Parliamentary immunity protects legislators from legal actions related to their official duties, ensuring independent lawmaking without fear of arrest or prosecution. Executive privilege allows government executives to withhold certain communications from other branches to preserve confidential decision-making processes. These doctrines balance the separation of powers by safeguarding legislative independence while enabling the executive branch to maintain confidential and effective governance.
Table of Comparison
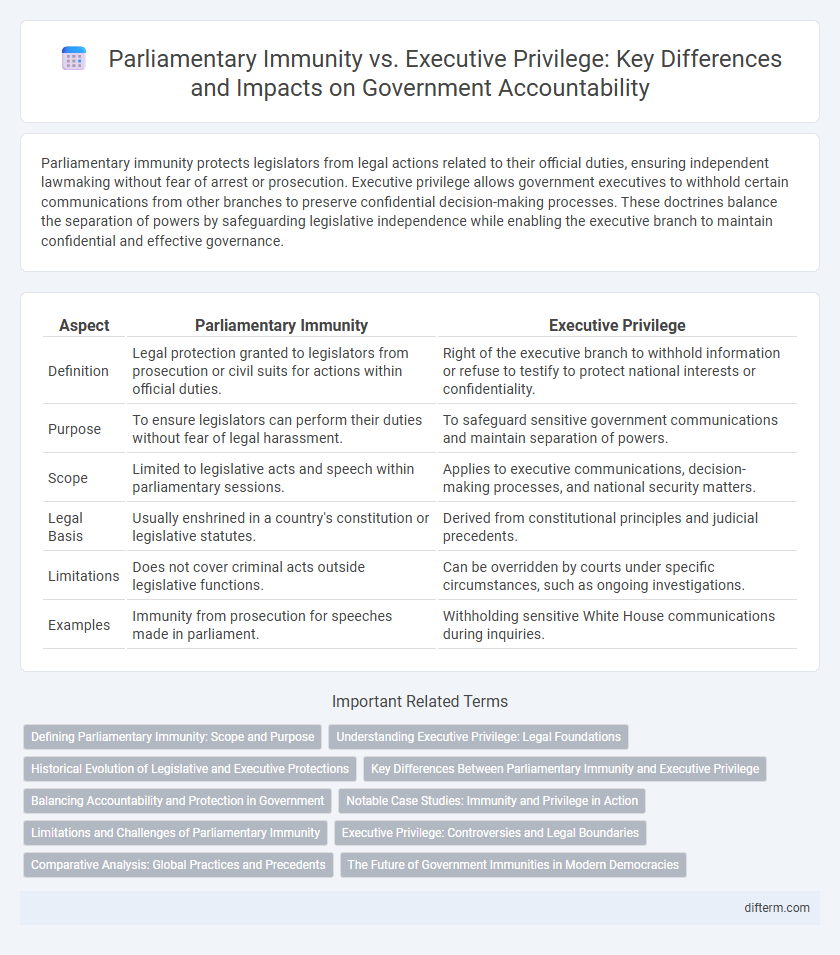
| Aspect | Parliamentary Immunity | Executive Privilege |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal protection granted to legislators from prosecution or civil suits for actions within official duties. | Right of the executive branch to withhold information or refuse to testify to protect national interests or confidentiality. |
| Purpose | To ensure legislators can perform their duties without fear of legal harassment. | To safeguard sensitive government communications and maintain separation of powers. |
| Scope | Limited to legislative acts and speech within parliamentary sessions. | Applies to executive communications, decision-making processes, and national security matters. |
| Legal Basis | Usually enshrined in a country's constitution or legislative statutes. | Derived from constitutional principles and judicial precedents. |
| Limitations | Does not cover criminal acts outside legislative functions. | Can be overridden by courts under specific circumstances, such as ongoing investigations. |
| Examples | Immunity from prosecution for speeches made in parliament. | Withholding sensitive White House communications during inquiries. |
Defining Parliamentary Immunity: Scope and Purpose
Parliamentary immunity protects legislators from legal actions related to their official duties, ensuring independence and free debate within legislative functions. It covers actions such as speeches, votes, and other parliamentary activities, preventing prosecution or civil liability during their term. This immunity is fundamental to maintaining legislative autonomy and safeguarding democratic processes by allowing legislators to perform their roles without external interference.
