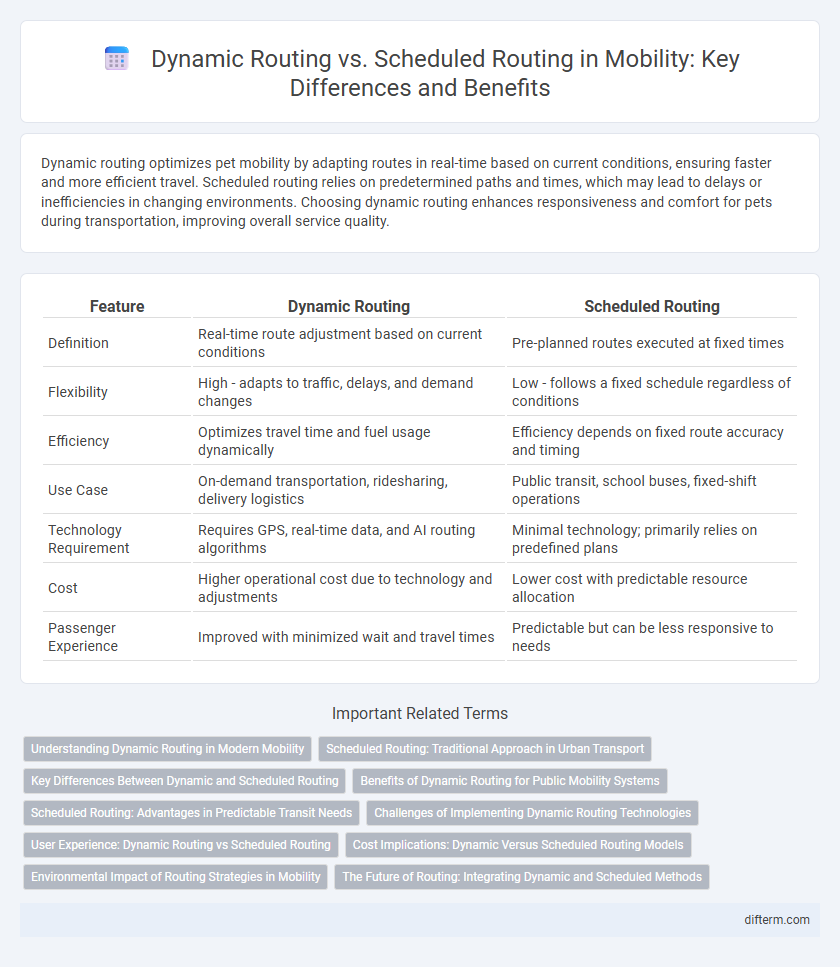
Dynamic routing optimizes pet mobility by adapting routes in real-time based on current conditions, ensuring faster and more efficient travel. Scheduled routing relies on predetermined paths and times, which may lead to delays or inefficiencies in changing environments. Choosing dynamic routing enhances responsiveness and comfort for pets during transportation, improving overall service quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dynamic Routing | Scheduled Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time route adjustment based on current conditions | Pre-planned routes executed at fixed times |
| Flexibility | High - adapts to traffic, delays, and demand changes | Low - follows a fixed schedule regardless of conditions |
| Efficiency | Optimizes travel time and fuel usage dynamically | Efficiency depends on fixed route accuracy and timing |
| Use Case | On-demand transportation, ridesharing, delivery logistics | Public transit, school buses, fixed-shift operations |
| Technology Requirement | Requires GPS, real-time data, and AI routing algorithms | Minimal technology; primarily relies on predefined plans |
| Cost | Higher operational cost due to technology and adjustments | Lower cost with predictable resource allocation |
| Passenger Experience | Improved with minimized wait and travel times | Predictable but can be less responsive to needs |
Understanding Dynamic Routing in Modern Mobility
Dynamic routing in modern mobility leverages real-time data and advanced algorithms to optimize travel paths based on current traffic conditions, demand fluctuations, and user preferences. Unlike scheduled routing, which follows predetermined routes and times, dynamic routing adapts continuously to minimize delays and enhance vehicle utilization in ride-sharing, public transit, and logistics. This flexibility reduces congestion, lowers operational costs, and improves overall system efficiency in urban transportation networks.
