Electric vehicle (EV) charging offers a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional fuel refueling by reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. Charging infrastructure increasingly integrates renewable energy sources, enabling eco-friendly mobility and lower operational costs over time. Advances in fast-charging technology continue to minimize wait times, making EVs more convenient and accessible for daily use compared to conventional refueling stations.
Table of Comparison
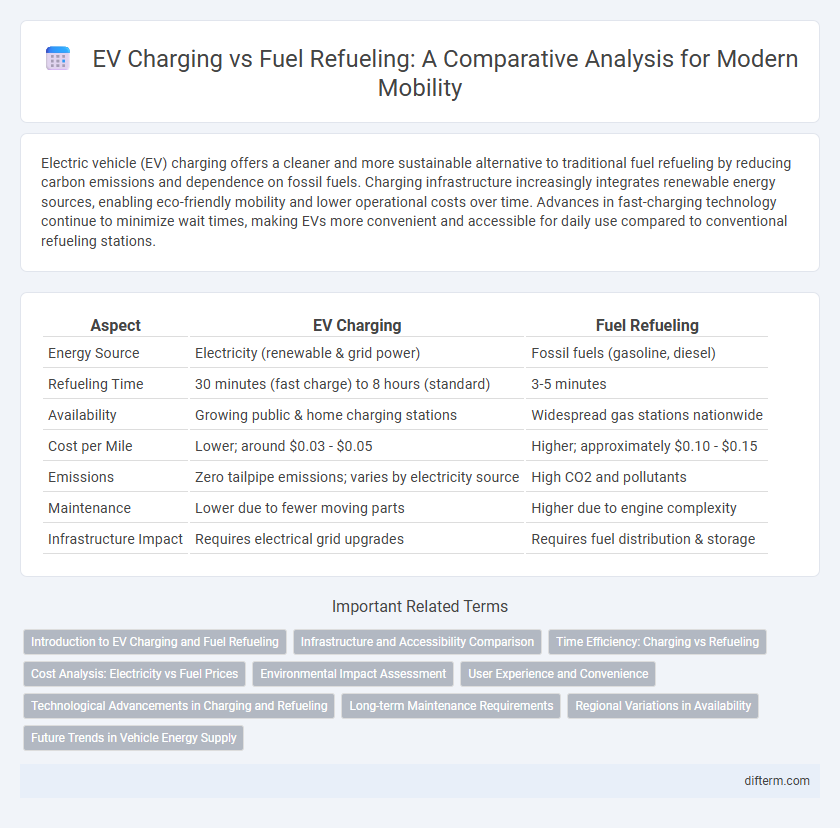
| Aspect | EV Charging | Fuel Refueling |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Electricity (renewable & grid power) | Fossil fuels (gasoline, diesel) |
| Refueling Time | 30 minutes (fast charge) to 8 hours (standard) | 3-5 minutes |
| Availability | Growing public & home charging stations | Widespread gas stations nationwide |
| Cost per Mile | Lower; around $0.03 - $0.05 | Higher; approximately $0.10 - $0.15 |
| Emissions | Zero tailpipe emissions; varies by electricity source | High CO2 and pollutants |
| Maintenance | Lower due to fewer moving parts | Higher due to engine complexity |
| Infrastructure Impact | Requires electrical grid upgrades | Requires fuel distribution & storage |
Introduction to EV Charging and Fuel Refueling
Electric vehicle (EV) charging involves replenishing battery energy through various charging stations, which range from slow Level 1 chargers to rapid DC fast chargers, enabling flexible fueling times adjusted to user needs. Fuel refueling for internal combustion engine vehicles relies on liquid fuel pumps delivering gasoline or diesel within minutes, supporting widespread infrastructure and quick turnaround times. The transition to EV charging emphasizes energy efficiency, renewable integration, and evolving charging networks that contrast traditional fuel station ubiquity and convenience.
