and operational efficiency in increasingly complex mobility ecosystems.
point-to-point mobility vs hub-and-spoke mobility Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com