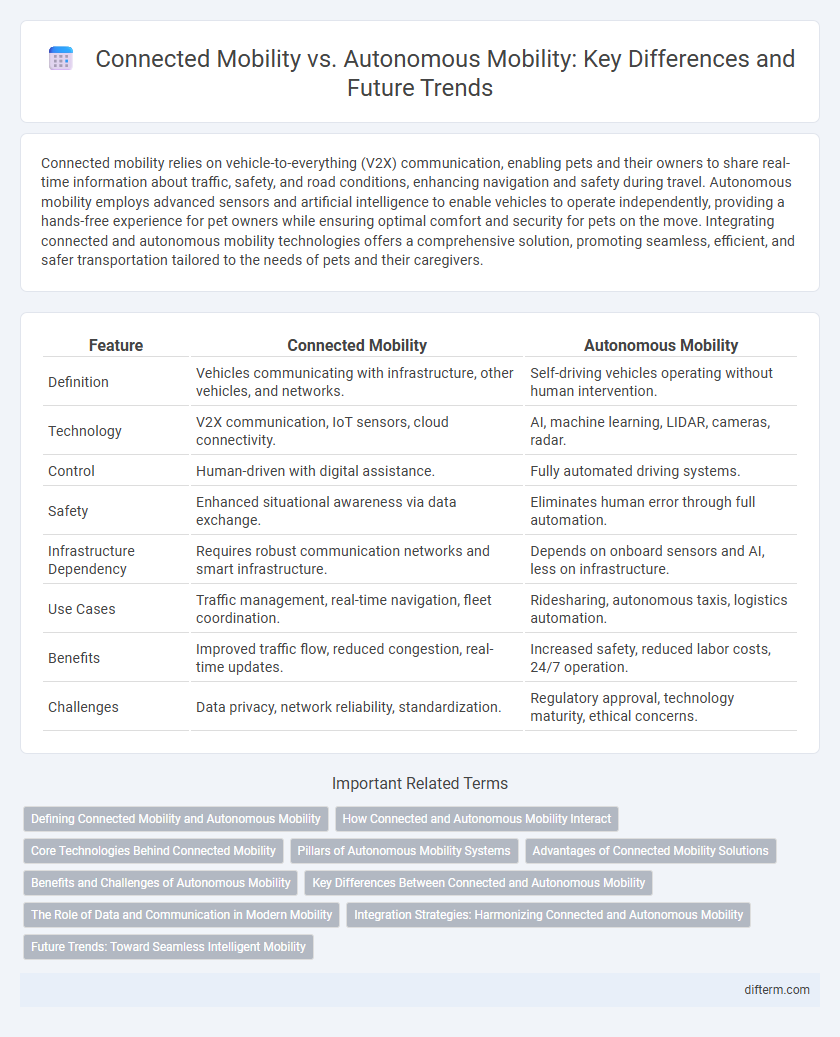
Connected mobility relies on vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, enabling pets and their owners to share real-time information about traffic, safety, and road conditions, enhancing navigation and safety during travel. Autonomous mobility employs advanced sensors and artificial intelligence to enable vehicles to operate independently, providing a hands-free experience for pet owners while ensuring optimal comfort and security for pets on the move. Integrating connected and autonomous mobility technologies offers a comprehensive solution, promoting seamless, efficient, and safer transportation tailored to the needs of pets and their caregivers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Connected Mobility | Autonomous Mobility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Vehicles communicating with infrastructure, other vehicles, and networks. | Self-driving vehicles operating without human intervention. |
| Technology | V2X communication, IoT sensors, cloud connectivity. | AI, machine learning, LIDAR, cameras, radar. |
| Control | Human-driven with digital assistance. | Fully automated driving systems. |
| Safety | Enhanced situational awareness via data exchange. | Eliminates human error through full automation. |
| Infrastructure Dependency | Requires robust communication networks and smart infrastructure. | Depends on onboard sensors and AI, less on infrastructure. |
| Use Cases | Traffic management, real-time navigation, fleet coordination. | Ridesharing, autonomous taxis, logistics automation. |
| Benefits | Improved traffic flow, reduced congestion, real-time updates. | Increased safety, reduced labor costs, 24/7 operation. |
| Challenges | Data privacy, network reliability, standardization. | Regulatory approval, technology maturity, ethical concerns. |
Defining Connected Mobility and Autonomous Mobility
Connected mobility refers to the integration of vehicles with communication technologies enabling real-time data exchange between vehicles, infrastructure, and users to enhance traffic management and safety. Autonomous mobility involves self-driving vehicles equipped with advanced sensors and artificial intelligence to navigate and operate without human intervention. Both technologies aim to transform transportation by improving efficiency, reducing accidents, and enabling seamless travel experiences.
