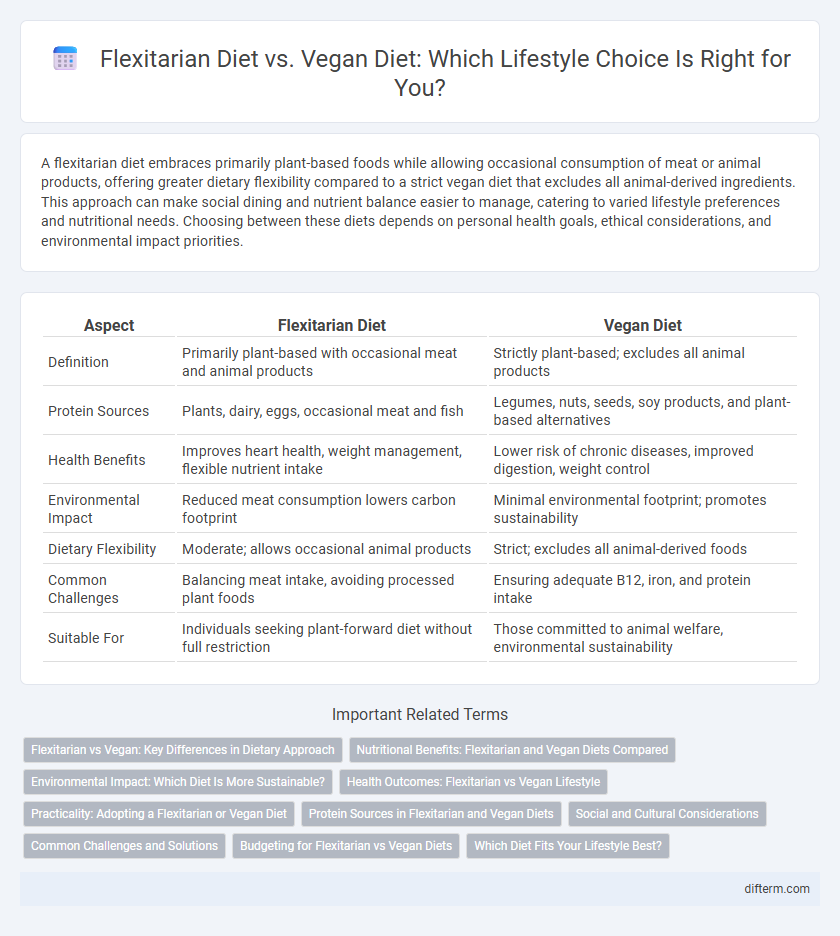
A flexitarian diet embraces primarily plant-based foods while allowing occasional consumption of meat or animal products, offering greater dietary flexibility compared to a strict vegan diet that excludes all animal-derived ingredients. This approach can make social dining and nutrient balance easier to manage, catering to varied lifestyle preferences and nutritional needs. Choosing between these diets depends on personal health goals, ethical considerations, and environmental impact priorities.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Flexitarian Diet | Vegan Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Primarily plant-based with occasional meat and animal products | Strictly plant-based; excludes all animal products |
| Protein Sources | Plants, dairy, eggs, occasional meat and fish | Legumes, nuts, seeds, soy products, and plant-based alternatives |
| Health Benefits | Improves heart health, weight management, flexible nutrient intake | Lower risk of chronic diseases, improved digestion, weight control |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced meat consumption lowers carbon footprint | Minimal environmental footprint; promotes sustainability |
| Dietary Flexibility | Moderate; allows occasional animal products | Strict; excludes all animal-derived foods |
| Common Challenges | Balancing meat intake, avoiding processed plant foods | Ensuring adequate B12, iron, and protein intake |
| Suitable For | Individuals seeking plant-forward diet without full restriction | Those committed to animal welfare, environmental sustainability |
Flexitarian vs Vegan: Key Differences in Dietary Approach
The flexitarian diet emphasizes flexible plant-based eating with occasional inclusion of meat and animal products, promoting balanced nutrition and sustainability, while the vegan diet strictly excludes all animal-derived ingredients, focusing entirely on plant-based foods to support ethical, environmental, and health goals. Flexitarians benefit from greater dietary variety and easier adherence, whereas vegans prioritize complete elimination of animal exploitation and often require careful planning to meet vitamin B12 and protein needs. Both diets contribute to reduced environmental impact compared to omnivorous diets, but the vegan approach offers the most comprehensive animal welfare benefits.
