Civil servants are employees specifically working within government departments, often holding permanent positions with clearly defined roles in executing government policies. Public servants encompass a broader category, including all individuals working in government-funded organizations and agencies that serve the public interest. Understanding the distinction helps clarify responsibilities and the scope of service within governmental structures.
Table of Comparison
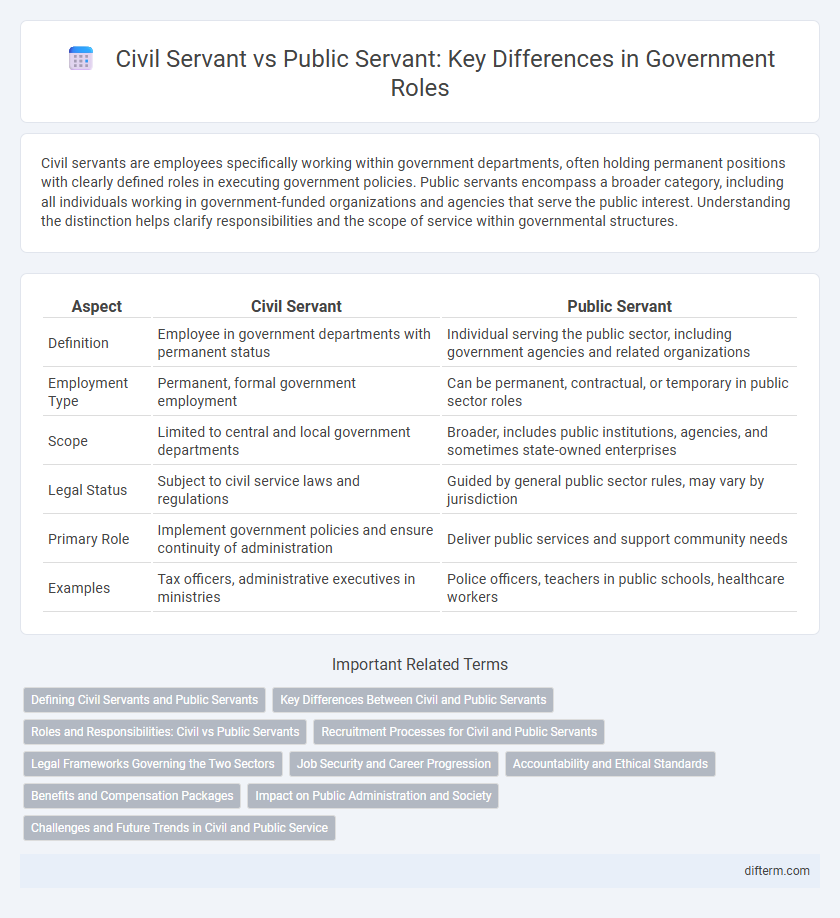
| Aspect | Civil Servant | Public Servant |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee in government departments with permanent status | Individual serving the public sector, including government agencies and related organizations |
| Employment Type | Permanent, formal government employment | Can be permanent, contractual, or temporary in public sector roles |
| Scope | Limited to central and local government departments | Broader, includes public institutions, agencies, and sometimes state-owned enterprises |
| Legal Status | Subject to civil service laws and regulations | Guided by general public sector rules, may vary by jurisdiction |
| Primary Role | Implement government policies and ensure continuity of administration | Deliver public services and support community needs |
| Examples | Tax officers, administrative executives in ministries | Police officers, teachers in public schools, healthcare workers |
Defining Civil Servants and Public Servants
Civil servants are government employees working within specific departments or agencies responsible for implementing public policies and delivering administrative functions. Public servants encompass a broader category, including civil servants as well as elected officials, public sector employees, and other individuals serving the public interest. Understanding the distinction clarifies roles, responsibilities, and the scope of authority within government institutions.
Key Differences Between Civil and Public Servants
Civil servants are government employees working in specific administrative departments, primarily responsible for implementing policies and maintaining public administration. Public servants encompass a broader category, including civil servants and other employees such as elected officials, police officers, and teachers, all serving the public interest. Key differences include scope of roles, job security, recruitment processes, and regulatory frameworks governing civil servants versus the more diverse public servant category.
Roles and Responsibilities: Civil vs Public Servants
Civil servants primarily work within government departments, implementing policies, managing public programs, and ensuring administrative continuity. Public servants encompass a broader category, including civil servants and elected officials, all dedicated to serving the public interest through policy development, service delivery, and regulatory enforcement. The distinct roles highlight civil servants' focus on execution and administration, while public servants emphasize governance and public accountability.
Recruitment Processes for Civil and Public Servants
Recruitment processes for civil servants typically involve rigorous examinations, merit-based evaluations, and strict eligibility criteria to ensure neutrality and competence in government administration. Public servant recruitment encompasses a broader spectrum, including local government roles and public sector positions, with varying requirements often tailored to the specific agency or department. Both processes emphasize transparency, equal opportunity, and adherence to legal frameworks to maintain integrity and public trust.
Legal Frameworks Governing the Two Sectors
Legal frameworks governing civil servants typically involve specific statutes and regulations outlining recruitment, duties, and disciplinary actions under public administration laws. Public servants, while encompassing civil servants, often operate under broader legal provisions that may include local government acts, public service commissions, and sector-specific legislation. Distinct legal codes ensure accountability and define roles within the administrative and political structures of government employment.
Job Security and Career Progression
Civil servants typically enjoy higher job security due to statutory protections and structured employment under government service rules, whereas public servants may include a broader range of workers with varying contractual terms that can affect job stability. Career progression for civil servants often follows formalized promotion pathways based on seniority, examinations, and performance assessments, ensuring systematic advancement. Public servants outside the civil service may experience less predictable career growth, influenced by organizational policies and funding availability.
Accountability and Ethical Standards
Civil servants operate within a structured government framework with strict accountability mechanisms ensuring adherence to ethical standards and legal obligations. Public servants encompass a broader category including elected officials and employees of government agencies, all held to high ethical expectations to maintain public trust. Both roles require transparency, responsibility, and commitment to serving the public interest without bias or corruption.
Benefits and Compensation Packages
Civil servants often receive structured benefits and compensation packages defined by specific government regulations, including pension plans, healthcare, and job security tailored to long-term employment. Public servants, while sometimes overlapping with civil servants, may have more varied benefits depending on the agency or public sector organization, encompassing performance bonuses and flexible work arrangements. Both categories typically enjoy comprehensive retirement plans and access to government-sponsored insurance programs, but civil servants generally benefit from more standardized and legally protected compensation frameworks.
Impact on Public Administration and Society
Civil servants are government employees who implement policies and manage public resources, ensuring efficient public administration and maintaining institutional continuity. Public servants encompass a broader category including both civil servants and elected officials, all dedicated to serving society's interests and promoting public welfare. The effectiveness and accountability of civil servants directly influence societal trust and the quality of government services, shaping public sector responsiveness and social stability.
Challenges and Future Trends in Civil and Public Service
Civil servants face challenges such as bureaucratic inefficiency, evolving regulatory demands, and the need for digital skill adaptation, which also impact public servants but with broader community engagement scopes. Increasing integration of artificial intelligence and data analytics is transforming decision-making processes, requiring continuous upskilling and ethical guidelines to address transparency and accountability. Future trends include mobile government services, enhanced citizen participation platforms, and emphasis on diversity and inclusion to improve public trust and service delivery.
civil servant vs public servant Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com