Green marketing promotes environmentally friendly products and practices with genuine commitments to sustainability, while greenwashing involves misleading consumers by falsely portraying products or companies as eco-friendly. Distinguishing between the two requires careful evaluation of a company's transparency, certifications, and actual environmental impact. Consumers increasingly demand authentic green marketing to support brands that truly prioritize environmental responsibility.
Table of Comparison
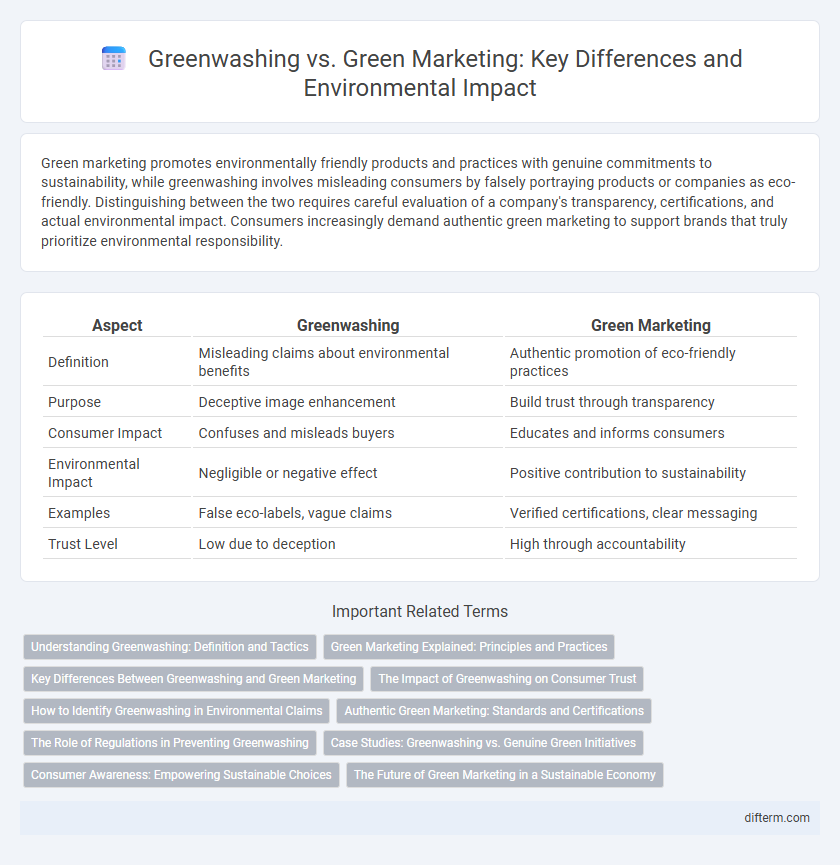
| Aspect | Greenwashing | Green Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Misleading claims about environmental benefits | Authentic promotion of eco-friendly practices |
| Purpose | Deceptive image enhancement | Build trust through transparency |
| Consumer Impact | Confuses and misleads buyers | Educates and informs consumers |
| Environmental Impact | Negligible or negative effect | Positive contribution to sustainability |
| Examples | False eco-labels, vague claims | Verified certifications, clear messaging |
| Trust Level | Low due to deception | High through accountability |
Understanding Greenwashing: Definition and Tactics
Greenwashing is a deceptive marketing practice where companies falsely portray their products or policies as environmentally friendly, misleading consumers about their actual environmental impact. Common tactics include vague claims, hidden trade-offs, and irrelevant certifications that create an illusion of sustainability without substantial action. Recognizing greenwashing involves scrutinizing claims for transparency, verifying third-party certifications, and assessing the company's overall environmental commitment beyond marketing messages.
