Wind energy harnesses the power of turbines to generate electricity with minimal land use, making it highly efficient in open and windy areas. Solar energy utilizes photovoltaic panels to convert sunlight into clean power, offering versatility and easy installation on rooftops and urban environments. Both renewable sources reduce carbon emissions significantly, but solar energy provides more consistent output in diverse locations, while wind energy excels during nighttime and stormy conditions.
Table of Comparison
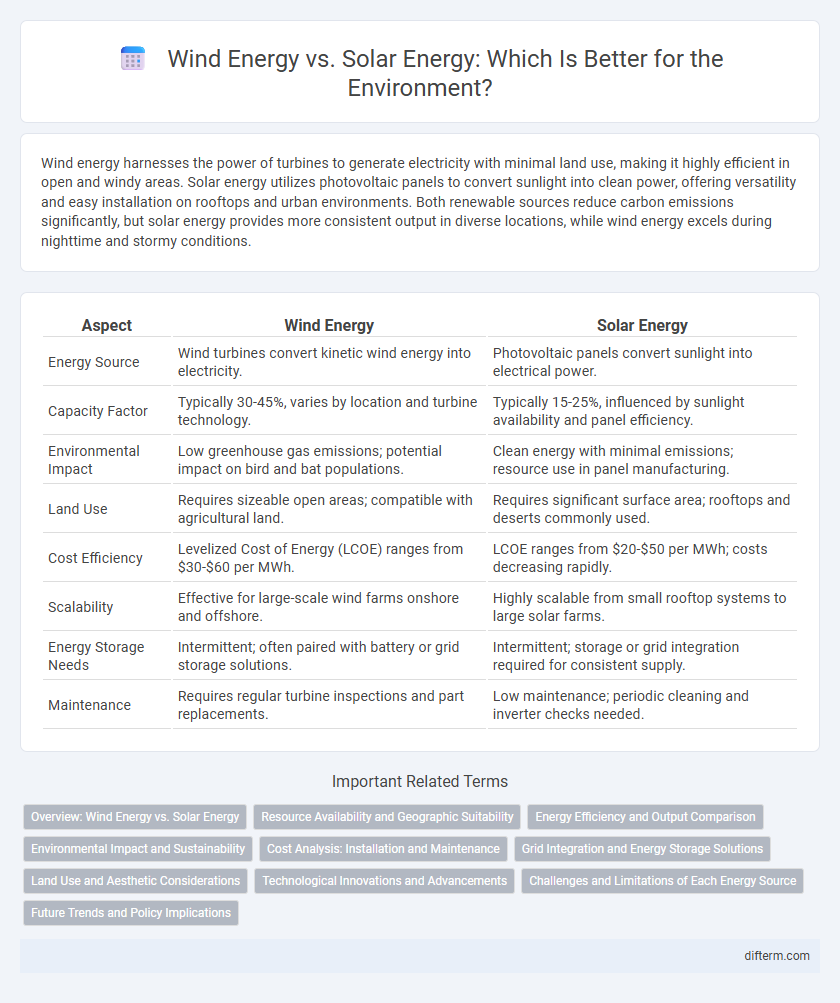
| Aspect | Wind Energy | Solar Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Wind turbines convert kinetic wind energy into electricity. | Photovoltaic panels convert sunlight into electrical power. |
| Capacity Factor | Typically 30-45%, varies by location and turbine technology. | Typically 15-25%, influenced by sunlight availability and panel efficiency. |
| Environmental Impact | Low greenhouse gas emissions; potential impact on bird and bat populations. | Clean energy with minimal emissions; resource use in panel manufacturing. |
| Land Use | Requires sizeable open areas; compatible with agricultural land. | Requires significant surface area; rooftops and deserts commonly used. |
| Cost Efficiency | Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) ranges from $30-$60 per MWh. | LCOE ranges from $20-$50 per MWh; costs decreasing rapidly. |
| Scalability | Effective for large-scale wind farms onshore and offshore. | Highly scalable from small rooftop systems to large solar farms. |
| Energy Storage Needs | Intermittent; often paired with battery or grid storage solutions. | Intermittent; storage or grid integration required for consistent supply. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular turbine inspections and part replacements. | Low maintenance; periodic cleaning and inverter checks needed. |
Overview: Wind Energy vs. Solar Energy
Wind energy harnesses kinetic power from air currents using turbines, offering high efficiency in areas with consistent wind patterns and producing substantial electricity with low land use impact. Solar energy captures sunlight through photovoltaic cells to convert it into electricity, excelling in regions with abundant sunshine and providing scalable options from small installations to large solar farms. Both renewable sources contribute significantly to reducing carbon emissions, with site selection and resource availability being key factors in determining the optimal energy solution.
