Chronotype refers to an individual's natural preference for sleep and activity times, influencing whether they are a morning person or a night owl, while circadian rhythm is the body's internal 24-hour clock regulating physiological processes. Understanding the interaction between chronotype and circadian rhythm is essential for optimizing sleep patterns, improving mental health, and enhancing overall well-being. Disruptions in either can lead to sleep disorders, affecting cognitive function and metabolic health.
Table of Comparison
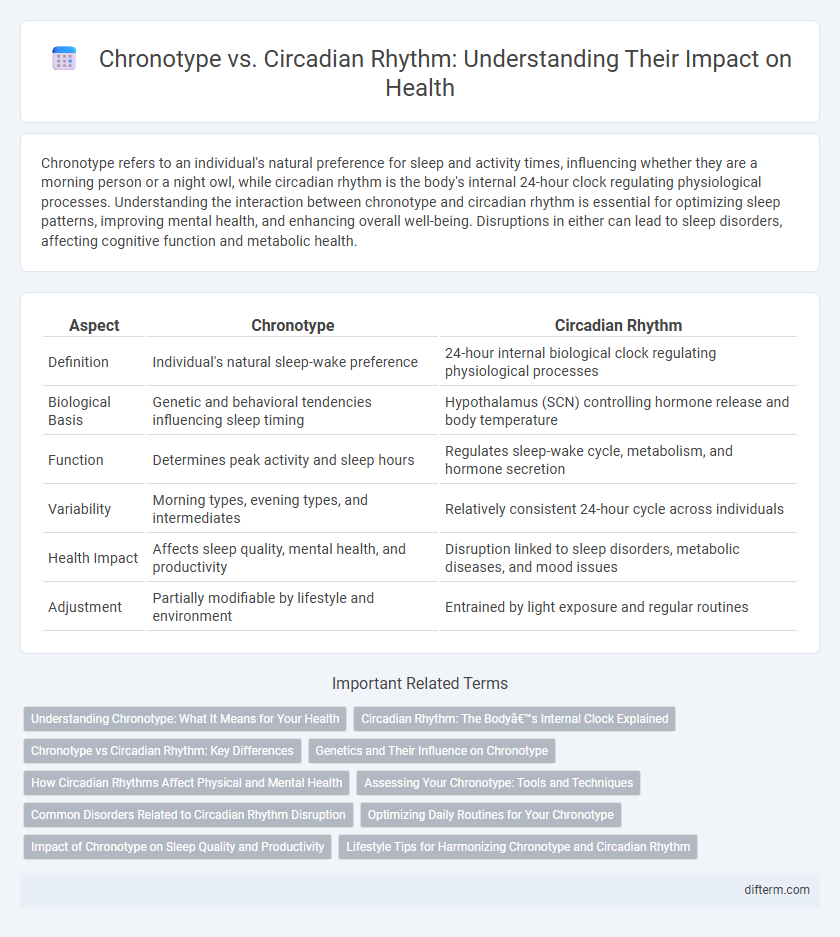
| Aspect | Chronotype | Circadian Rhythm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual's natural sleep-wake preference | 24-hour internal biological clock regulating physiological processes |
| Biological Basis | Genetic and behavioral tendencies influencing sleep timing | Hypothalamus (SCN) controlling hormone release and body temperature |
| Function | Determines peak activity and sleep hours | Regulates sleep-wake cycle, metabolism, and hormone secretion |
| Variability | Morning types, evening types, and intermediates | Relatively consistent 24-hour cycle across individuals |
| Health Impact | Affects sleep quality, mental health, and productivity | Disruption linked to sleep disorders, metabolic diseases, and mood issues |
| Adjustment | Partially modifiable by lifestyle and environment | Entrained by light exposure and regular routines |
Understanding Chronotype: What It Means for Your Health
Chronotype defines an individual's natural inclination toward sleep and wake times, aligning with specific periods of peak alertness and productivity. Its alignment or misalignment with the circadian rhythm--a 24-hour internal biological clock regulating physiological processes--significantly impacts mental health, metabolic function, and cardiovascular risk. Tailoring daily schedules to one's chronotype can improve sleep quality, hormone balance, and overall well-being.
