Geotargeting uses user location data to deliver tailored marketing content within broader geographic areas, enhancing relevance and engagement. Geofencing creates virtual boundaries around specific locations to trigger real-time, location-based notifications or ads when users enter or exit these zones. Both strategies increase marketing precision, but geofencing offers more immediate and context-sensitive interactions.
Table of Comparison
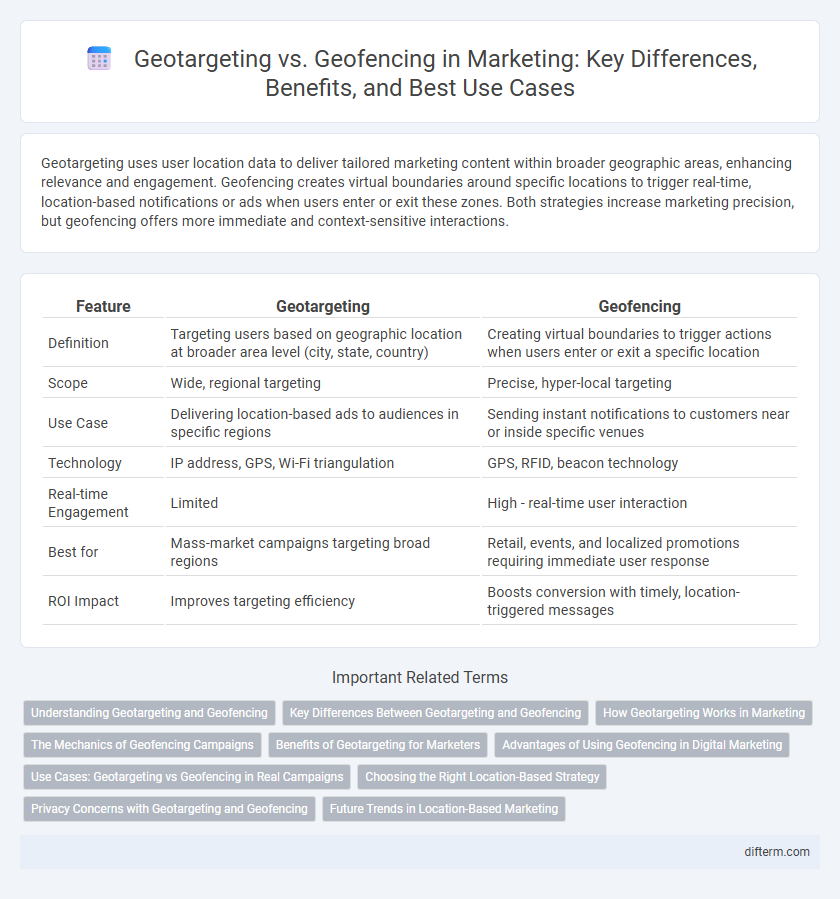
| Feature | Geotargeting | Geofencing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Targeting users based on geographic location at broader area level (city, state, country) | Creating virtual boundaries to trigger actions when users enter or exit a specific location |
| Scope | Wide, regional targeting | Precise, hyper-local targeting |
| Use Case | Delivering location-based ads to audiences in specific regions | Sending instant notifications to customers near or inside specific venues |
| Technology | IP address, GPS, Wi-Fi triangulation | GPS, RFID, beacon technology |
| Real-time Engagement | Limited | High - real-time user interaction |
| Best for | Mass-market campaigns targeting broad regions | Retail, events, and localized promotions requiring immediate user response |
| ROI Impact | Improves targeting efficiency | Boosts conversion with timely, location-triggered messages |
Understanding Geotargeting and Geofencing
Geotargeting and Geofencing are precise location-based marketing strategies that enhance customer engagement by delivering tailored content through GPS or IP data. Geotargeting focuses on reaching audiences based on broader geographic areas like cities or regions, optimizing ad relevance and campaign ROI. Geofencing creates virtual perimeters around specific locations, triggering real-time alerts or promotions when users enter or exit these predefined zones.
