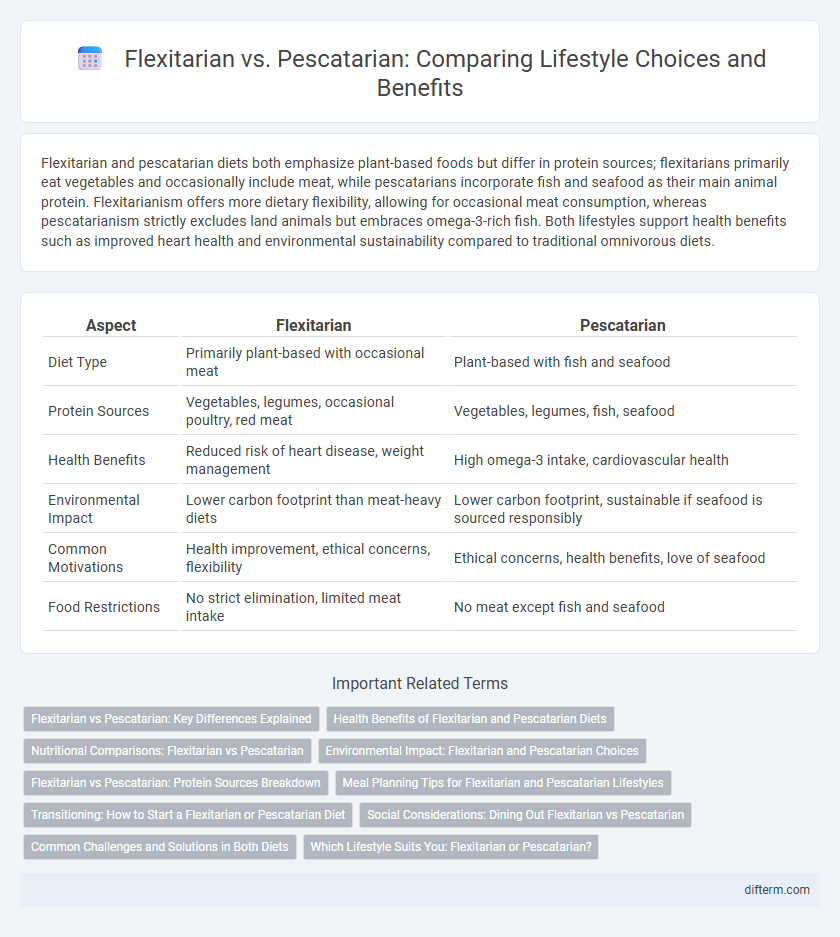
Flexitarian and pescatarian diets both emphasize plant-based foods but differ in protein sources; flexitarians primarily eat vegetables and occasionally include meat, while pescatarians incorporate fish and seafood as their main animal protein. Flexitarianism offers more dietary flexibility, allowing for occasional meat consumption, whereas pescatarianism strictly excludes land animals but embraces omega-3-rich fish. Both lifestyles support health benefits such as improved heart health and environmental sustainability compared to traditional omnivorous diets.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Flexitarian | Pescatarian |
|---|---|---|
| Diet Type | Primarily plant-based with occasional meat | Plant-based with fish and seafood |
| Protein Sources | Vegetables, legumes, occasional poultry, red meat | Vegetables, legumes, fish, seafood |
| Health Benefits | Reduced risk of heart disease, weight management | High omega-3 intake, cardiovascular health |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint than meat-heavy diets | Lower carbon footprint, sustainable if seafood is sourced responsibly |
| Common Motivations | Health improvement, ethical concerns, flexibility | Ethical concerns, health benefits, love of seafood |
| Food Restrictions | No strict elimination, limited meat intake | No meat except fish and seafood |
Flexitarian vs Pescatarian: Key Differences Explained
Flexitarian diets primarily emphasize plant-based foods while allowing occasional meat consumption, promoting flexible eating habits that blend vegetarianism with moderate meat intake. Pescatarian diets exclude all meat except fish and seafood, providing a high-protein option rich in omega-3 fatty acids, beneficial for cardiovascular health. Understanding these distinctions helps individuals tailor their dietary choices based on health goals, ethical considerations, and environmental impact.
