All-wheel-drive (AWD) systems automatically distribute power to all wheels for optimal traction on various surfaces, enhancing mobility and control in everyday driving conditions. Four-wheel-drive (4WD) systems offer manual control, allowing drivers to engage power to all wheels primarily for off-road or challenging terrains, providing superior traction when needed. Choosing between AWD and 4WD depends on the typical mobility environment, with AWD favoring consistent on-road stability and 4WD excelling in rugged, off-road scenarios.
Table of Comparison
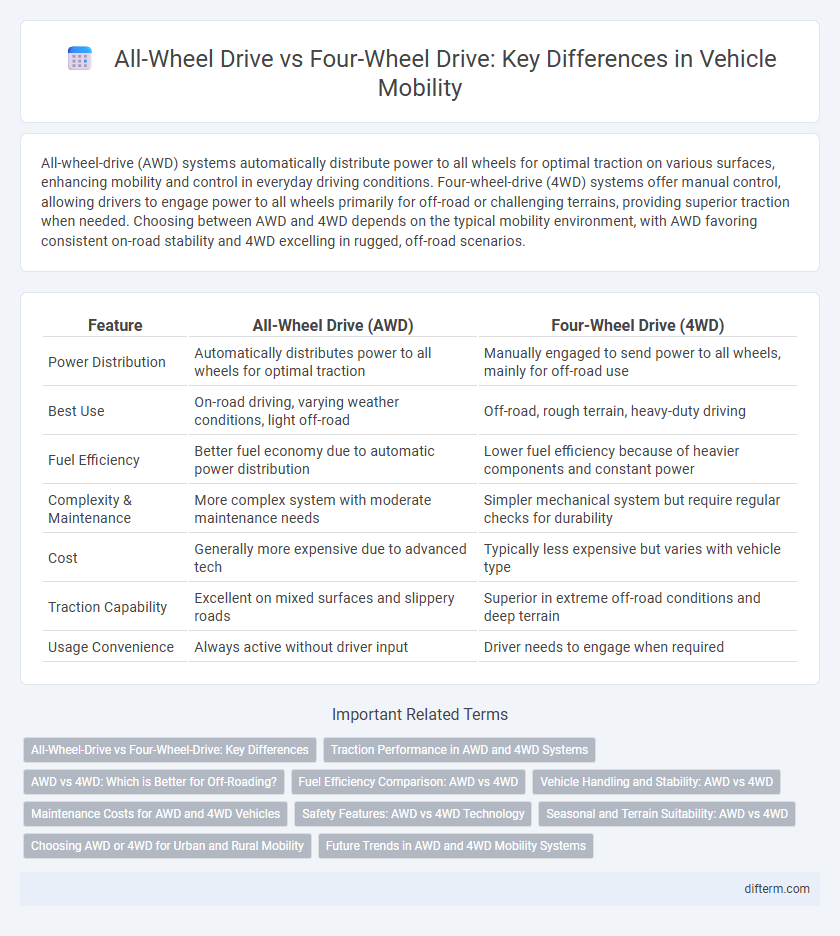
| Feature | All-Wheel Drive (AWD) | Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) |
|---|---|---|
| Power Distribution | Automatically distributes power to all wheels for optimal traction | Manually engaged to send power to all wheels, mainly for off-road use |
| Best Use | On-road driving, varying weather conditions, light off-road | Off-road, rough terrain, heavy-duty driving |
| Fuel Efficiency | Better fuel economy due to automatic power distribution | Lower fuel efficiency because of heavier components and constant power |
| Complexity & Maintenance | More complex system with moderate maintenance needs | Simpler mechanical system but require regular checks for durability |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to advanced tech | Typically less expensive but varies with vehicle type |
| Traction Capability | Excellent on mixed surfaces and slippery roads | Superior in extreme off-road conditions and deep terrain |
| Usage Convenience | Always active without driver input | Driver needs to engage when required |
All-Wheel-Drive vs Four-Wheel-Drive: Key Differences
All-wheel-drive (AWD) systems provide continuous power to all four wheels for improved traction in diverse driving conditions, making them ideal for on-road and light off-road use. Four-wheel-drive (4WD) systems deliver power to all wheels but can be manually engaged or disengaged, optimized for rugged off-road terrain and heavy-duty performance. AWD offers seamless control and enhanced safety in everyday driving, while 4WD focuses on maximum traction and durability for challenging environments.
