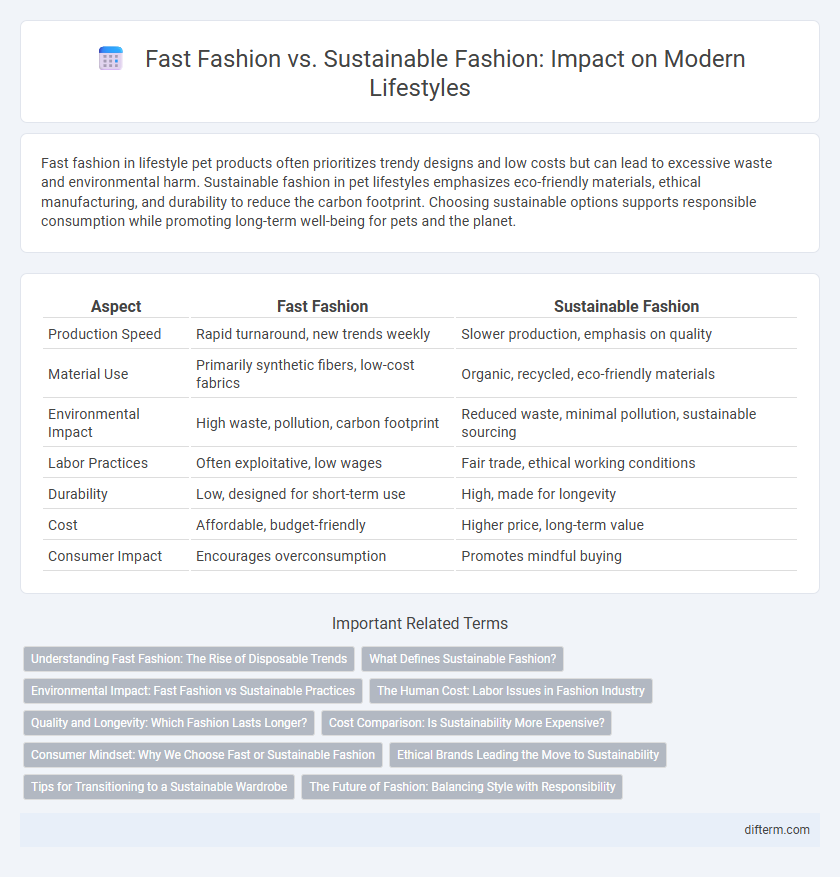
Fast fashion in lifestyle pet products often prioritizes trendy designs and low costs but can lead to excessive waste and environmental harm. Sustainable fashion in pet lifestyles emphasizes eco-friendly materials, ethical manufacturing, and durability to reduce the carbon footprint. Choosing sustainable options supports responsible consumption while promoting long-term well-being for pets and the planet.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fast Fashion | Sustainable Fashion |
|---|---|---|
| Production Speed | Rapid turnaround, new trends weekly | Slower production, emphasis on quality |
| Material Use | Primarily synthetic fibers, low-cost fabrics | Organic, recycled, eco-friendly materials |
| Environmental Impact | High waste, pollution, carbon footprint | Reduced waste, minimal pollution, sustainable sourcing |
| Labor Practices | Often exploitative, low wages | Fair trade, ethical working conditions |
| Durability | Low, designed for short-term use | High, made for longevity |
| Cost | Affordable, budget-friendly | Higher price, long-term value |
| Consumer Impact | Encourages overconsumption | Promotes mindful buying |
Understanding Fast Fashion: The Rise of Disposable Trends
Fast fashion rapidly produces low-cost clothing driven by ever-changing trends, leading to excessive waste and environmental harm. This model prioritizes quantity over quality, encouraging consumers to frequently discard garments. Understanding the rise of disposable trends highlights the urgent need to shift towards sustainable fashion practices that emphasize durability and ethical production.
What Defines Sustainable Fashion?