Resource Availability and Geographic Suitability
Wind energy thrives in regions with consistent, strong winds such as coastal areas, open plains, and offshore locations, making it highly suitable for places like the Midwest United States and Northern Europe. Solar energy requires abundant sunlight, excelling in sunny climates such as deserts and equatorial zones, which is ideal for regions like the Southwestern United States and North Africa. Geographic suitability directly impacts the efficiency and feasibility of each energy source, with wind farms benefiting from open, windy landscapes and solar panels needing clear skies and minimal shading.
Energy Efficiency and Output Comparison
Wind energy generates electricity with an average capacity factor of 35-45%, yielding higher energy output per installed capacity compared to solar panels, which typically have a capacity factor of 15-25% due to day-night cycles and weather dependency. Wind turbines convert kinetic energy into electrical energy more efficiently, often reaching efficiencies above 40%, while solar panels operate at 15-20% efficiency due to photovoltaic limitations. Both renewable sources reduce carbon emissions significantly, but wind farms typically offer greater energy efficiency and higher consistent output in optimal locations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wind energy produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation and requires less water compared to solar energy, making it highly sustainable in arid regions. Solar energy, while generating some emissions during manufacturing, offers scalable installation on rooftops and degraded lands, reducing habitat disruption. Both sources reduce reliance on fossil fuels, but wind energy's land use can affect bird populations, whereas solar panel waste management remains a growing environmental challenge.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
Wind energy installation costs typically range from $1,200 to $1,700 per kilowatt, influenced by turbine size and site conditions, while solar energy systems average $1,000 to $3,000 per kilowatt depending on panel quality and installation complexity. Maintenance expenses for wind turbines can reach $40,000 annually for utility-scale projects due to moving parts and mechanical wear, whereas solar panels require minimal upkeep, mostly cleaning and inverter replacement with costs around $10 to $20 per kilowatt per year. Overall, wind energy may involve higher upfront and operational maintenance costs, but often delivers greater energy output per unit, while solar energy benefits from lower maintenance demands and flexible scalability.
Grid Integration and Energy Storage Solutions
Wind energy and solar energy both require advanced grid integration techniques to manage variable power output and maintain grid stability. Energy storage solutions such as lithium-ion batteries and pumped hydro storage play crucial roles in smoothing supply fluctuations and ensuring consistent electricity delivery. Efficient demand response systems and smart grid technologies enhance the integration of these renewable sources by optimizing load balancing and reducing curtailment.
Land Use and Aesthetic Considerations
Wind energy installations require significantly less land footprint compared to solar farms, as turbines can be spaced apart allowing for continued agricultural or natural land use beneath them. Solar energy systems, particularly utility-scale photovoltaic panels, demand extensive land area which can disrupt local ecosystems and limit land availability for other uses. Aesthetically, wind turbines often face opposition due to their visibility and perceived noise, whereas solar panels typically blend more seamlessly into the landscape, impacting visual appeal minimally.
Technological Innovations and Advancements
Wind energy benefits from innovations such as advanced turbine blade design and offshore floating platforms that increase efficiency and enable energy generation in deeper waters. Solar energy advances include high-efficiency photovoltaic cells, bifacial panels capturing sunlight from both sides, and perovskite materials promising cost reductions and enhanced performance. Both technologies integrate smart grid systems and energy storage solutions to improve reliability and grid stability.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Energy Source
Wind energy faces challenges such as intermittency, noise pollution, and threats to wildlife, particularly birds and bats, while requiring significant land use and suitable wind conditions that limit its geographic applicability. Solar energy struggles with efficiency losses during cloudy or nighttime conditions, high initial installation costs, and the environmental impact of manufacturing and disposing of photovoltaic panels. Both energy sources face storage and grid integration issues that affect their reliability and scalability in meeting continuous energy demands.
Future Trends and Policy Implications
Wind energy is poised for rapid expansion due to technological advancements in turbine efficiency and offshore installations, supported by evolving policy frameworks favoring large-scale renewable infrastructure. Solar energy continues to benefit from declining photovoltaic costs and increasing integration with smart grid technologies, prompting governments to implement incentives and regulatory reforms to boost decentralized energy production. Future trends indicate a convergence of wind and solar in hybrid systems, driving policies toward flexible, resilient energy grids to meet ambitious carbon neutrality targets.
Wind energy vs Solar energy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com