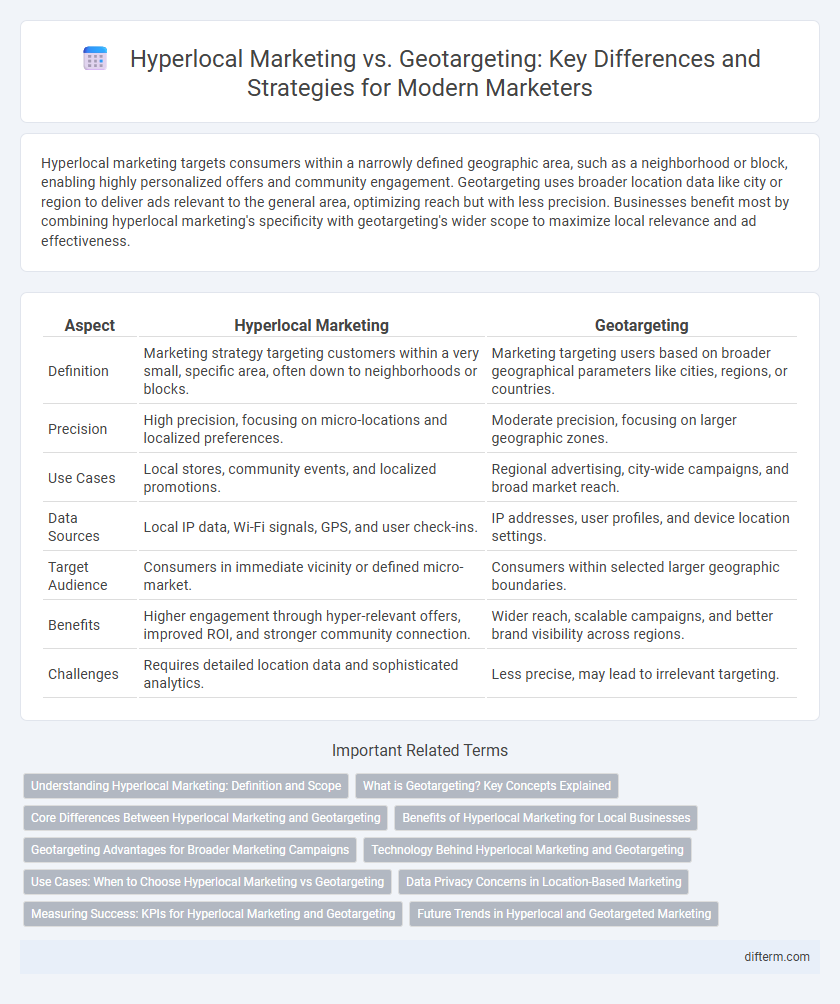
Hyperlocal marketing targets consumers within a narrowly defined geographic area, such as a neighborhood or block, enabling highly personalized offers and community engagement. Geotargeting uses broader location data like city or region to deliver ads relevant to the general area, optimizing reach but with less precision. Businesses benefit most by combining hyperlocal marketing's specificity with geotargeting's wider scope to maximize local relevance and ad effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hyperlocal Marketing | Geotargeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Marketing strategy targeting customers within a very small, specific area, often down to neighborhoods or blocks. | Marketing targeting users based on broader geographical parameters like cities, regions, or countries. |
| Precision | High precision, focusing on micro-locations and localized preferences. | Moderate precision, focusing on larger geographic zones. |
| Use Cases | Local stores, community events, and localized promotions. | Regional advertising, city-wide campaigns, and broad market reach. |
| Data Sources | Local IP data, Wi-Fi signals, GPS, and user check-ins. | IP addresses, user profiles, and device location settings. |
| Target Audience | Consumers in immediate vicinity or defined micro-market. | Consumers within selected larger geographic boundaries. |
| Benefits | Higher engagement through hyper-relevant offers, improved ROI, and stronger community connection. | Wider reach, scalable campaigns, and better brand visibility across regions. |
| Challenges | Requires detailed location data and sophisticated analytics. | Less precise, may lead to irrelevant targeting. |
Understanding Hyperlocal Marketing: Definition and Scope
Hyperlocal marketing focuses on targeting customers within a highly specific geographic area, such as a neighborhood or city block, using precise location data to deliver personalized promotions. This strategy emphasizes community engagement and relevance by tailoring messaging to local events, preferences, and consumer behavior. Unlike broader geotargeting, hyperlocal marketing leverages granular data analytics and real-time location tracking to optimize local brand visibility and drive foot traffic effectively.