Traction Performance in AWD and 4WD Systems
All-wheel-drive (AWD) systems provide continuous power to all wheels, optimizing traction on varying surfaces with improved stability in wet or slippery conditions. Four-wheel-drive (4WD) systems deliver power primarily to two wheels, engaging all four in low-traction scenarios like off-road or rugged terrain, enhancing grip and torque distribution. AWD excels in on-road traction and automatic adjustments, while 4WD offers superior control and traction in off-road or extreme conditions.
AWD vs 4WD: Which is Better for Off-Roading?
All-wheel-drive (AWD) systems provide continuous power to all four wheels, enhancing traction and control on varied terrain, making them suitable for light off-roading and adverse weather conditions. Four-wheel-drive (4WD) systems offer selectable power distribution, with low-range gearing for extreme off-road conditions such as rock crawling, deep mud, and steep inclines, providing superior durability and torque. For serious off-road enthusiasts, 4WD is generally better due to its robust setup and ability to handle more challenging environments, while AWD excels in everyday versatility and moderate off-road use.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison: AWD vs 4WD
All-wheel-drive (AWD) systems generally offer better fuel efficiency compared to four-wheel-drive (4WD) due to their lightweight design and automatic power distribution, which reduces energy loss during normal driving conditions. In contrast, 4WD systems often engage all wheels continuously or require manual activation, increasing drivetrain resistance and fuel consumption. Studies show AWD vehicles can improve fuel economy by up to 10-15% over traditional 4WD setups, making AWD more suitable for daily driving with occasional off-road use.
Vehicle Handling and Stability: AWD vs 4WD
All-wheel-drive (AWD) systems continuously distribute power to all four wheels, enhancing vehicle handling and stability on varied road surfaces, especially in wet or icy conditions. Four-wheel-drive (4WD) systems engage power to all wheels selectively, providing superior traction and control in off-road and rugged terrain but may reduce stability in everyday driving due to driveline binding. AWD improves cornering and maintains grip on paved roads, while 4WD excels in extreme off-road conditions where maximum torque and durability are required.
Maintenance Costs for AWD and 4WD Vehicles
Maintenance costs for all-wheel-drive (AWD) vehicles tend to be lower than those for four-wheel-drive (4WD) vehicles due to the simpler drivetrain components and fewer mechanical parts involved in AWD systems. AWD systems require less frequent servicing of transfer cases and locking differentials, reducing overall repair expenses over time. In contrast, 4WD vehicles often incur higher maintenance costs due to more complex off-road components and increased wear on drivetrain parts under rugged conditions.
Safety Features: AWD vs 4WD Technology
All-wheel-drive (AWD) systems enhance safety by automatically distributing power to all wheels for optimal traction on slippery or uneven surfaces, improving stability during cornering and sudden maneuvers. Four-wheel-drive (4WD) technology provides superior off-road capability and durability with selectable modes for challenging terrains, offering enhanced control in extreme conditions but often requiring manual engagement. AWD's seamless operation benefits everyday driving safety, while 4WD excels in rugged environments where maximum power delivery and traction are critical.
Seasonal and Terrain Suitability: AWD vs 4WD
All-wheel-drive (AWD) systems automatically distribute power to all four wheels, providing enhanced traction on wet, icy, or moderately uneven surfaces, making them ideal for year-round driving in varying weather conditions. Four-wheel-drive (4WD) systems offer manual control and high torque for off-road, rugged terrains, and severe winter conditions, making them better suited for seasonal use where maximum traction is critical. Choosing AWD benefits urban and suburban drivers facing regular but less extreme changes, while 4WD is preferred for harsh off-road environments and deep snow or mud.
Choosing AWD or 4WD for Urban and Rural Mobility
All-wheel-drive (AWD) systems continuously distribute power to all wheels, providing superior traction and stability for urban driving conditions with frequent stops and varied road surfaces. Four-wheel-drive (4WD) systems are designed for rugged, off-road terrain and demanding rural environments, offering selectable modes to maximize torque on challenging surfaces like mud, snow, or rocks. Selecting AWD benefits city commuters and mixed conditions, while 4WD is optimal for rural mobility where robust off-road capability is essential.
Future Trends in AWD and 4WD Mobility Systems
Future trends in all-wheel-drive (AWD) and four-wheel-drive (4WD) mobility systems emphasize electrification and integration with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Electrified AWD and 4WD platforms enable precise torque vectoring and enhanced energy efficiency, supporting both on-road stability and off-road capability. Increasing adoption of software-driven controls and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication further advances the adaptability and safety of these drivetrains in autonomous and connected mobility ecosystems.
all-wheel-drive vs four-wheel-drive Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com