Flexible mobility offers personalized routes and schedules that adapt to individual needs, enhancing convenience and accessibility for pet owners on the go. Unlike fixed-route mobility, which relies on predetermined paths and timetables, flexible options provide greater freedom and efficiency in navigating urban spaces with pets. This dynamic approach addresses changing demands and reduces wait times, improving overall travel experience for mobility pet services.
Table of Comparison
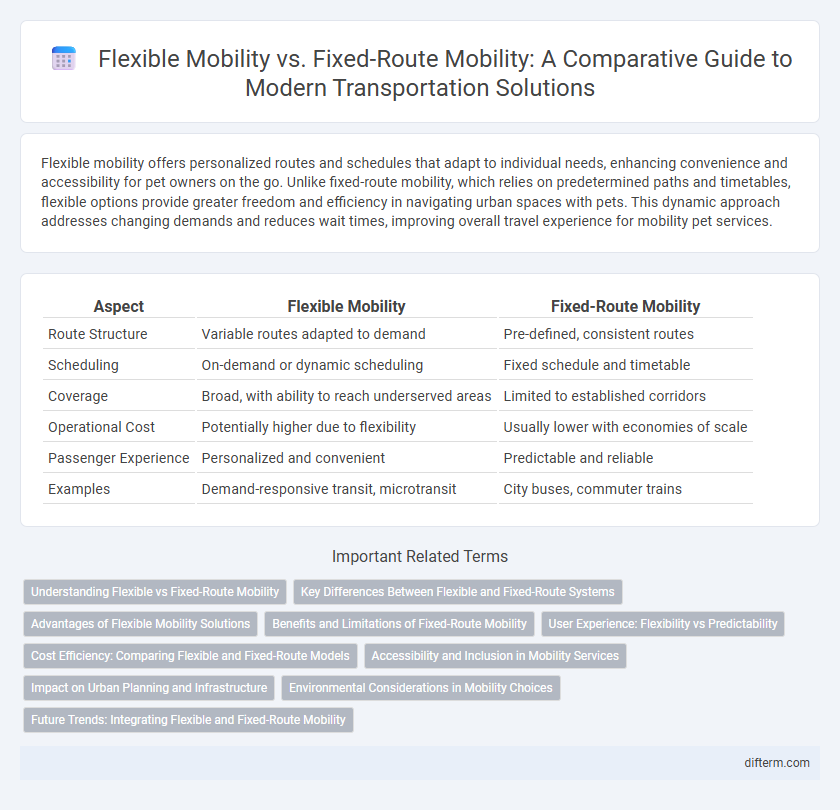
| Aspect | Flexible Mobility | Fixed-Route Mobility |
|---|---|---|
| Route Structure | Variable routes adapted to demand | Pre-defined, consistent routes |
| Scheduling | On-demand or dynamic scheduling | Fixed schedule and timetable |
| Coverage | Broad, with ability to reach underserved areas | Limited to established corridors |
| Operational Cost | Potentially higher due to flexibility | Usually lower with economies of scale |
| Passenger Experience | Personalized and convenient | Predictable and reliable |
| Examples | Demand-responsive transit, microtransit | City buses, commuter trains |
Understanding Flexible vs Fixed-Route Mobility
Flexible mobility offers adaptable routing and scheduling tailored to real-time passenger demand, enhancing accessibility in low-density or underserved areas. Fixed-route mobility operates on predetermined paths and timetables, optimizing efficiency and predictability for high-demand corridors. Understanding the contrast between these models is essential for designing integrated transportation systems that balance coverage, cost, and user convenience.
Key Differences Between Flexible and Fixed-Route Systems
Flexible mobility systems adapt routes and schedules based on real-time demand, offering personalized service and improved access in low-density areas. Fixed-route mobility operates on predetermined paths and timetables, maximizing efficiency and predictability in high-demand corridors. Key differences include route adaptability, service frequency, and operational costs, with flexible systems requiring dynamic scheduling and fixed-route systems benefiting from economies of scale.
Advantages of Flexible Mobility Solutions
Flexible mobility solutions improve accessibility by adapting routes and schedules to real-time demand, reducing wait times and expanding coverage in underserved areas. These systems enhance user convenience through on-demand services, offering personalized travel options that fixed-route systems cannot match. Cost efficiency is increased by optimizing vehicle deployment and minimizing empty miles, leading to lower operational expenses and environmental impact.
Benefits and Limitations of Fixed-Route Mobility
Fixed-route mobility offers predictable schedules and consistent service on designated paths, optimizing efficiency and operational costs for transit agencies. However, it lacks flexibility, often failing to accommodate spontaneous travel needs or serve low-density areas effectively, which can limit accessibility for some users. Fixed routes may also contribute to increased travel times for passengers whose origins or destinations are not near established stops.
User Experience: Flexibility vs Predictability
Flexible mobility offers users the advantage of personalized routes and schedules, enhancing convenience and adapting to real-time demand, which improves overall satisfaction. Fixed-route mobility, in contrast, provides predictable arrival and departure times, fostering reliability and ease of planning for daily commuters. Balancing flexibility with predictability is crucial to optimizing user experience in urban transportation systems.
Cost Efficiency: Comparing Flexible and Fixed-Route Models
Flexible mobility systems reduce operational costs by optimizing routes based on real-time demand, unlike fixed-route models that often incur expenses from underutilized capacity. Fixed-route mobility benefits from predictable scheduling and economies of scale but struggles with inefficiencies during off-peak hours. Cost efficiency in flexible mobility is enhanced through dynamic resource allocation, leading to lower per-trip expenses and improved service responsiveness.
Accessibility and Inclusion in Mobility Services
Flexible mobility services enhance accessibility by adapting routes and schedules to meet diverse user needs, especially benefiting individuals with disabilities and those in underserved areas. Fixed-route mobility often limits inclusion due to rigid schedules and predetermined paths that may not connect all communities effectively. Emphasizing flexible options promotes equitable transportation access, reducing mobility barriers and fostering community integration.
Impact on Urban Planning and Infrastructure
Flexible mobility systems reduce the demand for extensive fixed-route infrastructures, allowing urban planners to design more adaptable and space-efficient city layouts. These dynamic transportation options optimize road usage, decrease congestion, and support multimodal integration, enhancing overall urban functionality. Fixed-route mobility requires substantial investment in dedicated lanes, stations, and maintenance, often limiting the flexibility needed to respond to changing urban growth patterns and population densities.
Environmental Considerations in Mobility Choices
Flexible mobility options, such as on-demand shuttles and bike-sharing programs, reduce carbon emissions by optimizing routes and minimizing unnecessary travel, unlike fixed-route systems that often run underutilized vehicles. The environmental impact of fixed-route mobility includes higher greenhouse gas emissions due to less efficient resource utilization and rigid scheduling. Emphasizing flexible mobility supports sustainable urban transportation by lowering fossil fuel consumption and improving air quality.
Future Trends: Integrating Flexible and Fixed-Route Mobility
Future trends in urban transportation emphasize seamless integration of flexible mobility services like on-demand shuttles with fixed-route transit systems to enhance accessibility and reduce congestion. Advanced data analytics and AI-driven routing optimize real-time adjustments, improving service efficiency and passenger experience. This hybrid model supports sustainable mobility goals by balancing predictability with adaptability in transit networks.
flexible mobility vs fixed-route mobility Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com