Public-private partnerships enable governments to collaborate with private entities, leveraging shared resources and expertise while maintaining regulatory oversight and public accountability. Privatization transfers full ownership and control of government services or assets to private companies, often aiming for increased efficiency but risking reduced public influence and access. Evaluating the balance between public accountability and operational efficiency is crucial when deciding between these two approaches.
Table of Comparison
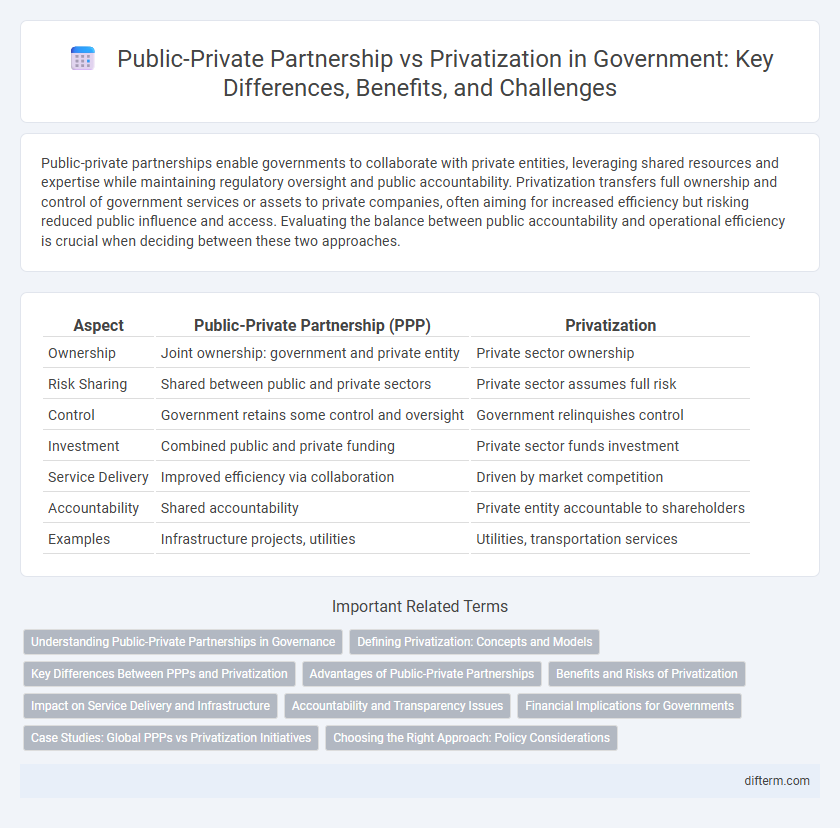
| Aspect | Public-Private Partnership (PPP) | Privatization |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Joint ownership: government and private entity | Private sector ownership |
| Risk Sharing | Shared between public and private sectors | Private sector assumes full risk |
| Control | Government retains some control and oversight | Government relinquishes control |
| Investment | Combined public and private funding | Private sector funds investment |
| Service Delivery | Improved efficiency via collaboration | Driven by market competition |
| Accountability | Shared accountability | Private entity accountable to shareholders |
| Examples | Infrastructure projects, utilities | Utilities, transportation services |
Understanding Public-Private Partnerships in Governance
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) in governance combine government oversight with private sector efficiency to deliver public services and infrastructure, balancing risk and investment between both entities. PPPs enable governments to leverage private capital and expertise while maintaining regulatory control, contrasting with full privatization where the private sector assumes complete ownership and operational responsibility. Understanding the distinct roles and benefits of PPPs helps optimize resource allocation, improve project outcomes, and foster sustainable economic development within public administration.
Defining Privatization: Concepts and Models
Privatization involves transferring ownership and management of public assets or services to private entities, aiming to enhance efficiency, reduce government expenditures, and foster innovation. Models of privatization include full divestiture, where government relinquishes all control, and partial privatization, which retains some public oversight while involving private participation through mechanisms like public-private partnerships (PPPs). These models vary in degrees of risk allocation, regulatory frameworks, and impact on service delivery, reflecting different governmental objectives and market dynamics.
Key Differences Between PPPs and Privatization
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) involve collaboration where the government retains ownership but contracts private entities for services or infrastructure development, sharing risks and rewards. Privatization transfers ownership and operational control entirely to the private sector, aiming for efficiency and cost reduction without direct government involvement in management. Key differences include risk allocation, control over assets, financial responsibilities, and long-term operational roles, with PPPs emphasizing partnership and shared goals while privatization focuses on divestiture and private sector autonomy.
Advantages of Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships leverage private sector expertise and capital to improve public infrastructure and services while sharing risks between government and private entities. These collaborations foster innovation, enhance efficiency, and ensure long-term project sustainability without fully relinquishing public control. Governments benefit from reduced upfront costs and accelerated project delivery, promoting economic growth and better resource allocation.
Benefits and Risks of Privatization
Privatization offers significant benefits such as increased efficiency, reduced government expenditure, and enhanced innovation through private sector competition. However, risks include potential loss of public control, reduced service accessibility for vulnerable populations, and possible neglect of social welfare objectives. Balancing these benefits and risks requires careful regulatory frameworks to ensure privatized entities meet public interest goals.
Impact on Service Delivery and Infrastructure
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) often enhance service delivery by leveraging private sector efficiency while maintaining public oversight, leading to improved infrastructure quality and maintenance. Privatization transfers full responsibility to private entities, which can increase innovation but may reduce accountability and equitable access to essential services. Empirical studies indicate PPPs balance risk and investment, resulting in sustainable infrastructure development without compromising public interest.
Accountability and Transparency Issues
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) often face challenges in maintaining accountability due to shared responsibilities between government entities and private firms, potentially leading to blurred lines in oversight. Privatization can enhance transparency by placing operations under strict regulatory frameworks, yet it risks reduced public accountability if private firms prioritize profit over public interest. Effective governance requires balancing transparency protocols and accountability mechanisms to ensure that both PPPs and privatization serve the public good without compromising ethical standards.
Financial Implications for Governments
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) enable governments to share financial risks and reduce upfront capital expenditures by leveraging private sector investment for infrastructure projects. Privatization transfers full financial responsibility and operational costs to private entities, potentially generating immediate revenue for governments through asset sales but sacrificing future income streams and control. Evaluating long-term fiscal impacts, including maintenance obligations and service quality, is critical for governments when choosing between PPPs and privatization models.
Case Studies: Global PPPs vs Privatization Initiatives
Case studies from global public-private partnerships (PPPs) reveal enhanced infrastructure development and service delivery in sectors like transportation and healthcare, balancing shared risks and investments between governments and private entities. In contrast, privatization initiatives in countries such as the UK and Brazil demonstrate mixed outcomes, with improved efficiency often offset by challenges in regulatory oversight and public accountability. Comparative analyses highlight that PPPs maintain public control while leveraging private sector expertise, whereas privatization transfers ownership, impacting long-term governance and societal equity.
Choosing the Right Approach: Policy Considerations
Evaluating the optimal approach between public-private partnerships (PPPs) and privatization requires analyzing factors such as service quality, fiscal impact, and long-term sustainability in public sector projects. Governments must assess risk allocation, accountability frameworks, and stakeholder engagement to ensure effective resource utilization and policy alignment. Strategic policy considerations emphasize balancing public interest protection with private sector efficiency to achieve sustainable infrastructure development and public service delivery.
public-private partnership vs privatization Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com