Proportional representation ensures that political parties gain seats in proportion to the votes they receive, promoting diverse and inclusive governance. In contrast, majoritarian representation awards seats to candidates with the most votes in single-member districts, often leading to a two-party dominance. This difference impacts government accountability and policy-making by reflecting either a broad spectrum of public opinion or clearer, decisive mandates.
Table of Comparison
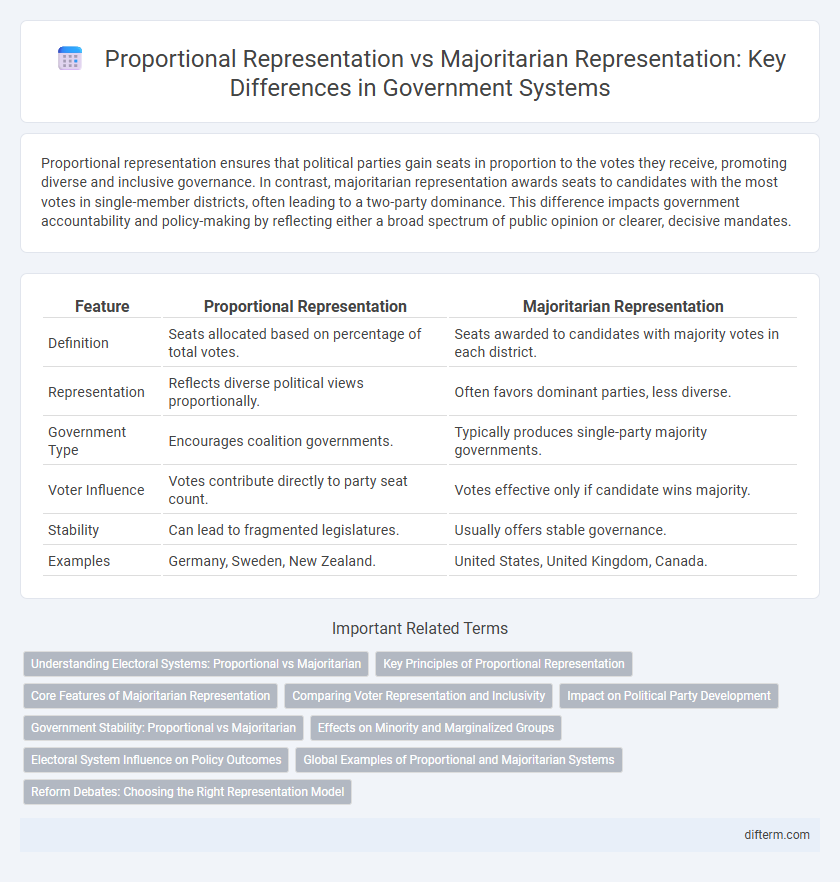
| Feature | Proportional Representation | Majoritarian Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seats allocated based on percentage of total votes. | Seats awarded to candidates with majority votes in each district. |
| Representation | Reflects diverse political views proportionally. | Often favors dominant parties, less diverse. |
| Government Type | Encourages coalition governments. | Typically produces single-party majority governments. |
| Voter Influence | Votes contribute directly to party seat count. | Votes effective only if candidate wins majority. |
| Stability | Can lead to fragmented legislatures. | Usually offers stable governance. |
| Examples | Germany, Sweden, New Zealand. | United States, United Kingdom, Canada. |
Understanding Electoral Systems: Proportional vs Majoritarian
Proportional representation allocates seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring a more accurate reflection of voter preferences and promoting multiparty systems. Majoritarian representation awards seats to candidates with the most votes in single-member districts, often leading to a two-party dominated legislature and more stable governments. Understanding these electoral systems highlights the trade-offs between inclusiveness in proportional representation and decisiveness in majoritarian frameworks.
Key Principles of Proportional Representation
Proportional representation ensures that political parties gain seats in a legislature in direct proportion to the percentage of votes they receive, promoting fairer and more inclusive governance. This system emphasizes multi-member districts and party lists to reflect the diversity of voter preferences, reducing wasted votes and enhancing minority representation. The key principle is to align seat distribution with actual vote shares, fostering a more accurate and representative democracy compared to majoritarian systems.
Core Features of Majoritarian Representation
Majoritarian representation centers on single-member districts where candidates securing the most votes win, emphasizing direct accountability between elected officials and their constituents. This system typically produces majority governments, promoting political stability and clear policy direction. It often marginalizes smaller parties, concentrating power within dominant political groups and reducing the diversity of legislative representation.
Comparing Voter Representation and Inclusivity
Proportional representation systems enhance voter representation by ensuring that political parties receive seats in proportion to the votes they secure, fostering greater inclusivity for minority groups and diverse political opinions. Majoritarian representation often leads to a winner-takes-all outcome, which can marginalize smaller parties and reduce the diversity of voices in the legislature. Empirical studies show that proportional systems tend to increase voter turnout and satisfaction by providing broader representation and reducing the disparity between vote shares and seat allocation.
Impact on Political Party Development
Proportional representation systems encourage the growth of multiple political parties by allocating seats based on the percentage of votes received, fostering political diversity and coalition governments. Majoritarian representation tends to favor a two-party system, as the winner-takes-all approach marginalizes smaller parties and consolidates power among dominant political forces. This dynamic significantly shapes party strategies, candidate selection, and voter engagement, influencing political stability and governance outcomes.
Government Stability: Proportional vs Majoritarian
Proportional representation systems often foster government stability by encouraging coalition governments that represent diverse political interests, reducing abrupt policy shifts. Majoritarian representation, while simplifying governance through single-party dominance, can lead to volatile administrations susceptible to sudden changes due to electoral swings. Empirical studies indicate that proportional systems correlate with longer government durations and more consistent policy implementation compared to majoritarian systems.
Effects on Minority and Marginalized Groups
Proportional representation systems enhance minority and marginalized group inclusion by allocating seats in proportion to votes received, ensuring diverse political voices are reflected in legislatures. Majoritarian representation often leads to winner-takes-all outcomes, marginalizing smaller groups and limiting their political influence. This structural difference significantly impacts policy responsiveness and the protection of minority rights in democratic governance.
Electoral System Influence on Policy Outcomes
Proportional representation systems tend to produce more diverse legislatures, enabling a broader spectrum of political parties to influence policy outcomes, often leading to coalition governments that prioritize consensus-building. Majoritarian representation typically results in single-party governments with clearer policy mandates, but it can marginalize smaller groups and reduce policy diversity. The choice between these systems significantly impacts legislative behavior, policy stability, and the inclusiveness of political decision-making processes.
Global Examples of Proportional and Majoritarian Systems
Countries like Germany and New Zealand use proportional representation systems to allocate legislative seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, promoting multi-party inclusivity and coalition governments. In contrast, majoritarian systems dominate in the United States and the United Kingdom, where single-member districts elect representatives through a winner-takes-all approach, often leading to two-party dominance and stable majority governments. These global examples highlight how proportional systems tend to enhance political diversity, while majoritarian systems prioritize governmental stability and clear electoral mandates.
Reform Debates: Choosing the Right Representation Model
Reform debates in government often center on choosing between proportional representation and majoritarian representation, as each model impacts political diversity and governance stability differently. Proportional representation ensures minority groups gain legislative seats commensurate with their vote share, promoting inclusivity and pluralism. Majoritarian representation tends to favor larger parties, often leading to single-party majority governments and potentially stronger accountability but less political diversity.
proportional representation vs majoritarian representation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com