How Connected and Autonomous Mobility Interact
Connected mobility relies on real-time data exchange between vehicles, infrastructure, and networks to enhance traffic efficiency and safety. Autonomous mobility uses onboard sensors and AI to navigate independently but benefits significantly from connected systems for better situational awareness and decision-making. The interaction between connected and autonomous mobility technologies creates a synergistic ecosystem that improves route optimization, reduces accidents, and supports dynamic traffic management.
Core Technologies Behind Connected Mobility
Connected mobility relies heavily on core technologies such as IoT sensors, 5G networks, and cloud computing to enable real-time data exchange between vehicles, infrastructure, and users. Advanced telematics systems gather and process vehicle data, facilitating efficient traffic management and enhanced safety measures. These technologies collectively support seamless communication and interoperability, distinguishing connected mobility from autonomous systems, which center more on AI and machine learning for independent navigation.
Pillars of Autonomous Mobility Systems
Autonomous mobility systems rely on core pillars such as perception, decision-making, control, and communication to enable vehicles to navigate complex environments without human intervention. Connected mobility enhances these pillars by integrating vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, allowing autonomous vehicles to exchange data with infrastructure, other vehicles, and cloud services for improved safety and efficiency. The synergy between connected and autonomous mobility advances real-time situational awareness, predictive analytics, and coordinated traffic management essential for scalable autonomous transport solutions.
Advantages of Connected Mobility Solutions
Connected mobility solutions enhance real-time data exchange between vehicles, infrastructure, and users, improving traffic management and reducing congestion. Integration of IoT sensors and V2X communication increases road safety by enabling proactive hazard detection and emergency response. These advantages lead to more efficient energy use and lower emissions, supporting sustainable urban transportation systems.
Benefits and Challenges of Autonomous Mobility
Autonomous mobility enhances road safety by reducing human error and increases efficiency through optimized traffic flow and reduced congestion. Challenges include the high cost of technology development, complex regulatory frameworks, and the need for robust cybersecurity measures to prevent system vulnerabilities. Integration with existing infrastructure and public acceptance remain critical hurdles for widespread adoption.
Key Differences Between Connected and Autonomous Mobility
Connected mobility emphasizes real-time data exchange between vehicles, infrastructure, and users to enhance traffic management and safety, whereas autonomous mobility relies on advanced AI and sensor systems to enable vehicles to navigate and operate independently without human intervention. Connected mobility primarily improves communication and information flow, while autonomous mobility focuses on self-driving capabilities and decision-making autonomy. Integration of both technologies aims to create smarter, safer, and more efficient transportation ecosystems.
The Role of Data and Communication in Modern Mobility
Connected mobility relies heavily on real-time data exchange between vehicles, infrastructure, and users to optimize traffic flow and enhance safety. Autonomous mobility integrates advanced sensors and AI-driven communication systems to interpret vast datasets, enabling vehicles to make independent driving decisions. Seamless communication networks and accurate data analytics are essential for synchronizing these technologies, reducing congestion, and improving overall transport efficiency.
Integration Strategies: Harmonizing Connected and Autonomous Mobility
Integration strategies for connected and autonomous mobility emphasize seamless interoperability between vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication systems and autonomous driving technologies to enhance safety and traffic efficiency. Leveraging edge computing and 5G networks facilitates real-time data exchange, enabling synchronized navigation and dynamic route optimization. Collaborative frameworks among stakeholders, including automakers, telecom providers, and urban planners, drive the development of unified platforms that harmonize these mobility solutions for smarter transportation ecosystems.
Future Trends: Toward Seamless Intelligent Mobility
Connected mobility integrates real-time data exchange between vehicles, infrastructure, and users to optimize traffic flow and enhance safety. Autonomous mobility leverages AI-powered vehicles capable of self-navigation, reducing human error and enabling on-demand transportation services. Future trends emphasize the convergence of these technologies to create seamless intelligent mobility ecosystems that offer efficiency, sustainability, and personalized travel experiences.
connected mobility vs autonomous mobility Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com