Sustainable fashion prioritizes eco-friendly materials, ethical labor practices, and reduced waste throughout the production cycle. It emphasizes durability, timeless design, and transparency in sourcing to minimize environmental impact and social exploitation. Unlike fast fashion's rapid turnover and mass production, sustainable fashion fosters a circular economy by encouraging recycling, upcycling, and responsible consumer choices.
Environmental Impact: Fast Fashion vs Sustainable Practices
Fast fashion contributes significantly to environmental degradation through excessive water consumption, chemical pollution, and massive textile waste. Sustainable fashion employs eco-friendly materials, ethical production methods, and circular economy principles to reduce carbon footprints and preserve natural resources. Prioritizing sustainable practices mitigates the negative impact of apparel production on climate change and biodiversity loss.
The Human Cost: Labor Issues in Fashion Industry
Fast fashion relies heavily on low-wage labor in developing countries, often exploiting workers with unsafe conditions, excessive hours, and lack of fair compensation. In contrast, sustainable fashion prioritizes ethical labor practices by ensuring transparency, fair wages, and safe working environments throughout the supply chain. Addressing labor issues reduces human suffering and promotes a more equitable fashion industry worldwide.
Quality and Longevity: Which Fashion Lasts Longer?
Sustainable fashion prioritizes high-quality materials and craftsmanship, resulting in garments that maintain their appearance and functionality over time, contrasting with fast fashion's emphasis on quick production and low-cost fabrics that often lead to rapid wear and tear. Consumers investing in sustainable clothing benefit from durable items that reduce frequent replacements, contributing to less textile waste and a smaller environmental footprint. Brands like Patagonia and Eileen Fisher exemplify longevity through rigorous quality standards, proving that sustainable fashion outlasts fast fashion by a significant margin.
Cost Comparison: Is Sustainability More Expensive?
Sustainable fashion often involves higher upfront costs due to ethical sourcing and eco-friendly materials, yet fast fashion's low prices frequently mask long-term expenses such as environmental damage and poor labor conditions. Studies highlight that investing in durable, sustainable pieces reduces replacement frequency and waste, ultimately balancing initial cost disparities. Consumers prioritizing sustainability benefit from lower overall lifecycle costs and enhanced social impact compared to the transient affordability of fast fashion.
Consumer Mindset: Why We Choose Fast or Sustainable Fashion
Consumers gravitate towards fast fashion due to its affordability, trendy designs, and immediate availability, catering to a desire for constant wardrobe updates without significant financial commitment. Sustainable fashion appeals to environmentally conscious buyers prioritizing ethical production, durability, and reduced ecological impact, often willing to invest more for quality and responsibility. The consumer mindset balances convenience and cost against long-term environmental and social benefits, shaping purchasing decisions in the evolving fashion landscape.
Ethical Brands Leading the Move to Sustainability
Ethical fashion brands like Patagonia and Stella McCartney prioritize sustainability through the use of organic materials and fair labor practices, setting a new industry standard in contrast to fast fashion's rapid, wasteful production cycles. These brands focus on transparency, supply chain accountability, and circular economy models to minimize environmental impact and promote social responsibility. Consumers increasingly favor these ethical labels, driving market demand for sustainable alternatives and encouraging global fashion brands to adopt greener practices.
Tips for Transitioning to a Sustainable Wardrobe
Choose versatile, high-quality pieces made from organic or recycled materials to build a sustainable wardrobe that reduces waste and environmental impact. Incorporate secondhand shopping and clothing swaps to minimize consumption while keeping your style fresh and unique. Prioritize brands with transparent production practices and certifications like Fair Trade or GOTS to ensure ethical and eco-friendly fashion choices.
The Future of Fashion: Balancing Style with Responsibility
Fast fashion dominates the market with rapid production cycles and low prices, contributing significantly to environmental pollution and waste. Sustainable fashion emphasizes eco-friendly materials, ethical labor practices, and circular design to reduce the carbon footprint of the industry. The future of fashion relies on integrating innovative technologies and consumer awareness to balance style trends with social and environmental responsibility.
fast fashion vs sustainable fashion Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com