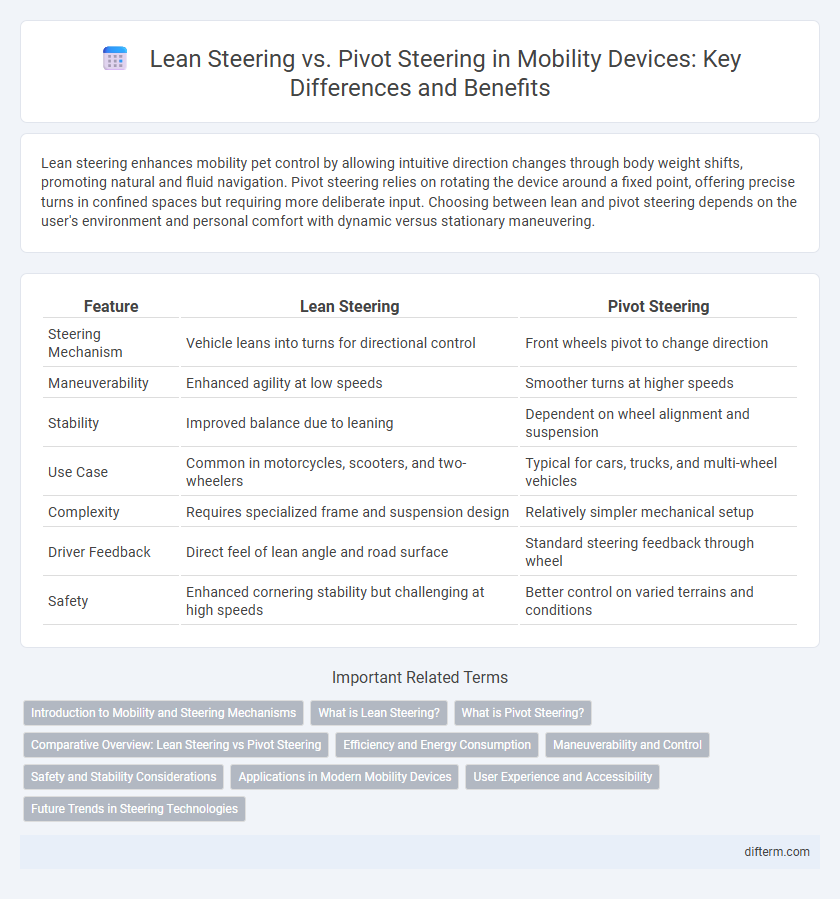
Lean steering enhances mobility pet control by allowing intuitive direction changes through body weight shifts, promoting natural and fluid navigation. Pivot steering relies on rotating the device around a fixed point, offering precise turns in confined spaces but requiring more deliberate input. Choosing between lean and pivot steering depends on the user's environment and personal comfort with dynamic versus stationary maneuvering.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lean Steering | Pivot Steering |
|---|---|---|
| Steering Mechanism | Vehicle leans into turns for directional control | Front wheels pivot to change direction |
| Maneuverability | Enhanced agility at low speeds | Smoother turns at higher speeds |
| Stability | Improved balance due to leaning | Dependent on wheel alignment and suspension |
| Use Case | Common in motorcycles, scooters, and two-wheelers | Typical for cars, trucks, and multi-wheel vehicles |
| Complexity | Requires specialized frame and suspension design | Relatively simpler mechanical setup |
| Driver Feedback | Direct feel of lean angle and road surface | Standard steering feedback through wheel |
| Safety | Enhanced cornering stability but challenging at high speeds | Better control on varied terrains and conditions |
Introduction to Mobility and Steering Mechanisms
Mobility systems in robotics and vehicles rely heavily on efficient steering mechanisms to ensure precise maneuverability and control. Lean steering adjusts direction by tilting or leaning the entire vehicle or platform, offering smoother turns and enhanced stability, especially in narrow or uneven environments. Pivot steering rotates the platform around a fixed point, enabling sharp turns and excellent agility, commonly used in zero-radius turn vehicles like forklifts and certain robotics applications.