Scheduled Routing: Traditional Approach in Urban Transport
Scheduled routing in urban transport relies on fixed timetables and predetermined routes, ensuring consistent service regardless of real-time demand fluctuations. This traditional approach optimizes resource allocation for predictable passenger volumes, enhancing reliability and operational efficiency during peak hours. While less flexible than dynamic routing, scheduled routing supports regular commuter patterns and facilitates better planning in congested city environments.
Key Differences Between Dynamic and Scheduled Routing
Dynamic routing adapts routes in real-time based on traffic conditions, demand fluctuations, and vehicle availability, optimizing efficiency and reducing travel time. Scheduled routing follows predetermined paths and timetables, ensuring predictability but lacking flexibility to respond to unforeseen changes or delays. Key differences include real-time adaptability versus fixed schedules, enhanced responsiveness in dynamic routing, and greater operational stability in scheduled routing systems.
Benefits of Dynamic Routing for Public Mobility Systems
Dynamic routing in public mobility systems enhances efficiency by adapting routes in real time based on current traffic, passenger demand, and road conditions, reducing wait times and travel duration. This approach optimizes fleet utilization and decreases operational costs by minimizing unnecessary mileage and avoiding congested areas. Improved flexibility and responsiveness contribute to better overall service quality, increasing rider satisfaction and system accessibility.
Scheduled Routing: Advantages in Predictable Transit Needs
Scheduled routing in mobility ensures consistent and reliable transit services by operating on fixed timetables and designated routes, ideal for predictable passenger demand. This method enhances resource allocation efficiency, reduces wait times, and improves overall service punctuality. Public transit systems and corporate shuttle services benefit significantly from scheduled routing, optimizing operational planning and passenger satisfaction.
Challenges of Implementing Dynamic Routing Technologies
Implementing dynamic routing technologies in mobility systems faces challenges such as real-time data processing demands and the need for robust communication networks to handle fluctuating traffic conditions. Integration with existing infrastructure and ensuring system reliability amid unpredictable route changes complicate deployment. Security vulnerabilities and high operational costs further limit widespread adoption of dynamic routing solutions.
User Experience: Dynamic Routing vs Scheduled Routing
Dynamic routing offers a flexible user experience by adapting routes in real-time based on traffic conditions and rider demand, reducing wait times and improving overall satisfaction. Scheduled routing follows a fixed timetable, which can lead to predictable service but often results in longer waits and less efficient travel during off-peak hours. User engagement and convenience are typically higher with dynamic routing systems due to their responsiveness and personalized navigation.
Cost Implications: Dynamic Versus Scheduled Routing Models
Dynamic routing reduces operational costs by optimizing routes in real-time based on current traffic, demand, and service conditions, leading to lower fuel consumption and improved vehicle utilization. Scheduled routing, while simpler to implement, often incurs higher fixed costs due to predetermined routes that may not adapt to fluctuating demand or unexpected delays, resulting in inefficiencies and increased fuel expenses. The cost-effectiveness of dynamic models grows significantly in environments with variable demand and complex delivery networks, enabling businesses to minimize waste and enhance overall mobility performance.
Environmental Impact of Routing Strategies in Mobility
Dynamic routing optimizes mobility by minimizing total travel distance and congestion, significantly reducing fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to scheduled routing. Scheduled routing often results in fixed routes regardless of real-time conditions, leading to increased idle times and higher environmental costs. Implementing dynamic routing strategies leverages real-time data to enhance energy efficiency and lower the carbon footprint of transportation networks.
The Future of Routing: Integrating Dynamic and Scheduled Methods
Dynamic routing leverages real-time data and AI algorithms to optimize routes based on current traffic conditions, enhancing efficiency and reducing travel time. Scheduled routing relies on fixed itineraries to ensure predictable and consistent service, which is essential for maintaining regularity in high-demand areas. The future of routing lies in seamlessly integrating dynamic and scheduled methods, creating adaptive systems that balance reliability with responsiveness to fluctuating demand and traffic patterns.
Dynamic routing vs scheduled routing Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com