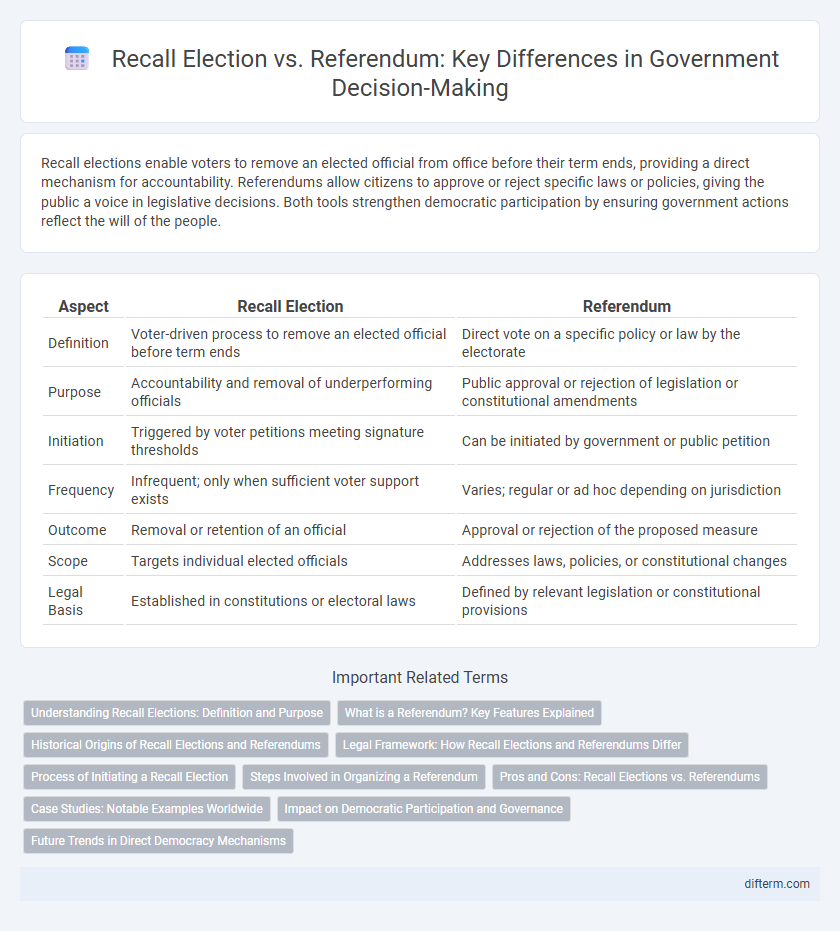
Recall elections enable voters to remove an elected official from office before their term ends, providing a direct mechanism for accountability. Referendums allow citizens to approve or reject specific laws or policies, giving the public a voice in legislative decisions. Both tools strengthen democratic participation by ensuring government actions reflect the will of the people.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Recall Election | Referendum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voter-driven process to remove an elected official before term ends | Direct vote on a specific policy or law by the electorate |
| Purpose | Accountability and removal of underperforming officials | Public approval or rejection of legislation or constitutional amendments |
| Initiation | Triggered by voter petitions meeting signature thresholds | Can be initiated by government or public petition |
| Frequency | Infrequent; only when sufficient voter support exists | Varies; regular or ad hoc depending on jurisdiction |
| Outcome | Removal or retention of an official | Approval or rejection of the proposed measure |
| Scope | Targets individual elected officials | Addresses laws, policies, or constitutional changes |
| Legal Basis | Established in constitutions or electoral laws | Defined by relevant legislation or constitutional provisions |
Understanding Recall Elections: Definition and Purpose
Recall elections allow voters to remove elected officials from office before their term ends by petitioning for a special vote, providing a direct mechanism for political accountability. This process empowers citizens to address dissatisfaction with an official's performance without waiting for the next scheduled election. Unlike referendums, which focus on deciding specific policy issues, recall elections specifically target individual officeholders.