Green Marketing Explained: Principles and Practices
Green marketing emphasizes authentic communication about a company's sustainable practices, products, and environmental initiatives, differentiating itself from greenwashing by ensuring transparency and verifiable claims. Key principles include promoting eco-friendly materials, reducing carbon footprints, and engaging consumers through credible certifications and clear messaging. Effective green marketing practices build consumer trust, foster brand loyalty, and contribute to broader environmental responsibility by aligning business operations with sustainability goals.
Key Differences Between Greenwashing and Green Marketing
Greenwashing involves misleading claims about a product's environmental benefits to create a false impression of sustainability, often lacking third-party verification or transparent data. In contrast, green marketing emphasizes genuine eco-friendly practices, backed by verifiable certifications, transparent supply chain information, and measurable environmental impact reductions. Key differences include authenticity, consumer trust, regulatory compliance, and the long-term commitment to sustainability goals.
The Impact of Greenwashing on Consumer Trust
Greenwashing significantly erodes consumer trust by misleading buyers about a company's environmental practices and sustainability claims. Studies reveal that when consumers detect false or exaggerated green marketing, their skepticism toward not only the brand but the entire industry intensifies, reducing the effectiveness of genuine environmental initiatives. Transparency and verified eco-labels are essential to restore confidence and ensure that green marketing drives positive environmental impact rather than deception.
How to Identify Greenwashing in Environmental Claims
Identifying greenwashing in environmental claims requires scrutinizing vague language, such as excessive use of terms like "eco-friendly" without supporting evidence or certifications. Consumers should look for credible third-party labels and transparent information about the product's entire lifecycle, including sourcing, manufacturing, and disposal practices. Misleading visuals or claims that exaggerate environmental benefits often indicate greenwashing tactics designed to exploit growing demand for sustainable products.
Authentic Green Marketing: Standards and Certifications
Authentic green marketing relies on verified standards and certifications such as LEED, Fair Trade, and USDA Organic to ensure environmental claims are credible and transparent. These certifications help distinguish genuine sustainable practices from greenwashing by providing third-party validation and measurable criteria for eco-friendly products. Companies adhering to recognized environmental standards build consumer trust and promote accountability in their green marketing efforts.
The Role of Regulations in Preventing Greenwashing
Effective regulations play a critical role in differentiating genuine green marketing from deceptive greenwashing by enforcing transparency and accuracy in environmental claims. Regulatory frameworks such as the Federal Trade Commission's Green Guides require companies to substantiate their sustainability assertions with credible evidence, reducing misleading eco-friendly messaging. Strong enforcement mechanisms and standardized guidelines foster consumer trust and promote authentic corporate environmental responsibility.
Case Studies: Greenwashing vs. Genuine Green Initiatives
Case studies reveal that greenwashing often involves misleading claims without verifiable data, as seen in the Volkswagen emissions scandal where marketing falsely portrayed environmental responsibility. Genuine green initiatives, exemplified by Patagonia's transparent supply chain and commitment to sustainable materials, provide measurable environmental benefits. Analyzing these cases highlights the importance of third-party certifications like B Corp and LEED in distinguishing authentic sustainability efforts from deceptive practices.
Consumer Awareness: Empowering Sustainable Choices
Consumer awareness plays a crucial role in distinguishing genuine green marketing from deceptive greenwashing practices. Transparent communication about sustainable product attributes enables consumers to make informed choices that support environmental responsibility. Enhanced verification standards and eco-labeling certifications further empower buyers to identify truly eco-friendly products amidst misleading claims.
The Future of Green Marketing in a Sustainable Economy
Green marketing is rapidly evolving to emphasize transparency, authentic environmental impact, and measurable sustainability goals, steering clear of greenwashing practices that mislead consumers about a company's eco-friendly efforts. Advances in technology and increased consumer demand for accountability drive businesses to adopt genuine sustainable practices, integrating circular economy principles and carbon footprint reduction strategies. The future of green marketing hinges on verified eco-labels, stakeholder engagement, and regulatory frameworks that promote real environmental benefits over superficial green claims.
greenwashing vs green marketing Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com