Statutory law comprises laws enacted by legislatures, providing the legal framework and specific regulations that govern government operations and citizens' rights. Administrative law, on the other hand, consists of rules and regulations created and enforced by government agencies to implement statutory laws effectively. Understanding the distinction between statutory and administrative law ensures proper governance and regulatory compliance within the scope of government authority.
Table of Comparison
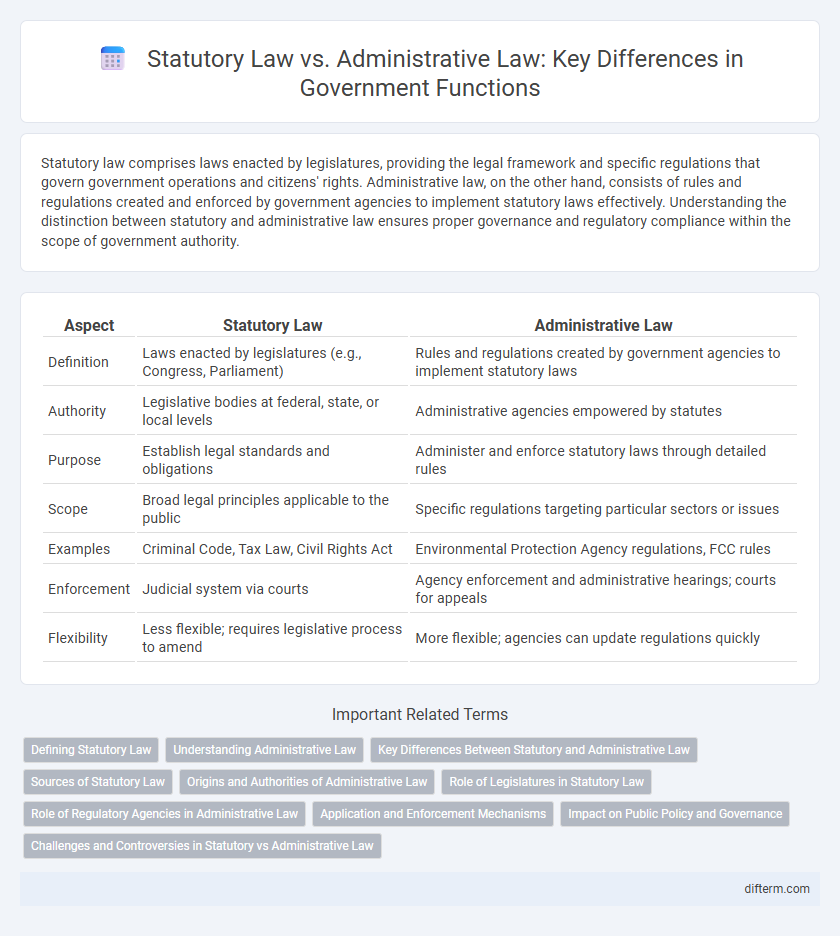
| Aspect | Statutory Law | Administrative Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Laws enacted by legislatures (e.g., Congress, Parliament) | Rules and regulations created by government agencies to implement statutory laws |
| Authority | Legislative bodies at federal, state, or local levels | Administrative agencies empowered by statutes |
| Purpose | Establish legal standards and obligations | Administer and enforce statutory laws through detailed rules |
| Scope | Broad legal principles applicable to the public | Specific regulations targeting particular sectors or issues |
| Examples | Criminal Code, Tax Law, Civil Rights Act | Environmental Protection Agency regulations, FCC rules |
| Enforcement | Judicial system via courts | Agency enforcement and administrative hearings; courts for appeals |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; requires legislative process to amend | More flexible; agencies can update regulations quickly |
Defining Statutory Law
Statutory law consists of laws enacted by legislative bodies such as Congress or state legislatures, providing a formal written framework that governs society. These laws are codified in statutes and serve as the primary source of legal authority, guiding judicial interpretation and administrative enforcement. Statutory law establishes clear legal standards and obligations, differentiating it from administrative law, which involves rules created by government agencies based on statutory authority.