What is a Referendum? Key Features Explained
A referendum is a direct voting process allowing citizens to approve or reject specific legislative measures or constitutional amendments proposed by the government. Key features include its binding nature, the ability to address broad policy issues, and its function as a tool for direct democracy that empowers voters to influence decision-making without intermediary representatives. Referendums are distinct from recall elections, which specifically target the removal of elected officials before their term ends.
Historical Origins of Recall Elections and Referendums
Recall elections originated in the early 20th century United States as a progressive reform tool enabling voters to remove elected officials before their terms expired, with the first successful use in Los Angeles in 1903. Referendums trace back to ancient democratic practices, notably in Swiss cantons and New England town meetings, evolving into a formal mechanism for direct voter decision-making on legislation and public policy. Both recall elections and referendums embody elements of direct democracy, offering citizens the power to influence government accountability and legislative outcomes beyond representative elections.
Legal Framework: How Recall Elections and Referendums Differ
Recall elections are governed by specific legal frameworks allowing voters to remove elected officials before their term ends, typically initiated through petition processes with defined thresholds for signatures. Referendums operate under separate legislative guidelines that enable citizens to approve or reject laws, policies, or constitutional amendments directly, often triggered by government decision or citizen petition. The key legal distinction lies in recall elections targeting individual officials' tenure, while referendums address broader legislative or policy issues.
Process of Initiating a Recall Election
Initiating a recall election requires submitting a petition signed by a specified percentage of registered voters within a designated timeframe, often ranging from 10% to 25%, depending on jurisdictional laws. This petition must clearly state the reasons for recalling the elected official and is subject to verification by election authorities to ensure legitimacy. Upon validation, the recall election is scheduled, allowing voters to decide whether to remove the official before the end of their term.
Steps Involved in Organizing a Referendum
Organizing a referendum involves several key steps, starting with the initiation phase where a proposal is drafted and supported by a required number of voter signatures or legislative approval. The next step includes official validation by electoral authorities to ensure compliance with legal and procedural requirements. Finally, the referendum is scheduled, public information campaigns are conducted, and voting takes place to directly gauge public opinion on the proposed issue.
Pros and Cons: Recall Elections vs. Referendums
Recall elections enable voters to remove elected officials before their term ends, providing a direct accountability mechanism but can lead to political instability and frequent election costs. Referendums allow citizens to vote on specific policies or laws, enhancing democratic participation and policy legitimacy, though they may oversimplify complex issues and be influenced by populist appeals. Both tools strengthen democratic engagement but require careful regulation to balance responsiveness with effective governance.
Case Studies: Notable Examples Worldwide
Notable case studies of recall elections include the 2003 California governor recall that temporarily removed Gray Davis, illustrating direct voter authority to oust elected officials. In contrast, referendums like the 2016 Brexit vote in the United Kingdom demonstrate public decision-making on policy issues rather than individual officeholders. These examples highlight differing applications of direct democracy mechanisms across global governments, emphasizing recall elections as tools for political accountability and referendums for shaping national policies.
Impact on Democratic Participation and Governance
Recall elections empower citizens to remove elected officials before their terms end, increasing accountability and responsiveness in governance but potentially leading to political instability. Referendums provide a direct voice on specific policies or laws, enhancing democratic participation by allowing voters to influence decision-making beyond representative elections. Both mechanisms strengthen democratic engagement but must be balanced to prevent governance disruption and ensure effective policy implementation.
Future Trends in Direct Democracy Mechanisms
Recall elections and referendums represent key instruments in the evolution of direct democracy, with increasing adoption driven by demands for greater governmental accountability and citizen engagement. Future trends indicate enhanced use of digital platforms to streamline petition processes and voting, expanding accessibility and participation while ensuring robust verification methods to maintain electoral integrity. Emerging frameworks prioritize integrating data analytics and AI to predict public sentiment and tailor referendum topics, fostering more responsive and adaptive governance structures globally.
Recall Election vs Referendum Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com