Circadian Rhythm: The Body’s Internal Clock Explained
Circadian rhythm is the body's natural 24-hour internal clock that regulates sleep-wake cycles, hormone release, body temperature, and other vital functions. This rhythm synchronizes physiological processes with environmental cues like light and darkness, promoting optimal health and well-being. Disruptions to the circadian rhythm can lead to sleep disorders, metabolic issues, and reduced cognitive performance.
Chronotype vs Circadian Rhythm: Key Differences
Chronotype refers to an individual's natural preference for sleep and wake times, determining whether they are a morning, evening, or intermediate type. Circadian rhythm is the 24-hour internal clock regulating physiological processes, including sleep-wake cycles, hormone release, and body temperature. The key difference lies in chronotype representing personal sleep pattern tendencies, while circadian rhythm is the broader biological system that synchronizes these patterns with environmental cues.
Genetics and Their Influence on Chronotype
Genetics play a crucial role in determining an individual's chronotype by influencing the circadian rhythm through specific gene variants such as PER3, CLOCK, and BMAL1. These genes regulate the timing of melatonin release, sleep-wake cycles, and alertness patterns, leading to variations in morningness or eveningness preferences. Understanding the genetic basis of chronotype aids in personalized health strategies and optimizing sleep hygiene for improved overall well-being.
How Circadian Rhythms Affect Physical and Mental Health
Circadian rhythms regulate the sleep-wake cycle, hormonal secretions, and body temperature, playing a crucial role in maintaining physical and mental health. Disruptions to these rhythms, such as shift work or irregular sleep patterns, increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, depression, and anxiety. Synchronizing daily activities with natural circadian rhythms optimizes cognitive function, mood stability, immune response, and overall well-being.
Assessing Your Chronotype: Tools and Techniques
Assessing your chronotype involves using tools such as the Morningness-Eveningness Questionnaire (MEQ) and the Munich Chronotype Questionnaire (MCTQ) to determine individual sleep-wake preferences. Wearable devices that monitor sleep patterns and body temperature provide objective data helping to identify one's natural circadian phase. Combining subjective surveys with biometric data enables precise evaluation of chronotype, optimizing personalized health and productivity strategies.
Common Disorders Related to Circadian Rhythm Disruption
Circadian rhythm disruption is linked to common disorders such as insomnia, delayed sleep phase syndrome, and shift work disorder, which impair sleep quality and overall health. Chronotype differences influence individual susceptibility to these disorders by affecting the timing of sleep and activity patterns. Proper alignment between chronotype and circadian rhythm is essential to mitigate risks of metabolic syndrome, depression, and cardiovascular disease associated with circadian misalignment.
Optimizing Daily Routines for Your Chronotype
Understanding your chronotype allows you to tailor daily routines that align with your peak energy levels, enhancing productivity and well-being. Synchronizing tasks like work, exercise, and meals with your natural circadian rhythm supports hormone balance, improves sleep quality, and boosts mental clarity. Personalized scheduling based on chronotype reduces fatigue and maximizes efficiency throughout the day.
Impact of Chronotype on Sleep Quality and Productivity
Chronotype significantly influences sleep quality by determining an individual's preferred sleep-wake timing, which affects the alignment of sleep patterns with natural circadian rhythms. Misalignment between chronotype and conventional schedules often leads to sleep deprivation, reduced alertness, and impaired cognitive function. Optimizing daily activities according to chronotype enhances productivity, mood stability, and overall health by improving sleep efficiency and circadian synchronization.
Lifestyle Tips for Harmonizing Chronotype and Circadian Rhythm
Aligning lifestyle habits with your chronotype enhances synchronization with the circadian rhythm, optimizing sleep quality and daytime energy levels. Tailor exposure to natural light by morning for morning chronotypes and shift light intake later for evening types to regulate melatonin production effectively. Consistent meal timings and exercise routines that match your biological rhythm support metabolic health and cognitive function.
Chronotype vs Circadian rhythm Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com