The majority whip supports party discipline by ensuring members vote according to party lines, while the majority leader sets the legislative agenda and represents the party floor strategy. The whip acts as an intermediary between rank-and-file members and leadership, mobilizing votes and maintaining communication. In contrast, the majority leader prioritizes policy initiatives and manages the party's overall legislative priorities in the chamber.
Table of Comparison
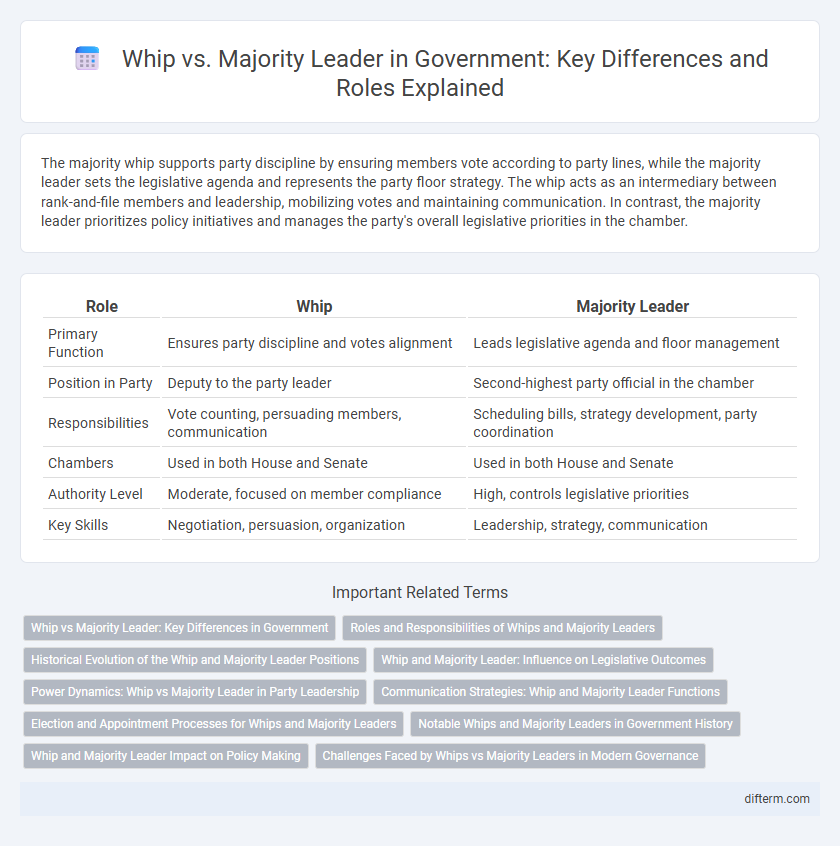
| Role | Whip | Majority Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Ensures party discipline and votes alignment | Leads legislative agenda and floor management |
| Position in Party | Deputy to the party leader | Second-highest party official in the chamber |
| Responsibilities | Vote counting, persuading members, communication | Scheduling bills, strategy development, party coordination |
| Chambers | Used in both House and Senate | Used in both House and Senate |
| Authority Level | Moderate, focused on member compliance | High, controls legislative priorities |
| Key Skills | Negotiation, persuasion, organization | Leadership, strategy, communication |
Whip vs Majority Leader: Key Differences in Government
The Whip and Majority Leader hold distinct roles within government legislative bodies; the Whip focuses on party discipline by securing votes and ensuring member attendance, while the Majority Leader manages the legislative agenda and strategy for the majority party. The Whip often acts as a liaison between party leadership and rank-and-file members, utilizing vote counting and persuasion techniques. In contrast, the Majority Leader coordinates floor activities, schedules debates, and represents the majority party's policy priorities in legislative processes.
Roles and Responsibilities of Whips and Majority Leaders
Whips are responsible for maintaining party discipline, ensuring members vote according to party lines, and counting votes before key legislative decisions. Majority Leaders manage the legislative agenda, coordinate party strategy on the floor, and act as the primary spokesperson for the majority party. Both roles are essential for legislative efficiency, with Whips focusing on vote mobilization and Majority Leaders overseeing overall party strategy.
Historical Evolution of the Whip and Majority Leader Positions
The positions of Whip and Majority Leader in government evolved during the late 19th and early 20th centuries as political parties sought more structured leadership within legislative bodies. The term "Whip" was borrowed from British hunting terminology, reflecting the role's function in enforcing party discipline and securing votes, while the Majority Leader emerged to coordinate legislative agendas and strategies for the dominant party. Over time, these roles have become central to party organization and legislative effectiveness, with the Whip focusing on vote counting and member persuasion, and the Majority Leader managing policy priorities and floor activities.
Whip and Majority Leader: Influence on Legislative Outcomes
The Whip plays a crucial role in maintaining party discipline by ensuring legislators vote according to the party line, directly influencing legislative outcomes through vote counting and persuasion. The Majority Leader shapes the legislative agenda by scheduling debates, prioritizing bills, and coordinating party strategy, thereby steering the passage of key legislation. Together, the Whip and Majority Leader sustain party cohesion and effectiveness, enhancing the party's ability to advance its legislative goals within Congress.
Power Dynamics: Whip vs Majority Leader in Party Leadership
The majority leader holds significant authority by setting the legislative agenda and coordinating party strategy, effectively steering the party's policy priorities in government. The whip operates as the majority leader's key enforcer, responsible for securing votes and maintaining discipline among party members, ensuring alignment with leadership goals. This power dynamic creates a balance where the majority leader directs vision and strategy, while the whip manages compliance and vote mobilization to achieve legislative success.
Communication Strategies: Whip and Majority Leader Functions
The Whip manages internal party communication by gathering vote counts and persuading members to align with party decisions, ensuring legislative cohesion. The Majority Leader serves as the primary spokesperson and strategist, coordinating with committee chairs and communicating the party's agenda to both legislators and the public. Effective communication strategies between the Whip and Majority Leader are crucial for maintaining party discipline and advancing legislative priorities efficiently.
Election and Appointment Processes for Whips and Majority Leaders
Whips are typically elected by their party members within the legislative chamber, often requiring a majority vote among colleagues to secure the position. Majority leaders are usually appointed or elected by the party caucus or conference, reflecting broader support across the party's elected officials. Both roles involve internal party elections, but majority leaders often face a more formalized appointment process due to their higher leadership status.
Notable Whips and Majority Leaders in Government History
Notable government figures such as James E. Clyburn and Steve Scalise have served as influential Whips, playing crucial roles in party discipline and legislative strategy. Prominent Majority Leaders like Senate's Lyndon B. Johnson and House's Steny Hoyer have shaped policy agendas and maintained party unity during pivotal legislative sessions. The strategic coordination by Whips and Majority Leaders remains essential in advancing governmental priorities and legislative efficiency.
Whip and Majority Leader Impact on Policy Making
The Whip plays a crucial role in policy making by ensuring party discipline and securing votes essential for passing legislation, thereby influencing legislative outcomes. The Majority Leader manages the legislative agenda, prioritizing bills and coordinating with committee chairs to align policy goals with party strategies. Together, these roles drive the efficiency and direction of policymaking within government bodies.
Challenges Faced by Whips vs Majority Leaders in Modern Governance
Whips face the challenge of maintaining party discipline and securing votes amidst diverse political factions, often contending with internal dissent and fluctuating loyalty. Majority leaders must balance legislative agenda setting with coalition management, navigating complex negotiations between party members, minority opposition, and external stakeholders. Both roles require strategic communication and adaptability to respond to rapid political shifts and intense media scrutiny in modern governance.
whip vs majority leader Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com