What is Lean Steering?
Lean steering in mobility refers to the technique where the rider shifts their body weight and leans into a turn to steer the vehicle, enhancing control and stability, especially at higher speeds. This method is commonly used in motorcycles and bicycles, allowing for more precise and dynamic maneuvering compared to pivot steering, which relies on turning the handlebars or front wheels. Lean steering optimizes traction and balance by aligning the center of gravity with the direction of the turn, reducing the risk of skidding or losing control.
What is Pivot Steering?
Pivot steering is a mobility technique that allows a vehicle or device to rotate around a fixed point, enabling sharp turns with minimal space. It enhances maneuverability in tight environments by reducing the turning radius compared to traditional lean steering, which relies on body tilt to initiate directional change. Common in robotics and compact vehicles, pivot steering improves precision control and agility.
Comparative Overview: Lean Steering vs Pivot Steering
Lean steering enhances maneuverability by tilting the vehicle into turns, significantly improving stability and cornering performance, especially in motorcycles and three-wheeled vehicles. Pivot steering operates by rotating wheels around a vertical axis, offering precise control and sharper turning radii ideal for compact mobility devices and forklifts. Comparing both, lean steering excels in dynamic stability and rider feedback, while pivot steering provides superior maneuverability in tight, low-speed environments.
Efficiency and Energy Consumption
Lean steering enhances mobility efficiency by allowing vehicles to tilt into turns, reducing lateral forces and improving traction, which results in lower energy consumption during cornering. Pivot steering, while offering precise maneuverability by rotating around a vertical axis, often demands higher energy use due to increased mechanical complexity and resistance. Thus, lean steering is generally more energy-efficient, making it optimal for sustained mobility applications where conserving power is crucial.
Maneuverability and Control
Lean steering provides enhanced maneuverability by allowing riders to naturally tilt into turns, improving balance and stability in dynamic conditions. Pivot steering offers precise control through direct handlebar input, enabling sharper turns and reduced steering effort in confined spaces. Combining lean steering's fluid motion with pivot steering's exact responsiveness optimizes overall vehicle handling and agility.
Safety and Stability Considerations
Lean steering enhances safety and stability by allowing vehicles, especially motorcycles and bicycles, to tilt into turns, reducing lateral slip and maintaining better tire contact with the road surface. Pivot steering, commonly found in articulated vehicles and some robotic mobility devices, offers precise directional control but may sacrifice stability during sharp turns due to a higher center of gravity and less natural weight distribution. Evaluating safety in mobility systems requires comparing lean steering's dynamic balance benefits against pivot steering's maneuverability to optimize vehicle performance in various conditions.
Applications in Modern Mobility Devices
Lean steering enhances maneuverability and intuitive control in modern mobility devices by allowing users to steer through body shifts, making it ideal for personal electric scooters and smart wheelchairs. Pivot steering, characterized by a fixed rotation point, offers precise turns suitable for tight indoor environments and robotic delivery vehicles. Combining these steering mechanisms optimizes mobility solutions across diverse applications, improving both agility and spatial navigation.
User Experience and Accessibility
Lean steering enhances user experience by providing intuitive, body-weight controlled maneuverability, improving accessibility for individuals with limited hand strength or dexterity. Pivot steering offers precise directional control through handle rotation, benefiting users requiring stable, tight turns in confined spaces. Optimizing steering mechanisms based on user mobility needs significantly increases overall accessibility and comfort in vehicle or device navigation.
Future Trends in Steering Technologies
Future trends in steering technologies emphasize the integration of lean steering and pivot steering systems to enhance vehicle agility and stability. Lean steering, which allows vehicles to tilt dynamically during turns, improves cornering performance and passenger comfort in two-wheelers and small urban vehicles. Pivot steering, often used in autonomous and heavy-duty vehicles, enables precise point-turning and maneuverability, supporting advancements in robotic vehicle navigation and urban mobility solutions.
lean steering vs pivot steering Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com