Infrastructure and Accessibility Comparison
EV charging infrastructure is rapidly expanding with over 150,000 public charging stations in the U.S. compared to approximately 168,000 fuel refueling stations, enhancing accessibility for electric vehicle users. Charging stations often require longer dwell times, but the growing adoption of fast chargers--capable of delivering 80% charge in under 30 minutes--improves convenience. Urban areas increasingly integrate EV chargers in parking garages and residential complexes, narrowing the accessibility gap traditionally dominated by fuel refueling stations.
Time Efficiency: Charging vs Refueling
EV charging requires significantly longer durations compared to traditional fuel refueling, with average fast chargers taking 20-40 minutes for an 80% battery charge versus under 5 minutes at gas stations. Innovations in ultra-fast charging technology aim to reduce EV charging times to parity with refueling, targeting 10-15 minutes per charge. Time efficiency remains a critical factor influencing consumer adoption rates in the transition from internal combustion engines to electric mobility.
Cost Analysis: Electricity vs Fuel Prices
Electric vehicle (EV) charging costs are significantly lower than traditional fuel refueling due to the declining price of electricity and higher efficiency of electric motors. On average, the cost per mile for an EV powered by electricity is nearly 50% less than gasoline-powered vehicles, influenced by fluctuating oil prices and regional electricity rates. Long-term savings on EV charging are amplified by reduced maintenance and improved energy conversion compared to internal combustion engines.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Electric vehicle (EV) charging demonstrates a significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional fuel refueling, primarily due to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and lower air pollutants during operation. Life cycle assessments highlight that EV charging powered by renewable energy sources minimizes carbon footprints, whereas fuel refueling relies heavily on fossil fuel extraction and combustion, contributing substantially to environmental degradation. Studies indicate that shifting from internal combustion engine vehicles to EVs with sustainable charging infrastructure can decrease total environmental burdens by up to 60% over the vehicle's lifespan.
User Experience and Convenience
EV charging offers a more convenient user experience with options like at-home, workplace, and public chargers, eliminating trips to fuel stations. Fast chargers reduce wait times significantly, aligning with users' busy schedules and enhancing overall mobility convenience. Unlike fuel refueling, EV charging integrates seamlessly into daily routines, providing a quieter, cleaner, and more accessible energy replenishment method.
Technological Advancements in Charging and Refueling
Rapid advancements in electric vehicle (EV) charging technology, including ultra-fast chargers and wireless charging pads, significantly reduce downtime compared to traditional fuel refueling. Smart charging infrastructure integrates with renewable energy sources and grid management systems to enhance energy efficiency and sustainability. Meanwhile, innovations in fuel refueling aim to improve speed and safety, but EV charging continues to outpace refueling in terms of environmental benefits and scalability.
Long-term Maintenance Requirements
Electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure demands lower long-term maintenance costs compared to traditional fuel refueling stations, due to fewer mechanical components and no need for fuel storage tanks. Charging stations primarily require software updates and occasional hardware inspections, whereas fuel pumps and underground storage tanks often undergo costly inspections, repairs, and environmental compliance measures. This difference results in more sustainable and cost-effective upkeep for EV networks over time.
Regional Variations in Availability
EV charging station availability varies significantly across regions, with urban areas and developed countries like Norway and the Netherlands exhibiting high density and accessibility. In contrast, rural regions and developing countries often face limited EV infrastructure, making fuel refueling stations more prevalent and reliable for long-distance travel. Government policies and investments also play a crucial role in shaping the regional disparities in EV charging versus traditional fuel refueling availability.
Future Trends in Vehicle Energy Supply
Electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure is rapidly evolving with advancements in fast-charging technology, wireless charging, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration, promising greater convenience and grid stability. In contrast, fuel refueling remains reliant on traditional gas stations but faces challenges due to increasing environmental regulations and shifting consumer preferences. Future trends indicate a significant shift towards decentralized energy solutions, renewable-powered charging networks, and smart energy management systems to support the growing EV market.
EV charging vs fuel refueling Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com