Health Benefits of Flexitarian and Pescatarian Diets
Flexitarian and pescatarian diets both promote health by emphasizing plant-based foods rich in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, which support heart health and reduce inflammation. Flexitarians benefit from occasional meat consumption, providing essential protein and iron, while pescatarians gain omega-3 fatty acids from fish, contributing to improved brain function and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. Both diets can lead to lower body mass index and better metabolic health when compared to traditional meat-heavy eating patterns.
Nutritional Comparisons: Flexitarian vs Pescatarian
Flexitarians embrace a primarily plant-based diet with occasional meat consumption, optimizing nutrient intake by combining fiber-rich vegetables, whole grains, and lean meats. Pescatarians exclude land animals but consume fish and seafood, benefiting from omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and high-quality protein sources. Both diets offer balanced nutrition, but pescatarians may gain more heart-healthy fats, while flexitarians enjoy broader nutrient diversity through varied animal protein options.
Environmental Impact: Flexitarian and Pescatarian Choices
Flexitarian diets reduce environmental impact by primarily emphasizing plant-based foods while allowing occasional meat consumption, significantly lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional omnivorous diets. Pescatarian diets, focusing on fish and seafood alongside plant foods, can also have a lower carbon footprint but may contribute to overfishing and marine ecosystem disruption if not managed sustainably. Choosing flexitarian options generally supports more diverse agricultural practices and greater soil health, whereas sustainable pescatarian choices rely heavily on responsible fisheries management to minimize environmental harm.
Flexitarian vs Pescatarian: Protein Sources Breakdown
Flexitarian diets emphasize plant-based proteins such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and occasional meat, providing a flexible approach to protein intake with lower environmental impact. Pescatarian diets prioritize fish and seafood as primary protein sources, offering omega-3 fatty acids and lean protein benefits while excluding other meats. Both dietary patterns support diverse, nutrient-rich protein options tailored to individual health goals and ethical considerations.
Meal Planning Tips for Flexitarian and Pescatarian Lifestyles
Meal planning for flexitarian and pescatarian lifestyles centers on balancing plant-based ingredients with occasional animal proteins or seafood to ensure nutritional variety and adequacy. Incorporating a wide range of vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and select fish like salmon or tuna can optimize omega-3 intake and support heart health. Utilizing batch cooking methods and versatile recipes helps maintain dietary flexibility while simplifying weekly meal preparation.
Transitioning: How to Start a Flexitarian or Pescatarian Diet
Transitioning to a flexitarian or pescatarian diet begins with gradually incorporating more plant-based meals and seafood while reducing red meat consumption to ease adaptation and maintain nutritional balance. Prioritize nutrient-dense foods like legumes, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 rich fish such as salmon or mackerel to support health during the transition. Monitoring protein sources and planning meals ahead ensures a sustainable and enjoyable shift towards these semi-vegetarian lifestyles.
Social Considerations: Dining Out Flexitarian vs Pescatarian
Flexitarians enjoy a versatile dining experience with a wide range of menu options that accommodate occasional meat consumption, making social gatherings more flexible and inclusive. Pescatarians may face limited choices at certain restaurants, especially those prioritizing vegetarian or vegan dishes without seafood options, which can require more careful planning. Both lifestyles foster social adaptability but depend on local cuisine and dining culture for seamless integration into social dining scenarios.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Both Diets
Both flexitarian and pescatarian diets often face challenges in ensuring adequate protein intake and maintaining balanced nutrient profiles, particularly with vitamins B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids. Incorporating diverse plant-based proteins, such as legumes and nuts, alongside seafood in pescatarian diets or occasional meat in flexitarian plans can effectively address these nutritional gaps. Meal planning with fortified foods and regular monitoring of nutrient levels further supports long-term adherence and optimal health outcomes in both dietary approaches.
Which Lifestyle Suits You: Flexitarian or Pescatarian?
Choosing between a flexitarian and pescatarian lifestyle depends on your dietary preferences and health goals, as a flexitarian diet emphasizes mostly plant-based foods with occasional meat, while a pescatarian diet includes fish and seafood but excludes other meats. Flexitarianism suits those seeking flexibility and gradual reduction of meat consumption, offering benefits like improved heart health and weight management. Pescatarianism appeals to individuals looking for high-quality protein and omega-3 fatty acids from fish, supporting brain health and reducing inflammation.
flexitarian vs pescatarian Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com