Understanding Executive Privilege: Legal Foundations
Executive privilege is a constitutional doctrine allowing the President and high-level executive branch officials to withhold information from Congress, the courts, or the public to protect sensitive communications and national security. Rooted in the separation of powers, its legal foundations trace back to landmark Supreme Court cases such as United States v. Nixon (1974), which acknowledged executive privilege but limited its scope in the context of criminal investigations. This privilege maintains executive branch confidentiality, safeguarding candid advice and decision-making essential for effective governance while balancing transparency and accountability.
Historical Evolution of Legislative and Executive Protections
Parliamentary immunity originated in medieval England to ensure legislators could perform duties free from royal interference, evolving through the centuries to protect speech and actions within parliamentary proceedings. Executive privilege emerged in the 19th century, primarily in the United States, as a means for the executive branch to withhold information to preserve confidential communications and national security. Both protections reflect a balance of power between branches of government, shaped by historical conflicts and judicial interpretations that aimed to safeguard institutional functions while preventing abuse of power.
Key Differences Between Parliamentary Immunity and Executive Privilege
Parliamentary immunity protects legislators from legal prosecution or civil liability for actions and statements made during official legislative activities, ensuring independence in lawmaking and debate. Executive privilege allows the President and high-level executive officials to withhold information or refuse testimony to protect sensitive decision-making processes and national security interests. The key difference lies in parliamentary immunity safeguarding legislative independence, while executive privilege emphasizes confidentiality within the executive branch.
Balancing Accountability and Protection in Government
Parliamentary immunity safeguards legislators from legal actions that could impede their legislative functions, ensuring independent lawmaking and robust debate. Executive privilege protects confidential communications within the executive branch, preserving candid advice crucial for national security and effective governance. Striking a balance between these doctrines is essential to uphold government accountability while protecting institutional integrity and separation of powers.
Notable Case Studies: Immunity and Privilege in Action
In the landmark case of United States v. Nixon (1974), the Supreme Court limited executive privilege, emphasizing that it cannot be used to obstruct justice, effectively balancing presidential confidentiality against judicial process. Conversely, in Powell v. McCormack (1969), the Court upheld parliamentary immunity by ruling that Congress could not exclude a duly elected member, reinforcing legislative independence from executive interference. These cases illustrate the nuanced boundaries and practical implications of immunity and privilege within the US government framework.
Limitations and Challenges of Parliamentary Immunity
Parliamentary immunity protects legislators from legal actions related to their official duties, but its limitations become evident when immunity obstructs investigations into corruption or criminal behavior. Challenges arise as courts often struggle to balance legislative independence with accountability, leading to potential abuses of power and impunity. Furthermore, some democratic systems impose restrictions to lift immunity in cases of serious offenses, yet political influence frequently complicates this process.
Executive Privilege: Controversies and Legal Boundaries
Executive privilege protects confidential communications within the executive branch to preserve national security and the separation of powers, yet it faces controversies regarding potential abuses of power and lack of transparency. Legal boundaries of executive privilege are defined by landmark Supreme Court cases such as United States v. Nixon, which limited its scope when it conflicts with the need for evidence in criminal investigations. Ongoing debates surround the balance between executive confidentiality and congressional oversight, especially in contexts of government accountability and checks on presidential power.
Comparative Analysis: Global Practices and Precedents
Parliamentary immunity protects legislators from legal actions related to their official duties, ensuring independent legislative functions, while executive privilege allows executive branch officials to withhold information to preserve confidential communications. Globally, parliamentary immunity is widespread in democratic systems, with variations in scope and duration, such as broad protections in France and immunity waivers in Germany. Executive privilege differs significantly, with the United States establishing strong precedent since U.S. v. Nixon, whereas countries like the UK adopt narrower interpretations focused on national security and cabinet confidentiality.
The Future of Government Immunities in Modern Democracies
Parliamentary immunity and executive privilege serve distinct purposes in protecting legislative and executive branches, yet evolving demands for transparency and accountability challenge their traditional scope. Modern democracies are witnessing increased scrutiny and legal reforms aimed at balancing state officials' protections with public interest in combating corruption and abuse of power. Emerging frameworks emphasize clearer limits and judicial oversight to ensure that immunities do not undermine democratic governance and rule of law.
Parliamentary Immunity vs Executive Privilege Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com