Organic farming promotes environmental sustainability by avoiding synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which helps preserve soil health and biodiversity. Conventional farming often relies on chemical inputs that can lead to soil degradation and water pollution. Choosing organic methods reduces the environmental footprint and supports healthier ecosystems for pets and humans alike.
Table of Comparison
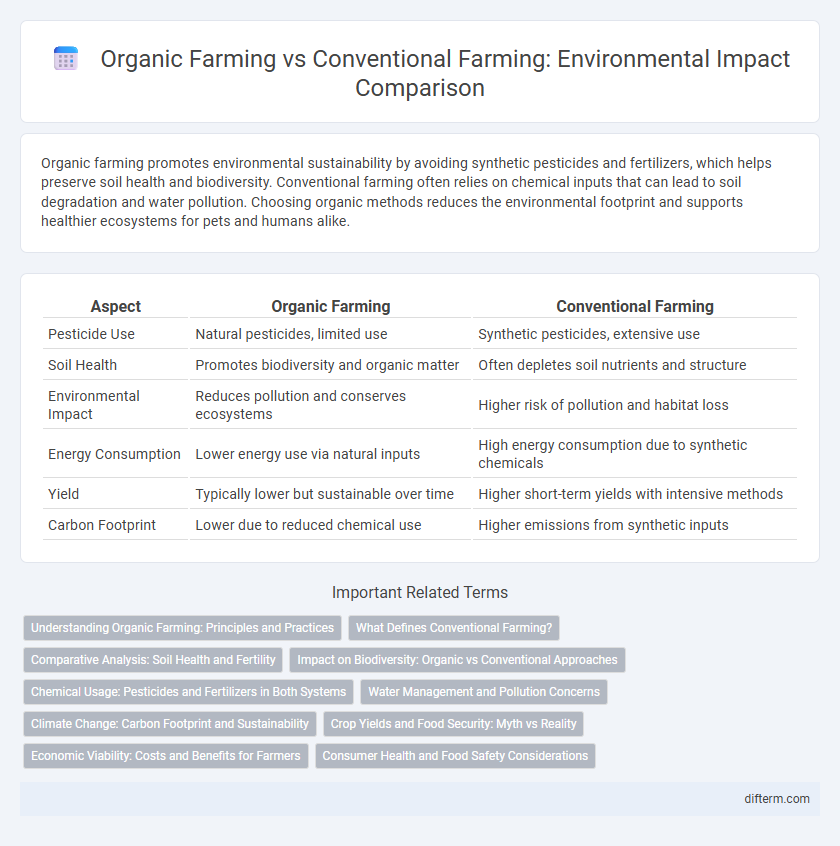
| Aspect | Organic Farming | Conventional Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Pesticide Use | Natural pesticides, limited use | Synthetic pesticides, extensive use |
| Soil Health | Promotes biodiversity and organic matter | Often depletes soil nutrients and structure |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces pollution and conserves ecosystems | Higher risk of pollution and habitat loss |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy use via natural inputs | High energy consumption due to synthetic chemicals |
| Yield | Typically lower but sustainable over time | Higher short-term yields with intensive methods |
| Carbon Footprint | Lower due to reduced chemical use | Higher emissions from synthetic inputs |
Understanding Organic Farming: Principles and Practices
Organic farming emphasizes soil health through natural processes, avoiding synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms. It prioritizes crop rotation, composting, and biological pest control to maintain ecological balance and enhance biodiversity. These practices contribute to sustainable agriculture by improving soil fertility and reducing environmental pollution.
What Defines Conventional Farming?
Conventional farming primarily relies on synthetic chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) to maximize crop yields and control pests. It often involves monocropping, intensive tillage, and extensive use of fossil fuels, which can contribute to soil degradation, water pollution, and loss of biodiversity. These practices contrast with organic farming methods that emphasize natural inputs, crop rotation, and sustainable land management.
Comparative Analysis: Soil Health and Fertility
Organic farming enhances soil health by increasing microbial diversity and organic matter content, which improves nutrient cycling and soil structure. Conventional farming often relies on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, leading to depletion of soil organic matter and reduced microbial activity over time. Studies show organic practices promote long-term soil fertility and resilience against erosion compared to conventional methods.
Impact on Biodiversity: Organic vs Conventional Approaches
Organic farming enhances biodiversity by promoting natural habitats through diverse crop rotations and reduced chemical inputs, fostering healthier ecosystems. Conventional farming often leads to habitat loss and soil degradation due to intensive monoculture practices and widespread pesticide use, negatively affecting species diversity. Studies reveal organic farms can support up to 30% more species, highlighting their critical role in conserving agricultural biodiversity.
Chemical Usage: Pesticides and Fertilizers in Both Systems
Organic farming minimizes chemical usage by relying on natural pesticides and compost-based fertilizers, promoting soil health and biodiversity. Conventional farming often depends heavily on synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers, which can lead to soil degradation and water contamination. These differences in chemical management directly impact environmental sustainability and ecosystem balance.
Water Management and Pollution Concerns
Organic farming employs natural water conservation techniques such as mulching and cover cropping, significantly reducing runoff and enhancing soil moisture retention compared to conventional farming. Conventional farming often relies on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides that contribute to water pollution through nutrient leaching and chemical runoff. Studies show organic systems decrease water contamination risks by minimizing agrochemical inputs, promoting healthier aquatic ecosystems and sustainable water management.
Climate Change: Carbon Footprint and Sustainability
Organic farming significantly reduces carbon footprint by eliminating synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional farming. Practices like crop rotation and composting enhance soil carbon sequestration, promoting long-term sustainability and resilience against climate change. Conversely, conventional farming often relies on fossil-fuel-based inputs and intensive tillage, contributing to higher emissions and soil degradation.
Crop Yields and Food Security: Myth vs Reality
Organic farming typically produces lower crop yields compared to conventional farming, with studies indicating a yield gap averaging 19-25%. Despite lower productivity, organic methods enhance soil health and biodiversity, offering long-term sustainability benefits crucial for food security. The perceived trade-off between organic farming and food security is a myth, as integrated approaches can balance yield demands with environmental stewardship.
Economic Viability: Costs and Benefits for Farmers
Organic farming often involves higher initial costs due to certification, organic seeds, and labor-intensive practices but can yield premium prices for crops, enhancing long-term profitability. Conventional farming benefits from established supply chains and subsidized inputs like synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, reducing short-term expenses yet facing market volatility and regulatory pressures. The economic viability for farmers depends on factors such as market demand for organic products, input cost fluctuations, and access to financial incentives or government support programs.
Consumer Health and Food Safety Considerations
Organic farming minimizes pesticide residues and synthetic chemical exposure, enhancing consumer health by reducing risks of chronic illnesses linked to toxic substances. Conventional farming often relies on synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which can leave harmful residues on food, posing potential health hazards. Ensuring food safety in organic produce involves adherence to strict regulations that limit contamination and promote nutrient-rich food quality.
organic farming vs conventional farming Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com