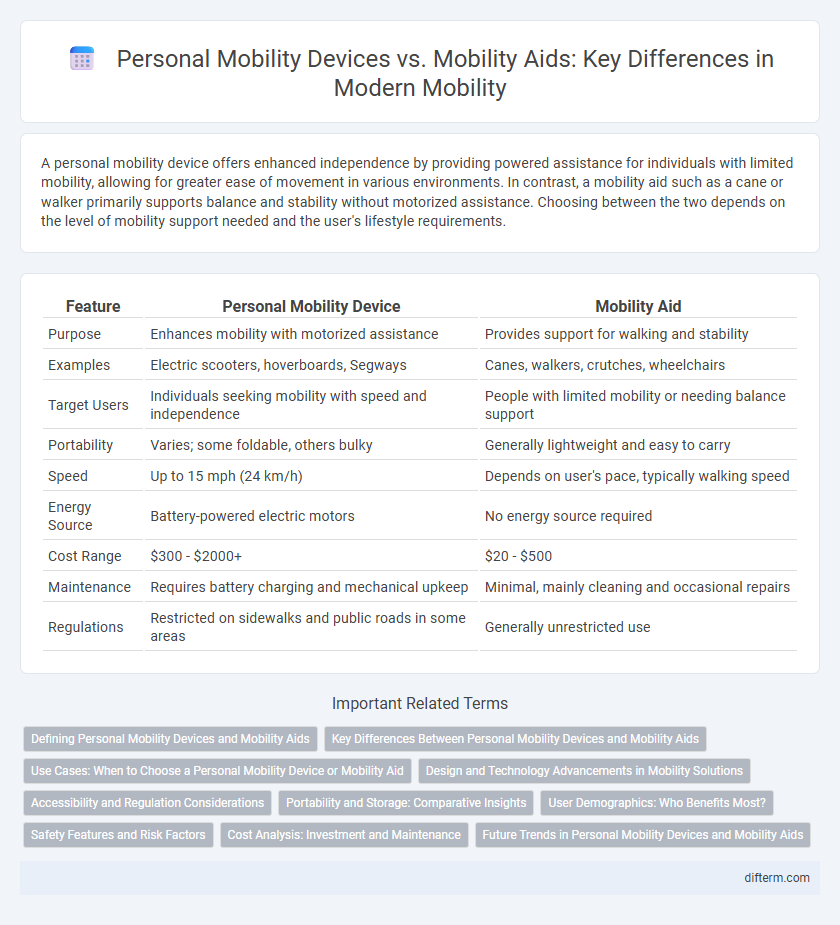
A personal mobility device offers enhanced independence by providing powered assistance for individuals with limited mobility, allowing for greater ease of movement in various environments. In contrast, a mobility aid such as a cane or walker primarily supports balance and stability without motorized assistance. Choosing between the two depends on the level of mobility support needed and the user's lifestyle requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Personal Mobility Device | Mobility Aid |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhances mobility with motorized assistance | Provides support for walking and stability |
| Examples | Electric scooters, hoverboards, Segways | Canes, walkers, crutches, wheelchairs |
| Target Users | Individuals seeking mobility with speed and independence | People with limited mobility or needing balance support |
| Portability | Varies; some foldable, others bulky | Generally lightweight and easy to carry |
| Speed | Up to 15 mph (24 km/h) | Depends on user's pace, typically walking speed |
| Energy Source | Battery-powered electric motors | No energy source required |
| Cost Range | $300 - $2000+ | $20 - $500 |
| Maintenance | Requires battery charging and mechanical upkeep | Minimal, mainly cleaning and occasional repairs |
| Regulations | Restricted on sidewalks and public roads in some areas | Generally unrestricted use |
Defining Personal Mobility Devices and Mobility Aids
Personal mobility devices are innovative tools such as electric scooters, hoverboards, and Segways designed for individual transportation, emphasizing convenience and speed. Mobility aids, including wheelchairs, walkers, and canes, primarily assist users with physical disabilities to enhance stability and mobility in daily activities. Both categories play crucial roles in promoting independence but serve distinct purposes based on the user's mobility requirements and functional abilities.
