Cradle-to-cradle design emphasizes creating products that can be fully recycled or safely composted, promoting a circular lifecycle that minimizes environmental impact. In contrast, cradle-to-grave follows a linear path from resource extraction to disposal, often leading to increased waste and pollution. Adopting cradle-to-cradle principles in pet products reduces landfill waste and supports sustainable resource use, benefiting both pets and the planet.
Table of Comparison
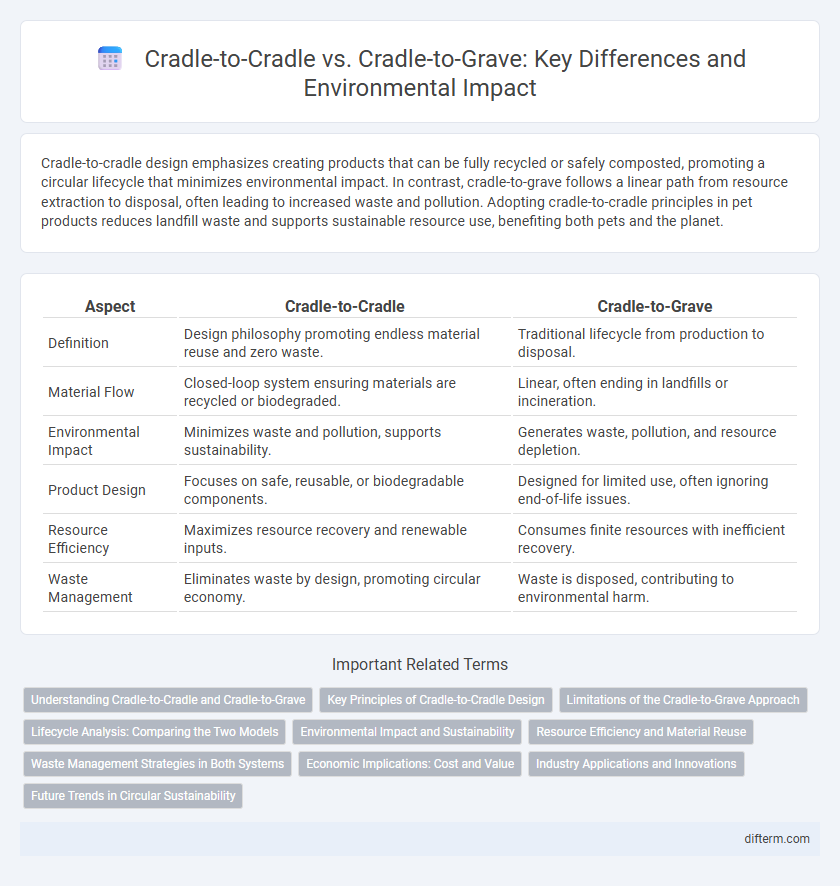
| Aspect | Cradle-to-Cradle | Cradle-to-Grave |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Design philosophy promoting endless material reuse and zero waste. | Traditional lifecycle from production to disposal. |
| Material Flow | Closed-loop system ensuring materials are recycled or biodegraded. | Linear, often ending in landfills or incineration. |
| Environmental Impact | Minimizes waste and pollution, supports sustainability. | Generates waste, pollution, and resource depletion. |
| Product Design | Focuses on safe, reusable, or biodegradable components. | Designed for limited use, often ignoring end-of-life issues. |
| Resource Efficiency | Maximizes resource recovery and renewable inputs. | Consumes finite resources with inefficient recovery. |
| Waste Management | Eliminates waste by design, promoting circular economy. | Waste is disposed, contributing to environmental harm. |
Understanding Cradle-to-Cradle and Cradle-to-Grave
Cradle-to-cradle design emphasizes creating products with materials that can be fully recycled or safely returned to the environment, promoting a circular economy and reducing waste. In contrast, cradle-to-grave approaches involve products ending in landfill or incineration, contributing to environmental pollution and resource depletion. Understanding these concepts highlights the shift toward sustainable product lifecycle management and zero-waste strategies.