Understanding Administrative Law
Administrative law governs the activities and operations of government agencies, ensuring compliance with statutory mandates and protecting citizens' rights through rulemaking, adjudication, and enforcement. It provides mechanisms for judicial review of agency decisions, promoting accountability and transparency within federal, state, and local governments. Understanding administrative law is essential for navigating government regulations, agency procedures, and administrative hearings that impact public policy and individual rights.
Key Differences Between Statutory and Administrative Law
Statutory law consists of laws enacted by legislative bodies such as Congress or state legislatures, establishing clear legal standards and obligations. Administrative law governs the actions and regulations of government agencies, focusing on rulemaking, enforcement, and adjudication within their delegated authority. The key differences lie in their origin--statutory law derives from legislatures, while administrative law stems from executive agencies interpreting and implementing those statutes.
Sources of Statutory Law
Sources of statutory law primarily include constitutions, legislatures, and referenda, where laws are formally enacted by elected bodies or direct public votes. Constitutional provisions establish the foundational legal framework from which statutory laws derive authority, while legislatures pass statutes that address specific policy issues in detail. These sources ensure that statutory laws are codified, publicly accessible, and enforceable within the government's legal system.
Origins and Authorities of Administrative Law
Statutory law originates from legislatures enacting formal statutes, while administrative law derives from agencies granted authority by these statutes to implement and enforce specific regulations. Administrative law's authority stems from enabling statutes that delegate power to government agencies, allowing them to create rules, adjudicate disputes, and enforce compliance within their specialized areas. The origins of administrative law reflect the need for expertise and efficiency in regulating complex sectors, distinguishing it from the broader scope of statutory law passed by elected officials.
Role of Legislatures in Statutory Law
Legislatures play a crucial role in statutory law by enacting statutes that establish legal standards and frameworks governing society. These elected bodies draft, debate, and pass laws that provide the foundation for regulatory agencies to implement and enforce rules under administrative law. Statutory law reflects the formal legislative process and democratic accountability, distinguishing it from the rule-making authority delegated to administrative agencies.
Role of Regulatory Agencies in Administrative Law
Regulatory agencies play a crucial role in administrative law by creating and enforcing rules that implement statutory laws passed by the legislature. These agencies possess specialized expertise enabling them to regulate complex sectors such as environmental protection, finance, and public health. Their rulemaking, adjudication, and enforcement functions ensure that statutory objectives are effectively translated into practical regulations and compliance standards.
Application and Enforcement Mechanisms
Statutory law is created by legislative bodies and provides clear, codified rules that govern behavior and are enforced through judicial processes, ensuring legal standards in diverse areas such as criminal justice and civil rights. Administrative law governs the activities of government agencies, enabling them to implement regulations, conduct investigations, and enforce compliance through mechanisms like administrative hearings and fines. Enforcement of statutory law typically involves courts and legal penalties, while administrative law relies on agency authority and procedures to ensure regulatory adherence and policy execution.
Impact on Public Policy and Governance
Statutory law, enacted by legislatures, establishes clear legal frameworks that directly shape public policy by defining rights and obligations, thereby guiding governance structures and decision-making processes. Administrative law governs the implementation and enforcement of these statutes through government agencies, ensuring regulatory compliance and operational efficiency in public administration. The interplay between statutory and administrative law influences policy outcomes by balancing legislative intent with practical regulatory flexibility, affecting transparency, accountability, and service delivery in governance.
Challenges and Controversies in Statutory vs Administrative Law
Statutory law faces challenges in rigidity and slow adaptation to societal changes, often leading to outdated provisions that fail to address emerging issues effectively. Administrative law controversies revolve around the scope of agency power and potential overreach, raising concerns over transparency and accountability in rulemaking and enforcement. The tension between legislative statutes and administrative regulations creates complexities in legal interpretation and enforcement, complicating the balance of authority among government branches.
Statutory Law vs Administrative Law Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com