Key Differences Between Personal Mobility Devices and Mobility Aids
Personal mobility devices, such as electric scooters and Segways, are designed primarily for enhancing independent transportation and recreational use, offering speed and range advantages. Mobility aids, including wheelchairs, walkers, and canes, focus on providing support, stability, and safety for individuals with physical disabilities or mobility impairments. Key distinctions lie in their intended purpose, regulatory classification, and user dependency levels, with personal mobility devices often requiring operational skills, while mobility aids emphasize accessibility and ergonomic support.
Use Cases: When to Choose a Personal Mobility Device or Mobility Aid
Personal mobility devices, such as electric scooters and hoverboards, are ideal for users seeking independence and convenience in navigating urban environments or campuses with moderate physical ability. Mobility aids, including wheelchairs and walkers, are essential for individuals requiring enhanced stability and support due to mobility impairments or chronic conditions. Choosing between these options depends on factors like the user's physical capabilities, terrain complexity, and the need for safety features.
Design and Technology Advancements in Mobility Solutions
Personal mobility devices leverage cutting-edge technology such as lightweight materials, AI-powered navigation, and enhanced battery life to offer greater independence and convenience, distinguishing them from traditional mobility aids like canes and walkers. Innovations in ergonomic design improve user comfort and adaptability, while integration with smart systems enables real-time health monitoring and seamless connectivity. Advanced mobility solutions prioritize both functionality and aesthetics, reflecting significant progress in personalized, tech-driven mobility support.
Accessibility and Regulation Considerations
Personal mobility devices, such as electric scooters and hoverboards, offer enhanced accessibility for short-distance travel but face varied regulatory frameworks across regions, impacting their legal use on sidewalks and public roads. Mobility aids, including wheelchairs and walkers, are universally recognized with standardized accessibility accommodations and stricter regulations ensuring safe integration into public spaces. Harmonizing policies for both categories is essential to improve inclusive mobility while addressing safety and accessibility standards.
Portability and Storage: Comparative Insights
Personal mobility devices, such as electric scooters and foldable e-bikes, excel in portability with lightweight designs and compact folding mechanisms, making them ideal for urban commuters requiring easy storage and transport. Mobility aids, including walkers and wheelchairs, prioritize stability and support but often compromise on compactness, presenting challenges in tight storage spaces and public transport. Choosing between these options depends on balancing portability needs versus functional mobility support for diverse user requirements.
User Demographics: Who Benefits Most?
Personal mobility devices, such as electric scooters and hoverboards, primarily benefit tech-savvy younger adults and urban commuters seeking convenience and speed for short-distance travel. Mobility aids, including walkers and wheelchairs, are essential for elderly individuals and people with physical disabilities who require stability and support for daily movement. Understanding these user demographics enables targeted product development and enhances accessibility solutions tailored to specific mobility needs.
Safety Features and Risk Factors
Personal mobility devices, such as electric scooters and hoverboards, incorporate advanced safety features like automatic brakes, speed limiters, and LED lighting to enhance visibility and control. Mobility aids, including walkers and wheelchairs, prioritize stability and ergonomic design to minimize fall risk and provide user support. Risk factors for personal mobility devices often include higher speeds and less tactile feedback, while mobility aids face challenges related to user strength and environmental obstacles.
Cost Analysis: Investment and Maintenance
Personal mobility devices, such as electric scooters and e-bikes, typically require a higher initial investment but offer lower long-term maintenance costs compared to traditional mobility aids like wheelchairs and walkers, which often involve frequent servicing and part replacements. The durability of battery-operated devices reduces recurring expenses, while mobility aids may incur higher costs due to specialized repairs and accessories. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals personal mobility devices as cost-effective solutions for users prioritizing both initial affordability and ongoing maintenance efficiency.
Future Trends in Personal Mobility Devices and Mobility Aids
Future trends in personal mobility devices emphasize smart integration, with AI-powered features enhancing navigation and user safety for improved independence. Mobility aids are evolving toward lightweight, ergonomic designs incorporating advanced materials and sensor technology to provide adaptive support and increased comfort. The convergence of wearable technology and connectivity in both personal mobility devices and aids promises seamless interaction with urban infrastructure and personalized mobility solutions.
personal mobility device vs mobility aid Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com