Static stretching involves holding a muscle in a fixed position for an extended period, which helps improve flexibility and reduce muscle stiffness. Dynamic stretching consists of controlled, active movements that mimic the activity about to be performed, enhancing blood flow and preparing muscles for exercise. Choosing between static and dynamic stretching depends on the timing and goals, with dynamic stretching preferred before workouts and static stretching beneficial during cool-downs.
Table of Comparison
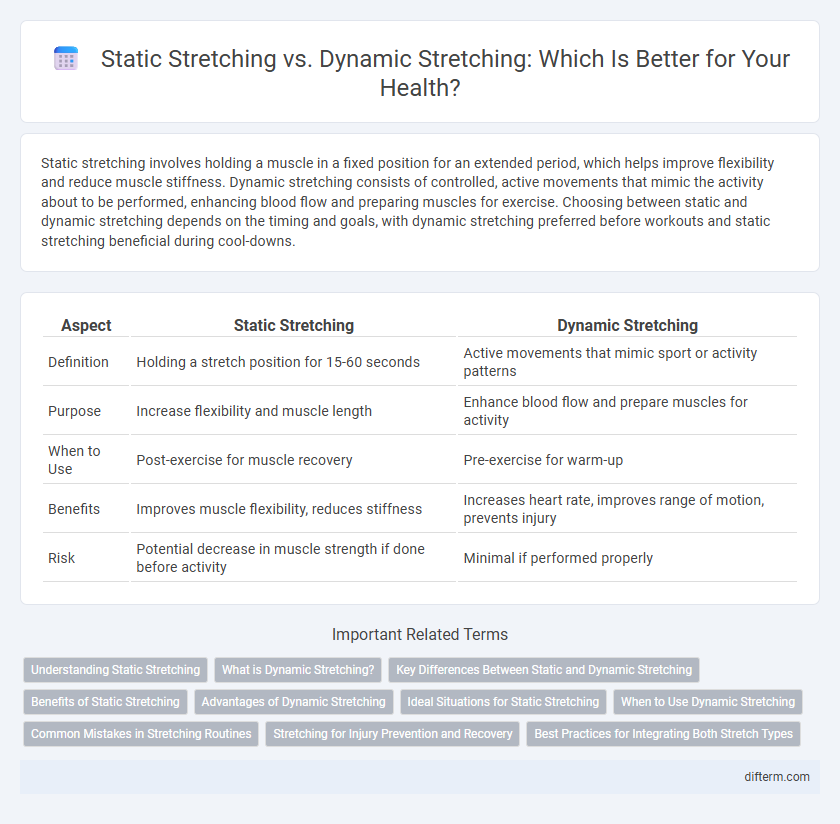
| Aspect | Static Stretching | Dynamic Stretching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Holding a stretch position for 15-60 seconds | Active movements that mimic sport or activity patterns |
| Purpose | Increase flexibility and muscle length | Enhance blood flow and prepare muscles for activity |
| When to Use | Post-exercise for muscle recovery | Pre-exercise for warm-up |
| Benefits | Improves muscle flexibility, reduces stiffness | Increases heart rate, improves range of motion, prevents injury |
| Risk | Potential decrease in muscle strength if done before activity | Minimal if performed properly |
Understanding Static Stretching
Static stretching involves holding a muscle in a fixed position for 15-60 seconds to improve flexibility and range of motion. It primarily targets specific muscle groups, aiding in muscle relaxation and reducing stiffness after exercise. Research shows static stretching enhances muscle elasticity but may temporarily decrease muscle strength if performed before intense physical activity.
What is Dynamic Stretching?
Dynamic stretching involves active movements that take muscles through their full range of motion, enhancing flexibility and increasing blood flow prior to physical activity. Common examples include leg swings, arm circles, and walking lunges, which prepare muscles and joints for more intense exercise. Research shows dynamic stretching can improve performance and reduce injury risk by warming up muscles effectively.
Key Differences Between Static and Dynamic Stretching
Static stretching involves holding a muscle in a fixed position for 15-60 seconds to improve flexibility and increase muscle length, primarily benefiting post-exercise recovery. Dynamic stretching consists of controlled, active movements that mimic specific sports or activities, enhancing blood flow, muscle temperature, and range of motion before workouts. Key differences include static stretching's focus on muscle relaxation and elongation versus dynamic stretching's emphasis on preparing muscles for movement and improving functional performance.
Benefits of Static Stretching
Static stretching enhances muscle flexibility by gradually elongating muscle fibers, reducing the risk of injury during physical activities. It improves joint range of motion and promotes muscle relaxation, which aids in recovery and decreases muscle stiffness. Consistent static stretching can contribute to better posture and alleviate muscle tension, supporting overall musculoskeletal health.
Advantages of Dynamic Stretching
Dynamic stretching enhances muscle flexibility and joint mobility by actively moving muscles through their full range of motion, which improves blood flow and prepares the body for physical performance. It activates the nervous system, increasing muscle temperature and reducing the risk of injury during exercise or sports activities. This type of stretching also enhances coordination and muscle activation, contributing to better overall athletic performance and functional movement.
Ideal Situations for Static Stretching
Static stretching is ideal post-exercise to improve flexibility and promote muscle relaxation by holding stretches for 15-60 seconds. It is effective in reducing muscle stiffness and enhancing the range of motion after intense physical activities. Static stretching should be avoided before high-intensity workouts to prevent decreased muscle performance.
When to Use Dynamic Stretching
Dynamic stretching is most effective before physical activities that require power, speed, and agility, such as running, jumping, or sports performance. It helps increase blood flow, enhance muscle temperature, and improve range of motion, preparing the body for intense movement. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts use dynamic stretching in warm-ups to reduce injury risk and boost overall performance.
Common Mistakes in Stretching Routines
Common mistakes in stretching routines include holding static stretches for too long or performing dynamic stretches too quickly, which can increase the risk of injury. Neglecting proper warm-up before static stretching reduces muscle elasticity and effectiveness. Failing to target specific muscle groups and overstretching beyond natural range of motion also compromise flexibility gains and joint health.
Stretching for Injury Prevention and Recovery
Static stretching involves holding muscles in a fixed position to improve flexibility and reduce muscle stiffness, which aids in injury prevention by enhancing muscle length and joint range of motion. Dynamic stretching uses controlled, active movements that mimic sport-specific activities, increasing blood flow and muscle temperature, thus accelerating recovery by promoting circulation and reducing muscle soreness. Integrating both static and dynamic stretching optimizes injury prevention and recovery by balancing muscle preparation with flexibility enhancement.
Best Practices for Integrating Both Stretch Types
Incorporate dynamic stretching into warm-ups to enhance blood flow and prepare muscles for activity, targeting major muscle groups with controlled, active movements. Use static stretching post-exercise to improve flexibility and aid recovery by holding stretches for 15-60 seconds, focusing on muscles used during the workout. Balancing both stretching types optimizes performance and reduces injury risk, aligning with guidelines from organizations like the American College of Sports Medicine.
Static Stretching vs Dynamic Stretching Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com