Primary elections allow registered voters to cast secret ballots to select a party's candidate, offering a straightforward and private voting process. Caucuses involve local gatherings where party members openly discuss and choose candidates, emphasizing community involvement and debate. Understanding the differences between primaries and caucuses is crucial for participating effectively in the government election process.
Table of Comparison
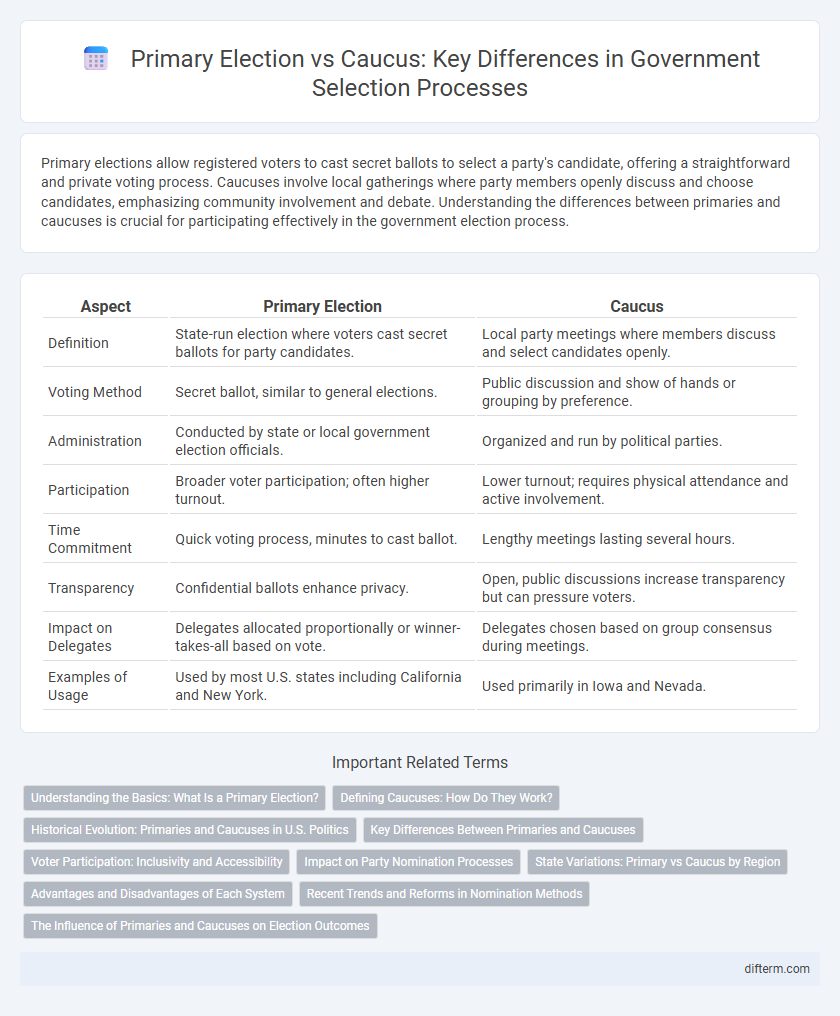
| Aspect | Primary Election | Caucus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | State-run election where voters cast secret ballots for party candidates. | Local party meetings where members discuss and select candidates openly. |
| Voting Method | Secret ballot, similar to general elections. | Public discussion and show of hands or grouping by preference. |
| Administration | Conducted by state or local government election officials. | Organized and run by political parties. |
| Participation | Broader voter participation; often higher turnout. | Lower turnout; requires physical attendance and active involvement. |
| Time Commitment | Quick voting process, minutes to cast ballot. | Lengthy meetings lasting several hours. |
| Transparency | Confidential ballots enhance privacy. | Open, public discussions increase transparency but can pressure voters. |
| Impact on Delegates | Delegates allocated proportionally or winner-takes-all based on vote. | Delegates chosen based on group consensus during meetings. |
| Examples of Usage | Used by most U.S. states including California and New York. | Used primarily in Iowa and Nevada. |
Understanding the Basics: What Is a Primary Election?
