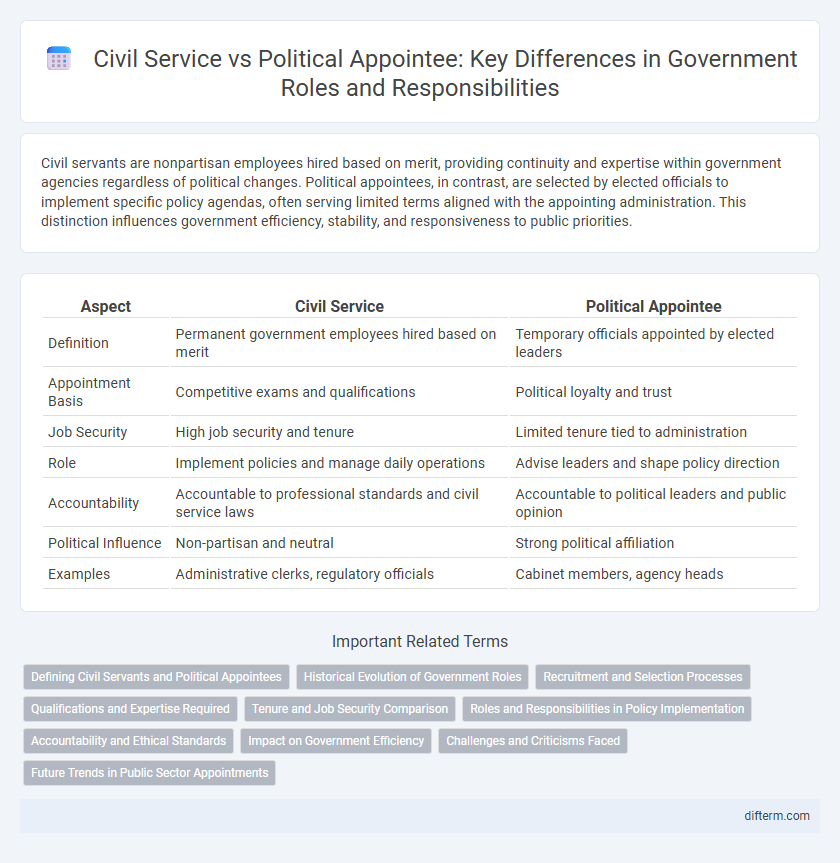
Civil servants are nonpartisan employees hired based on merit, providing continuity and expertise within government agencies regardless of political changes. Political appointees, in contrast, are selected by elected officials to implement specific policy agendas, often serving limited terms aligned with the appointing administration. This distinction influences government efficiency, stability, and responsiveness to public priorities.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Civil Service | Political Appointee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent government employees hired based on merit | Temporary officials appointed by elected leaders |
| Appointment Basis | Competitive exams and qualifications | Political loyalty and trust |
| Job Security | High job security and tenure | Limited tenure tied to administration |
| Role | Implement policies and manage daily operations | Advise leaders and shape policy direction |
| Accountability | Accountable to professional standards and civil service laws | Accountable to political leaders and public opinion |
| Political Influence | Non-partisan and neutral | Strong political affiliation |
| Examples | Administrative clerks, regulatory officials | Cabinet members, agency heads |
Defining Civil Servants and Political Appointees
Civil servants are career employees hired based on merit, tasked with implementing government policies and maintaining administrative continuity across different political administrations. Political appointees are selected by elected officials, often aligned with the current administration's agenda, serving in advisory or leadership roles with limited tenure linked to the appointing authority. The distinction lies in job security, recruitment methods, and the nature of their responsibilities within the government structure.
Historical Evolution of Government Roles
Civil service roles have evolved from ancient bureaucratic systems, such as Imperial China's merit-based examinations, to modern professional administrations emphasizing neutrality and expertise. Political appointees emerged prominently in democratic systems during the 19th and 20th centuries to align executive agencies with elected officials' policy goals. This historical evolution reflects ongoing tensions between administrative continuity and political responsiveness within government structures.
Recruitment and Selection Processes
Civil Service recruitment relies on merit-based examinations, standardized criteria, and competitive selection to ensure qualified candidates are appointed based on expertise and experience. Political appointee selection centers on loyalty, alignment with elected officials' agendas, and discretionary appointment without standardized testing. This distinction affects transparency, accountability, and the overall efficiency of government operations.
Qualifications and Expertise Required
Civil service positions demand specialized qualifications and extensive expertise in public administration, policy implementation, and technical skills relevant to government operations. Political appointees often require strong leadership abilities, political acumen, and alignment with the current administration's goals rather than specific technical credentials. The distinction ensures civil servants maintain continuity and professionalism, while appointees bring strategic direction aligned with elected officials.
Tenure and Job Security Comparison
Civil service employees typically enjoy greater job security due to merit-based hiring and protection from arbitrary dismissal, ensuring longer tenure irrespective of political changes. Political appointees, in contrast, serve at the pleasure of elected officials and often face tenure linked to the appointing administration's duration. This fundamental difference impacts continuity and institutional knowledge within government operations.
Roles and Responsibilities in Policy Implementation
Civil Service employees ensure continuity and neutrality in policy implementation by executing government programs based on established laws and regulations, maintaining institutional knowledge regardless of political changes. Political appointees shape and guide policy direction, making strategic decisions that align with the current administration's priorities and providing leadership to ensure policies reflect elected officials' mandates. This division allows a balance between stable, consistent public service and dynamic, responsive governance in adapting policies to evolving political goals.
Accountability and Ethical Standards
Civil service employees are held to strict accountability standards through formal codes of conduct and an emphasis on impartiality, ensuring ethical behavior independent of political changes. Political appointees, by contrast, are accountable primarily to elected officials and are often subject to shifting ethical guidelines aligned with administration priorities. Maintaining clear ethical distinctions helps uphold public trust and prevents conflicts of interest within government operations.
Impact on Government Efficiency
Civil service employees ensure government efficiency through continuity and expertise, maintaining stable operations regardless of political changes. Political appointees bring strategic direction and align government priorities with the current administration's agenda but may disrupt institutional knowledge with frequent turnover. Balancing the professional competence of civil servants with the adaptability of political appointees optimizes overall government performance.
Challenges and Criticisms Faced
Civil service employees often face challenges related to bureaucratic rigidity and limited flexibility, hindering swift policy implementation. Political appointees encounter criticism for perceived partisanship and lack of long-term commitment, which can disrupt agency continuity. Both roles struggle with accountability issues, balancing expertise and political loyalty in government operations.
Future Trends in Public Sector Appointments
Future trends in public sector appointments emphasize increasing reliance on hybrid models combining merit-based civil service with strategic political appointees to enhance agility and policy responsiveness. Automation and data analytics are driving more transparent, efficient candidate selection processes, ensuring alignment with evolving governance priorities and diversity goals. Emphasis on lifelong learning and adaptive skill development prepares both civil servants and appointees for complex challenges posed by digital transformation and global policy shifts.
Civil Service vs Political Appointee Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com