Public policy refers to the broad principles and goals established by government authorities to address societal issues and guide decision-making. Administrative policy consists of the specific procedures and rules implemented by government agencies to execute and manage these public policies effectively. Clear differentiation between the two ensures coherent governance and efficient service delivery.
Table of Comparison
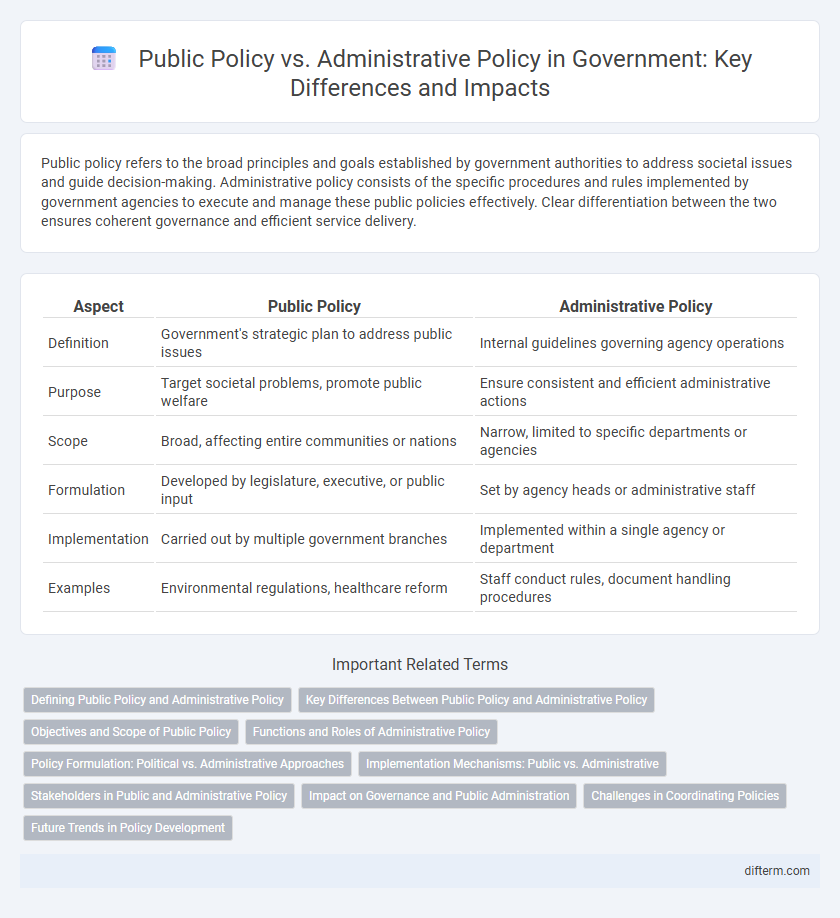
| Aspect | Public Policy | Administrative Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government's strategic plan to address public issues | Internal guidelines governing agency operations |
| Purpose | Target societal problems, promote public welfare | Ensure consistent and efficient administrative actions |
| Scope | Broad, affecting entire communities or nations | Narrow, limited to specific departments or agencies |
| Formulation | Developed by legislature, executive, or public input | Set by agency heads or administrative staff |
| Implementation | Carried out by multiple government branches | Implemented within a single agency or department |
| Examples | Environmental regulations, healthcare reform | Staff conduct rules, document handling procedures |
Defining Public Policy and Administrative Policy
Public policy refers to the broad set of principles and actions formulated by government bodies to address societal issues and guide decision-making at the national or regional level. Administrative policy, on the other hand, consists of the specific rules and procedures established within government agencies to implement and manage public policies efficiently. Understanding the distinction between these helps clarify how overarching goals translate into operational guidelines within the public sector.
Key Differences Between Public Policy and Administrative Policy
Public policy refers to the laws, regulations, and actions formulated by government authorities to address societal issues and achieve specific goals, while administrative policy involves the internal guidelines and procedures that government agencies implement to execute and manage these public policies effectively. Public policy is designed by legislatures and elected officials, focusing on broader societal impacts, whereas administrative policy is developed by bureaucratic agencies to ensure efficiency, consistency, and compliance within government operations. The key differences lie in their scope, purpose, and level of formulation, with public policy shaping societal priorities and administrative policy ensuring practical application and management.
Objectives and Scope of Public Policy
Public policy is designed to address broad societal goals and long-term public interests by setting priorities and guidelines for government action across multiple sectors. Its objectives include promoting social welfare, economic stability, and justice, reaching a wide range of stakeholders and geographic areas. The scope of public policy encompasses legislation, regulations, and governmental programs aimed at solving public issues on a national or community level.
Functions and Roles of Administrative Policy
Administrative policy shapes the implementation and operational framework of public policies by providing detailed guidelines and procedures for government agencies. It ensures consistency, efficiency, and accountability in public administration by directing resource allocation, personnel management, and service delivery. The role of administrative policy is crucial in translating legislative mandates into actionable programs and maintaining organizational discipline within government institutions.
Policy Formulation: Political vs. Administrative Approaches
Policy formulation in government distinguishes between political approaches, which emphasize stakeholder engagement, legislative priorities, and electoral mandates, and administrative approaches, focused on technical analysis, feasibility studies, and bureaucratic processes. Political policy formulation integrates public opinion, interest group lobbying, and elected officials' agendas to shape broad policy goals. Administrative policy formulation relies on expert assessments, regulatory frameworks, and organizational capacity to develop detailed implementation plans.
Implementation Mechanisms: Public vs. Administrative
Public policy implementation mechanisms involve legislative acts, regulatory frameworks, and public engagement to enforce laws and achieve societal goals. Administrative policy focuses on internal procedures, resource allocation, and bureaucratic management within government agencies to ensure efficiency and compliance. The distinction lies in public policy targeting broad social change while administrative policy governs operational execution within governmental structures.
Stakeholders in Public and Administrative Policy
Stakeholders in public policy encompass a wide range of actors including government agencies, elected officials, interest groups, and the general public, all of whom influence policy formulation and implementation to address societal issues. Administrative policy stakeholders primarily involve internal government officials, agency staff, and bureaucrats responsible for the execution and management of policies within specific administrative frameworks. Effective engagement and communication with these distinct stakeholder groups are crucial for aligning policy objectives with public needs and ensuring efficient administrative operations.
Impact on Governance and Public Administration
Public policy shapes governance by establishing broad goals and legal frameworks that guide societal development, while administrative policy focuses on the implementation of these policies through government agencies, affecting operational efficiency and resource allocation. The impact on public administration is significant, as public policy drives strategic decision-making and regulatory priorities, whereas administrative policy directs day-to-day management practices, staff behavior, and procedural consistency. Effective alignment between public and administrative policies enhances transparency, accountability, and service delivery in government institutions.
Challenges in Coordinating Policies
Public policy and administrative policy face significant challenges in coordination due to differing objectives and timelines within government institutions. Public policy, shaped by elected officials, emphasizes long-term societal goals, while administrative policy focuses on efficient implementation within bureaucratic constraints. These divergent priorities often lead to misalignment, communication gaps, and delays in achieving cohesive governance outcomes.
Future Trends in Policy Development
Future trends in public policy emphasize data-driven decision making and greater citizen engagement through digital platforms, enhancing transparency and accountability. Administrative policy is increasingly integrating automation and AI to streamline government operations, improve efficiency, and reduce bureaucratic delays. Both policy types will likely converge around adaptive frameworks that respond dynamically to societal changes and technological advancements.
public policy vs administrative policy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com