A primary election is a statewide voting process where registered voters cast secret ballots to select their preferred candidates for a party's nomination, directly influencing the general election lineup. Unlike a caucus, which involves in-person meetings and open discussions, primaries provide a more accessible and efficient method for broader voter participation. This system enhances democratic representation by allowing political parties to gauge public support in a structured and confidential manner.
Defining Caucuses: How Do They Work?
Caucuses are local gatherings where registered party members discuss and vote for their preferred candidates in a primary election system, emphasizing community involvement and deliberation. Unlike primary elections that use secret ballots, caucuses involve open voting and often require participants to physically align with their candidate's supporters, fostering direct engagement. This interactive process influences delegate allocation and reflects grassroots support within political parties.
Historical Evolution: Primaries and Caucuses in U.S. Politics
The historical evolution of primaries and caucuses in U.S. politics reflects the gradual shift from party-controlled conventions to more democratized candidate selection processes. Primaries gained prominence in the early 20th century as states sought to empower voters directly, while caucuses, with roots in the early republic, traditionally involved party insiders deliberating to choose nominees. Over time, states have increasingly favored primaries to enhance voter participation and transparency, though caucuses persist in some regions due to their grassroots engagement and party organizational benefits.
Key Differences Between Primaries and Caucuses
Primaries are state-run elections where registered voters cast secret ballots for their preferred candidate, ensuring a straightforward and private voting process. Caucuses are party-organized meetings where voters openly discuss and physically align with candidates, emphasizing community engagement and deliberation. Primaries typically have higher voter turnout due to easier access, while caucuses demand active participation and time commitment from voters.
Voter Participation: Inclusivity and Accessibility
Primary elections typically offer higher voter participation due to their straightforward voting process and broader accessibility through standardized polling locations and extended voting hours. Caucuses often experience lower turnout as they require in-person attendance at specific times, which can limit participation among individuals with time constraints, disabilities, or transportation challenges. Ensuring inclusivity and accessibility in the electoral process is critical for representative democracy, making primary elections a more effective mechanism for maximizing voter engagement.
Impact on Party Nomination Processes
Primary elections provide a more direct and inclusive method for voters to select party nominees by allowing a broader electorate to participate through secret ballots, increasing representation in the nomination process. Caucuses engage party members in local meetings to discuss and decide on candidates, fostering deeper party involvement but often limiting participation due to time and format constraints. The choice between primaries and caucuses significantly influences the momentum of candidates, delegate allocation methods, and overall party unity heading into general elections.
State Variations: Primary vs Caucus by Region
State election procedures vary significantly, with Western states predominantly using primary elections, while many Southern and Midwestern states favor caucuses for candidate selection. Primary elections offer a secret ballot system managed by state governments, promoting higher voter turnout. In contrast, caucuses involve local party meetings and public voting, which can lead to lower participation but greater party member engagement in rural and smaller communities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each System
Primary elections provide a more straightforward voting process, allowing for greater voter participation and anonymity, while caucuses encourage active political engagement but tend to have lower turnout due to their time-intensive nature. Primaries offer broader accessibility with standardized rules across states but can be more costly and less community-oriented compared to caucuses, which foster in-depth discussion and coalition-building among participants. The choice between primaries and caucuses impacts the representativeness of candidate selection, influencing party dynamics and electoral outcomes.
Recent Trends and Reforms in Nomination Methods
Recent reforms in nomination methods have seen a decline in caucus participation due to their less inclusive nature compared to primaries, which offer broader access and higher voter turnout. States are increasingly shifting from caucuses to primary elections to enhance transparency, reduce costs, and accommodate a wider electorate, reflecting a modernized approach to candidate selection. Data from the past decade indicates a steady increase in primary adoption, with over 30 states abandoning caucuses in favor of primaries by the 2024 election cycle.
The Influence of Primaries and Caucuses on Election Outcomes
Primaries and caucuses serve as critical mechanisms in the U.S. electoral process, shaping candidate viability and momentum by allocating delegate support essential for securing party nominations. Primaries tend to encourage broader voter participation through secret ballots, reflecting wider public preference, while caucuses engage party activists in in-depth candidate discussions, often benefiting well-organized campaigns with strong grassroots networks. The influence of these selection methods directly affects election outcomes by determining which candidates gain early endorsements and media attention, thereby impacting voter perceptions and subsequent general election dynamics.
primary election vs caucus Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com