Key Differences Between Geotargeting and Geofencing
Geotargeting delivers personalized marketing content based on the user's general location, often defined by country, city, or region, to increase relevance and engagement. Geofencing creates a virtual boundary around a specific geographic area, triggering real-time notifications or ads when a user enters or exits that zone, enabling hyper-localized marketing campaigns. The key difference lies in the scale and interaction: geotargeting works broadly with location data, while geofencing provides precise, immediate, and location-specific engagement opportunities.
How Geotargeting Works in Marketing
Geotargeting works in marketing by using IP addresses, GPS data, or Wi-Fi signals to identify a user's geographic location, allowing brands to deliver personalized content, advertisements, or offers tailored to specific regions or cities. This location-based strategy enables marketers to increase relevance and engagement by targeting users based on their physical proximity without requiring them to enter predefined zones. Enhanced with customer data and behavioral insights, geotargeting improves conversion rates through timely, location-specific messaging across digital platforms and mobile devices.
The Mechanics of Geofencing Campaigns
Geofencing campaigns operate by establishing a virtual perimeter around a specific geographic area using GPS or RFID technology, enabling marketers to trigger targeted messages when users enter or exit the defined zone. This precise location-based mechanism allows brands to deliver real-time promotions, updates, or alerts directly to mobile devices, enhancing engagement and conversion rates. Unlike broader geotargeting, geofencing offers granular control over audience interaction by focusing on narrowly defined physical spaces for more personalized marketing efforts.
Benefits of Geotargeting for Marketers
Geotargeting enables marketers to deliver personalized ads based on users' geographic locations, increasing relevance and engagement rates by up to 50%. This precision helps optimize ad spend by focusing budgets on high-potential local audiences, improving return on investment (ROI). Enhanced customer insights from geotargeting allow for tailored promotions that drive foot traffic and boost sales in specific regions.
Advantages of Using Geofencing in Digital Marketing
Geofencing offers precise location-based targeting by creating virtual boundaries around specific areas, enabling businesses to deliver highly relevant ads to potential customers in real time. This technology increases engagement rates and conversion by triggering personalized notifications and promotions when users enter or exit predefined zones, enhancing local marketing effectiveness. Marketers benefit from improved customer insights and measurable campaign performance, driving better ROI compared to broader geotargeting approaches.
Use Cases: Geotargeting vs Geofencing in Real Campaigns
Geotargeting enables marketers to deliver personalized ads to users based on their broader geographic locations, such as cities or regions, making it ideal for campaigns aiming at regional promotions or local store awareness. Geofencing, by creating virtual boundaries around specific locations like stores or events, allows brands to trigger real-time notifications or offers when users enter the defined area, boosting immediate engagement and foot traffic. Real campaigns often combine both strategies to optimize audience reach and interaction, tailoring messages by macro location with geotargeting while leveraging geofencing for precise, location-driven call-to-actions.
Choosing the Right Location-Based Strategy
Selecting the right location-based marketing strategy depends on campaign goals and audience behavior. Geotargeting leverages broader geographic areas to deliver personalized ads based on regional data, ideal for targeting cities or ZIP codes. Geofencing offers precise, real-time engagement by triggering messages when users enter or exit a defined virtual boundary, making it effective for driving foot traffic to specific stores or events.
Privacy Concerns with Geotargeting and Geofencing
Geotargeting and geofencing utilize location data to deliver personalized marketing content but raise significant privacy concerns due to the collection and potential misuse of users' precise location information. Consumers may feel uneasy about being tracked continuously or having their whereabouts shared without explicit consent, which can lead to mistrust and regulatory scrutiny. Ensuring transparent data practices and compliance with privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA is essential to mitigate risks associated with geotargeted and geofenced marketing campaigns.
Future Trends in Location-Based Marketing
Geotargeting leverages GPS and IP data to deliver personalized ads to users in specific geographic areas, while geofencing creates virtual perimeters around physical locations to trigger real-time marketing messages. Future trends in location-based marketing emphasize AI-driven analytics and hyperlocal targeting to enhance customer engagement and increase conversion rates. Integration with IoT devices and 5G technology will further enable precision marketing, offering seamless, context-aware experiences for consumers.
Geotargeting vs Geofencing Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com