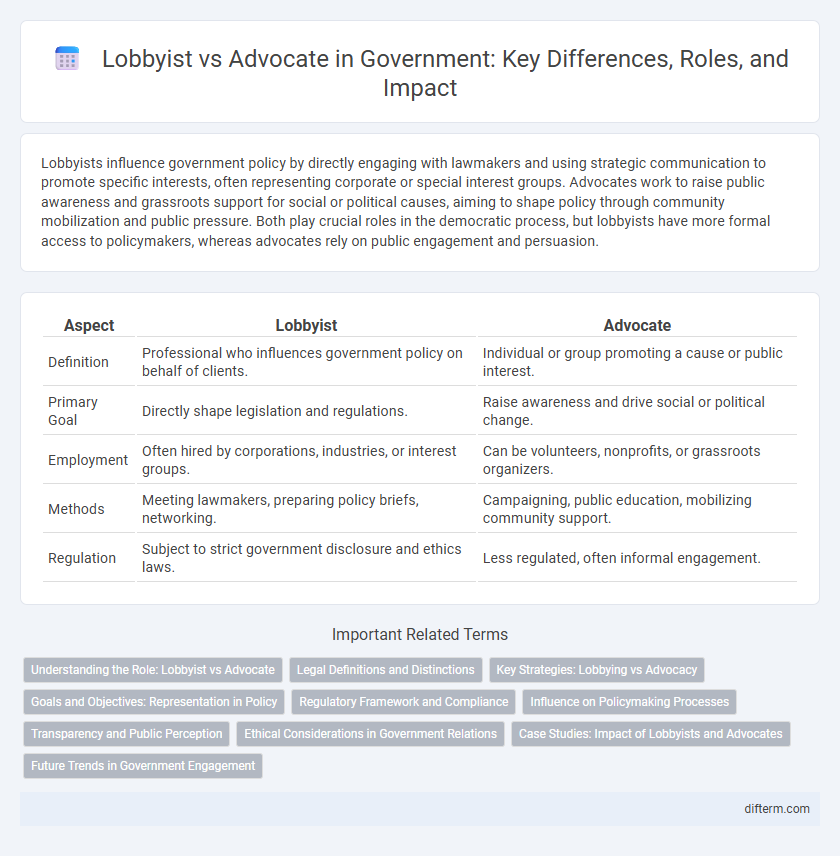
Lobbyists influence government policy by directly engaging with lawmakers and using strategic communication to promote specific interests, often representing corporate or special interest groups. Advocates work to raise public awareness and grassroots support for social or political causes, aiming to shape policy through community mobilization and public pressure. Both play crucial roles in the democratic process, but lobbyists have more formal access to policymakers, whereas advocates rely on public engagement and persuasion.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Lobbyist | Advocate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Professional who influences government policy on behalf of clients. | Individual or group promoting a cause or public interest. |
| Primary Goal | Directly shape legislation and regulations. | Raise awareness and drive social or political change. |
| Employment | Often hired by corporations, industries, or interest groups. | Can be volunteers, nonprofits, or grassroots organizers. |
| Methods | Meeting lawmakers, preparing policy briefs, networking. | Campaigning, public education, mobilizing community support. |
| Regulation | Subject to strict government disclosure and ethics laws. | Less regulated, often informal engagement. |
Understanding the Role: Lobbyist vs Advocate
Lobbyists are professionals hired to influence legislation and policy decisions on behalf of specific interest groups or corporations, using direct interaction with lawmakers and government officials. Advocates work to promote and support causes often driven by public interest or social change, mobilizing grassroots efforts and raising awareness among the general population. Understanding the distinct roles clarifies how government decisions are shaped through both strategic lobbying and community-driven advocacy.
Legal Definitions and Distinctions
Lobbyists are legally defined as individuals registered to influence government decisions through direct interaction with public officials, subject to strict disclosure and reporting requirements under laws such as the Lobbying Disclosure Act. Advocates operate more broadly by promoting causes or policies, often engaging the public or grassroots efforts without the mandatory registration and detailed lobbying activity reports required of lobbyists. The primary legal distinction hinges on the formal registration and regulated communication with policymakers that lobbyists must adhere to, while advocates enjoy greater flexibility in their methods and legal definitions.
Key Strategies: Lobbying vs Advocacy
Lobbyists employ targeted persuasion techniques such as direct meetings with policymakers, drafting legislation, and coalition-building to influence specific legislative outcomes. Advocates focus on mobilizing public opinion through grassroots campaigns, public education, and media outreach to create broad support for policy changes. Effective strategies for lobbyists hinge on insider access and relationship management, while advocates prioritize mobilizing constituents and raising awareness to drive systemic change.
Goals and Objectives: Representation in Policy
Lobbyists primarily aim to influence legislation and regulatory decisions by directly engaging with policymakers to secure favorable outcomes for their clients or interest groups. Advocates focus on representing the interests of a broader community or cause, often mobilizing public support and raising awareness to shape policy from the grassroots level. Both roles seek effective representation in policy, but lobbyists emphasize strategic negotiation with lawmakers, while advocates prioritize public persuasion and community empowerment.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
Lobbyists operate within a strict regulatory framework that mandates registration and disclosure of activities to ensure transparency and accountability in influencing government decisions. Advocates, while also subject to legal boundaries, focus more broadly on promoting public interest issues without necessarily engaging in formal lobbying activities. Compliance with these regulations is critical to maintain ethical standards and prevent conflicts of interest in government interactions.
Influence on Policymaking Processes
Lobbyists leverage formal channels and financial resources to shape legislation by directly engaging with lawmakers and regulatory agencies. Advocates mobilize community support and raise public awareness to influence policy decisions through grassroots efforts and public campaigns. Both play crucial roles in policymaking, with lobbyists focusing on strategic insider access and advocates driving external pressure for change.
Transparency and Public Perception
Lobbyists often face scrutiny due to opaque funding sources, which can undermine public trust in their influence on government policy. Advocates typically operate with greater transparency, openly representing specific causes or community interests, thereby fostering positive public perception. Enhancing disclosure requirements for lobbyists can improve transparency, aligning their activities with democratic accountability and reinforcing public confidence.
Ethical Considerations in Government Relations
Lobbyists and advocates play distinct roles in government relations, with ethical considerations centered on transparency, influence, and accountability. Lobbyists, often representing corporate or special interest groups, must disclose their activities and funding sources to prevent undue influence on policymakers. Advocates, typically working for public interest or nonprofit organizations, prioritize ethical engagement by promoting community needs and ensuring that their lobbying efforts align with democratic principles and public welfare.
Case Studies: Impact of Lobbyists and Advocates
Case studies reveal that lobbyists often secure legislative changes by leveraging established relationships and targeted financial contributions, as seen in the successful campaign for the Affordable Care Act's amendments. Advocates typically drive grassroots movements that influence public opinion and pressure policymakers, exemplified by environmental advocacy groups advancing renewable energy policies. Both roles shape government decisions differently, with lobbyists focusing on direct policy influence and advocates mobilizing broader community support.
Future Trends in Government Engagement
Lobbyists and advocates will increasingly harness data analytics and digital platforms to influence policymaking and public opinion more effectively. The integration of artificial intelligence in government engagement enables precise targeting of stakeholders and real-time monitoring of legislative developments. Emerging trends indicate a shift towards greater transparency and ethical standards to balance influence and accountability in governance.
lobbyist vs advocate Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com