What is Geotargeting? Key Concepts Explained
Geotargeting in marketing involves delivering content, advertisements, or promotions to users based on their specific geographic location, such as city, zip code, or neighborhood, to increase relevance and engagement. Key concepts include IP address targeting, GPS coordinates, and mobile device location data, which enable marketers to tailor campaigns to local preferences and behaviors. This method enhances conversion rates by reaching consumers with location-specific offers and messaging.
Core Differences Between Hyperlocal Marketing and Geotargeting
Hyperlocal marketing targets a highly specific local community or neighborhood using precise data such as postal codes, street-level data, or customer behavior, often emphasizing offline engagement and personalized offers. Geotargeting uses broader geographic parameters like city, region, or country based on IP addresses or GPS location to deliver tailored digital ads and content to users in those areas. The core difference lies in hyperlocal marketing's micro-level focus and integration with local physical environments, contrasting with geotargeting's macro-level approach primarily applied in digital campaigns.
Benefits of Hyperlocal Marketing for Local Businesses
Hyperlocal marketing enables local businesses to engage customers within a specific neighborhood or community using precise location data and personalized content, resulting in higher engagement and conversion rates. It drives foot traffic and boosts sales by delivering relevant promotions and offers based on real-time consumer behavior and preferences. This targeted approach fosters stronger customer relationships and enhances brand loyalty in competitive local markets.
Geotargeting Advantages for Broader Marketing Campaigns
Geotargeting enhances broader marketing campaigns by enabling precise audience segmentation based on location data, improving ad relevance and engagement across diverse regions. This approach allows marketers to optimize budget allocation by targeting high-potential areas, increasing conversion rates and overall campaign ROI. Leveraging geotargeting analytics also provides valuable insights into consumer behavior patterns, facilitating data-driven decisions and scalable marketing strategies.
Technology Behind Hyperlocal Marketing and Geotargeting
Hyperlocal marketing leverages advanced technologies such as GPS, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth beacons, and geofencing to deliver highly personalized content to users within precise physical locations, often down to a few meters. Geotargeting utilizes IP addresses, cell tower triangulation, and device location data to target broader regional or city-level audiences based on their geographic area. The technological distinction lies in hyperlocal marketing's emphasis on micro-location precision through real-time data capture, while geotargeting relies on less granular, aggregated location insights for targeted advertising.
Use Cases: When to Choose Hyperlocal Marketing vs Geotargeting
Hyperlocal marketing excels in targeting customers within a very specific neighborhood or community, ideal for small businesses like local restaurants, retail stores, or service providers aiming to drive foot traffic through personalized promotions. Geotargeting is better suited for brands seeking to reach broader regional audiences, leveraging location data to tailor ads for city-wide events, regional offers, or multi-location campaigns. Choosing hyperlocal marketing optimizes engagement for hyper-specific areas with high conversion potential, while geotargeting maximizes reach across larger geographic segments to build broader brand awareness.
Data Privacy Concerns in Location-Based Marketing
Hyperlocal marketing targets consumers within a very specific geographic area by leveraging detailed local data, while geotargeting uses broader location parameters to deliver ads. Both strategies raise significant data privacy concerns, as they rely heavily on collecting and analyzing user location data, potentially exposing sensitive information. Compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA is crucial to protect consumer privacy and maintain trust in location-based marketing campaigns.
Measuring Success: KPIs for Hyperlocal Marketing and Geotargeting
Measuring success in hyperlocal marketing involves tracking KPIs such as foot traffic increase, local engagement rates, and in-store sales attributed to targeted campaigns within a specific radius. Geotargeting effectiveness is often gauged by click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates from geo-fenced ads, and customer acquisition cost in defined geographic zones. Both strategies benefit from monitoring customer retention, local brand awareness, and ROI to optimize marketing efforts in precise locations.
Future Trends in Hyperlocal and Geotargeted Marketing
Hyperlocal marketing is evolving with advancements in AI and big data, enabling hyper-personalized content that aligns with consumer behavior within micro-geographies. Geotargeting will increasingly integrate augmented reality and IoT devices to deliver immersive, location-based experiences that drive engagement and conversions. Predictive analytics will refine these strategies by anticipating local market shifts, optimizing budgets, and enhancing real-time decision-making in campaigns.
Hyperlocal marketing vs geotargeting Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com