Government pet policies often fluctuate between autarky and protectionism, balancing self-sufficiency with trade barriers to shield domestic industries. Autarky emphasizes reducing dependence on foreign goods by promoting local production, while protectionism imposes tariffs and quotas to protect national markets from international competition. This strategic approach influences economic stability, employment rates, and consumer prices within the country.
Table of Comparison
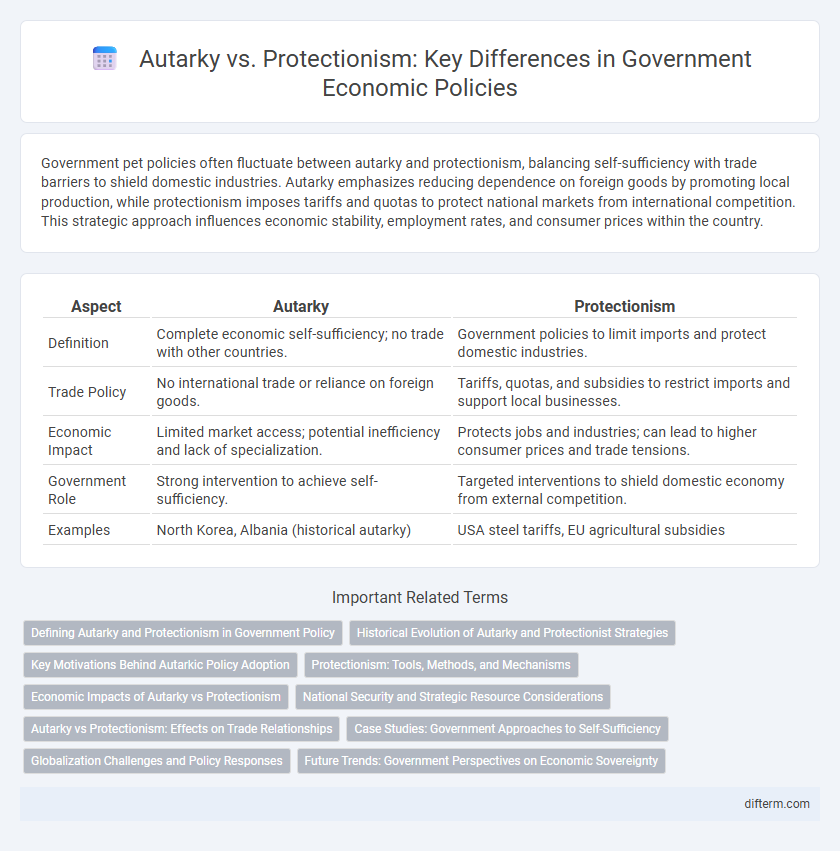
| Aspect | Autarky | Protectionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete economic self-sufficiency; no trade with other countries. | Government policies to limit imports and protect domestic industries. |
| Trade Policy | No international trade or reliance on foreign goods. | Tariffs, quotas, and subsidies to restrict imports and support local businesses. |
| Economic Impact | Limited market access; potential inefficiency and lack of specialization. | Protects jobs and industries; can lead to higher consumer prices and trade tensions. |
| Government Role | Strong intervention to achieve self-sufficiency. | Targeted interventions to shield domestic economy from external competition. |
| Examples | North Korea, Albania (historical autarky) | USA steel tariffs, EU agricultural subsidies |
Defining Autarky and Protectionism in Government Policy
Autarky refers to a government policy aimed at achieving economic self-sufficiency by minimizing reliance on international trade and promoting domestic production of goods and services. Protectionism involves the implementation of tariffs, quotas, and other trade barriers to shield domestic industries from foreign competition, thereby supporting local employment and economic stability. Both autarky and protectionism reflect strategies to control economic exposure and prioritize national economic interests.
Historical Evolution of Autarky and Protectionist Strategies
Autarky, implemented by nations such as Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy in the 1930s, emerged as a state-driven economic strategy aimed at achieving self-sufficiency and reducing reliance on foreign trade. Protectionist strategies evolved from mercantilist policies in the 16th and 17th centuries, gaining momentum during the Great Depression when countries imposed tariffs and quotas to shield domestic industries from global competition. Over time, autarky's emphasis on economic independence contrasted with protectionism's focus on regulating trade barriers, shaping government approaches to international commerce and national security.
Key Motivations Behind Autarkic Policy Adoption
Key motivations behind autarkic policy adoption include reducing dependence on foreign nations to enhance national security and economic sovereignty. Governments pursue autarky to safeguard strategic industries from global market volatility and external political pressures. Emphasis on self-sufficiency fosters domestic production, preserves jobs, and controls critical resources within national borders.
Protectionism: Tools, Methods, and Mechanisms
Protectionism employs tools such as tariffs, import quotas, and subsidies to shield domestic industries from foreign competition. Non-tariff barriers like licensing requirements, safety standards, and customs procedures restrict imports while promoting local production. These mechanisms aim to preserve jobs, support strategic sectors, and reduce trade deficits by limiting access to cheaper or subsidized foreign goods.
Economic Impacts of Autarky vs Protectionism
Autarky limits economic growth by restricting trade, leading to inefficiencies and higher production costs due to lack of competitive pressure and resource specialization. Protectionism imposes tariffs and quotas that can shield domestic industries but often results in higher consumer prices, reduced export competitiveness, and potential retaliation from trading partners. Both policies disrupt global supply chains, but autarky severely curtails market access, while protectionism selectively restricts imports to protect specific sectors.
National Security and Strategic Resource Considerations
Autarky emphasizes reducing reliance on foreign imports to safeguard national security by ensuring access to critical strategic resources like rare earth elements and energy supplies. Protectionism employs tariffs and trade barriers to shield domestic industries vital for defense and infrastructure from global supply disruptions. Both approaches prioritize securing supply chains to maintain sovereignty and resilience in geopolitical crises.
Autarky vs Protectionism: Effects on Trade Relationships
Autarky severely limits a country's trade relationships by promoting economic self-sufficiency and reducing dependence on international markets, resulting in decreased import and export activities. Protectionism, characterized by tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers, alters trade dynamics by shielding domestic industries but often leads to retaliatory measures from trading partners, escalating trade conflicts. Both autarky and protectionism can disrupt global supply chains and hinder market access, impacting international cooperation and economic growth.
Case Studies: Government Approaches to Self-Sufficiency
Government approaches to self-sufficiency vary significantly between autarky and protectionism, with North Korea exemplifying autarky through strict economic isolation and limited foreign trade to achieve complete national independence. In contrast, India employs protectionism by imposing tariffs and import restrictions to nurture domestic industries while maintaining selective foreign trade engagement. These case studies highlight how governments balance economic control and external interaction to safeguard national interests and promote sustainable development.
Globalization Challenges and Policy Responses
Autarky involves a country striving for economic self-sufficiency by minimizing imports, often leading to reduced international trade and limited access to global markets. Protectionism employs tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers to shield domestic industries from foreign competition, which can provoke retaliation and trade wars. Governments face the challenge of balancing these strategies to safeguard national interests while engaging with globalization, necessitating nuanced policy responses that promote competitiveness without undermining economic integration.
Future Trends: Government Perspectives on Economic Sovereignty
Governments increasingly emphasize economic sovereignty through balanced approaches between autarky and protectionism to safeguard national industries while engaging in global trade. Future trends indicate rising investment in strategic sectors like technology and energy independence to reduce external vulnerabilities. Policy shifts highlight adaptive trade regulations and enhanced domestic innovation to strengthen resilience against global economic disruptions.
autarky vs protectionism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com