Nutritional Benefits: Flexitarian and Vegan Diets Compared
Flexitarian and vegan diets both emphasize plant-based foods, but flexitarian allows occasional animal products, enhancing protein variety and nutrient diversity. Vegan diets offer high fiber, antioxidants, and lower saturated fats, promoting heart health and reducing inflammation. Flexitarian diets provide greater intake of vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids due to meat and dairy inclusion, supporting overall nutritional balance.
Environmental Impact: Which Diet Is More Sustainable?
The flexitarian diet, which incorporates mostly plant-based foods with occasional animal products, tends to have a lower environmental impact than traditional omnivorous diets but slightly higher than vegan diets. Vegan diets eliminate animal products entirely, leading to significantly reduced greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption. Research indicates that adopting a vegan diet can reduce an individual's carbon footprint by up to 50%, making it the more sustainable choice compared to flexitarianism.
Health Outcomes: Flexitarian vs Vegan Lifestyle
The flexitarian diet, emphasizing plant-based foods with occasional animal protein, offers balanced nutrient intake that supports cardiovascular health and weight management. Vegan diets eliminate all animal products, often leading to higher fiber and antioxidant consumption, which benefits digestive health and reduces chronic disease risk. Both diets promote improved metabolic markers, but the flexitarian approach may provide easier long-term adherence and reduced risk of nutrient deficiencies such as vitamin B12 and iron.
Practicality: Adopting a Flexitarian or Vegan Diet
A flexitarian diet offers greater practicality with its flexible approach, allowing occasional consumption of animal products while emphasizing plant-based foods, making it easier to maintain in diverse social and cultural settings. Vegan diets require strict avoidance of all animal-derived ingredients, which can demand more planning and vigilance, especially when dining out or shopping for groceries. Flexitarianism caters to gradual dietary transitions and broader food choices, enhancing long-term adherence for individuals seeking balanced nutrition and sustainability.
Protein Sources in Flexitarian and Vegan Diets
Protein sources in a flexitarian diet primarily include plant-based options like legumes, nuts, and seeds, complemented by occasional animal products such as eggs, dairy, and lean meats to ensure complete amino acid profiles. In contrast, vegan diets rely exclusively on plant-based proteins, emphasizing combinations of beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, quinoa, and seitan to meet daily protein requirements. Both diets prioritize nutrient-dense, whole foods but vary in protein diversity due to the inclusion or exclusion of animal-derived ingredients.
Social and Cultural Considerations
Flexitarian diets often offer greater social flexibility by allowing occasional animal products, which can facilitate participation in diverse cultural meals and family gatherings without dietary restrictions. Vegan diets emphasize ethical and environmental values, sometimes challenging traditional culinary practices deeply rooted in certain cultures, potentially leading to social isolation or the need for adaptation. Understanding these social and cultural dynamics is crucial for individuals choosing between flexitarian and vegan lifestyles, as both influence identity, community inclusion, and cultural expression.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Flexitarian and vegan diets both present challenges related to nutrient intake and social dining situations. Flexitarians may struggle with balancing plant-based meals and occasional animal products, while vegans often face difficulties meeting protein, vitamin B12, and iron requirements. Incorporating diverse plant proteins, fortified foods, and planning meals ahead can help address nutritional gaps and ease social interactions for both dietary approaches.
Budgeting for Flexitarian vs Vegan Diets
Flexitarian diets generally offer more budget-friendly options compared to vegan diets due to the flexibility of including affordable animal products like eggs, dairy, and occasional meat. Vegan diets often require purchasing specialty items such as plant-based meat alternatives, nutritional supplements, and organic produce, which can increase overall grocery costs. Budgeting effectively for either diet involves focusing on seasonal vegetables, bulk grains, and legumes to maximize nutrition while minimizing expenses.
Which Diet Fits Your Lifestyle Best?
The flexitarian diet offers a flexible approach by emphasizing plant-based foods while allowing occasional meat consumption, making it ideal for those seeking balance without strict restrictions. The vegan diet requires complete exclusion of animal products, suitable for individuals committed to ethical, environmental, or health reasons who prefer a fully plant-based lifestyle. Choosing between these diets depends on personal goals, ethical beliefs, and lifestyle adaptability, with flexitarianism providing flexibility and veganism emphasizing total plant-based commitment.
flexitarian diet vs vegan diet Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com