Key Principles of Cradle-to-Cradle Design
Cradle-to-cradle design emphasizes circularity by creating products with materials that can be perpetually reused or safely returned to the environment, eliminating waste entirely. Key principles include using non-toxic, biodegradable, or fully recyclable materials, employing renewable energy throughout production, and designing for easy disassembly and material recovery at the end of a product's life cycle. This approach contrasts with cradle-to-grave models, which typically lead to resource depletion and landfill accumulation by ignoring end-of-life product impacts.
Limitations of the Cradle-to-Grave Approach
The cradle-to-grave approach often leads to increased environmental degradation due to its linear process of production, use, and disposal, which generates substantial waste and resource depletion. This model fails to promote resource recovery or recycling, resulting in higher greenhouse gas emissions and landfill accumulation. In contrast, sustainable development requires shifting towards circular systems to minimize ecological footprints and conserve natural resources.
Lifecycle Analysis: Comparing the Two Models
Cradle-to-cradle lifecycle analysis emphasizes sustainable design by ensuring materials are perpetually reused, eliminating waste and minimizing environmental impact. In contrast, cradle-to-grave models track products from creation to disposal, often resulting in resource depletion and landfill accumulation. This comparison highlights cradle-to-cradle's advantage in promoting circular economy principles and reducing ecological footprints.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cradle-to-cradle design eliminates waste by promoting continuous reuse of materials, drastically reducing environmental impact and supporting circular economy principles. Cradle-to-grave models contribute to resource depletion and pollution through linear consumption and landfill disposal. By prioritizing closed-loop systems, cradle-to-cradle enhances sustainability and conserves natural ecosystems over traditional cradle-to-grave methods.
Resource Efficiency and Material Reuse
Cradle-to-cradle design prioritizes resource efficiency by ensuring materials are continuously reused in closed-loop systems, eliminating waste and reducing the need for virgin resources. Unlike cradle-to-grave processes that result in material degradation and landfill accumulation, cradle-to-cradle promotes circular economy principles, enhancing sustainable material recovery and recycling. This approach significantly lowers environmental impact by maximizing the lifespan and value of materials throughout multiple product lifecycles.
Waste Management Strategies in Both Systems
Cradle-to-cradle waste management emphasizes continuous material reuse, designing products for easy disassembly and recycling to eliminate landfill waste. Cradle-to-grave systems, by contrast, typically follow a linear path where waste is disposed of after use, often resulting in significant environmental impact through landfill accumulation. Optimizing circular waste management reduces resource extraction and pollution, supporting sustainable environmental stewardship.
Economic Implications: Cost and Value
Cradle-to-cradle design emphasizes circularity, reducing long-term costs by maximizing material reuse and minimizing waste disposal expenses, leading to enhanced economic value through sustainable resource management. Conversely, cradle-to-grave approaches incur higher costs associated with linear consumption, waste management, and environmental remediation. Integrating cradle-to-cradle strategies boosts corporate profitability by aligning product lifecycle with regenerative economic models and reducing dependence on finite raw materials.
Industry Applications and Innovations
Cradle-to-cradle principles drive industry innovations by promoting closed-loop manufacturing processes that minimize waste and enable materials to be fully recycled or repurposed, contrasting with cradle-to-grave models that often result in landfill accumulation. Key industries such as construction, textiles, and electronics are adopting cradle-to-cradle certifications to enhance sustainability, improve resource efficiency, and reduce environmental impact throughout product life cycles. These innovations facilitate the development of eco-friendly materials, modular designs, and advanced recycling technologies, fostering circular economies and reducing dependence on virgin resources.
Future Trends in Circular Sustainability
Cradle-to-cradle design revolutionizes circular sustainability by transforming materials into perpetually reusable resources, eliminating waste through regenerative cycles. Future trends emphasize integrating advanced biomaterials, smart manufacturing technologies, and closed-loop systems to extend product lifespans and minimize environmental impact. This shift from cradle-to-grave models promotes a restorative economy aligned with global climate goals and resource efficiency mandates.
cradle-to-cradle vs cradle-to-grave Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com