A conservation easement is a legal agreement that restricts land use to protect its environmental value, while a land trust is an organization that acquires and manages these easements or owns land for conservation purposes. Conservation easements provide landowners with a way to preserve their property's natural features without relinquishing ownership, whereas land trusts often facilitate long-term stewardship and monitoring. These tools work together to safeguard habitats, enhance biodiversity, and ensure sustainable land management for future generations.
Table of Comparison
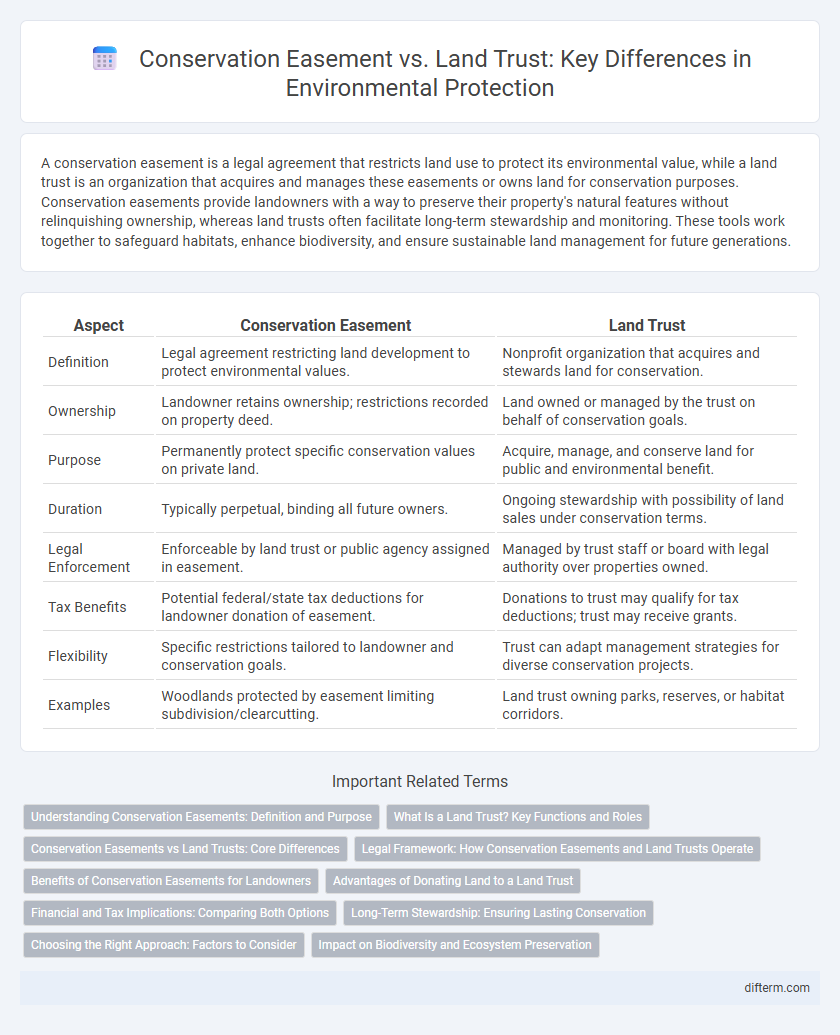
| Aspect | Conservation Easement | Land Trust |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal agreement restricting land development to protect environmental values. | Nonprofit organization that acquires and stewards land for conservation. |
| Ownership | Landowner retains ownership; restrictions recorded on property deed. | Land owned or managed by the trust on behalf of conservation goals. |
| Purpose | Permanently protect specific conservation values on private land. | Acquire, manage, and conserve land for public and environmental benefit. |
| Duration | Typically perpetual, binding all future owners. | Ongoing stewardship with possibility of land sales under conservation terms. |
| Legal Enforcement | Enforceable by land trust or public agency assigned in easement. | Managed by trust staff or board with legal authority over properties owned. |
| Tax Benefits | Potential federal/state tax deductions for landowner donation of easement. | Donations to trust may qualify for tax deductions; trust may receive grants. |
| Flexibility | Specific restrictions tailored to landowner and conservation goals. | Trust can adapt management strategies for diverse conservation projects. |
| Examples | Woodlands protected by easement limiting subdivision/clearcutting. | Land trust owning parks, reserves, or habitat corridors. |
Understanding Conservation Easements: Definition and Purpose
A conservation easement is a legally binding agreement that permanently limits land use to protect its conservation values, ensuring the preservation of natural resources and biodiversity. Land trusts are nonprofit organizations that acquire and manage conservation easements, working directly with landowners to safeguard ecologically important areas. Understanding the purpose of conservation easements highlights their role in preventing habitat destruction, maintaining open space, and enhancing environmental sustainability.
What Is a Land Trust? Key Functions and Roles
A land trust is a nonprofit organization dedicated to conserving land for environmental protection, recreation, or agriculture by acquiring land or conservation easements. Key functions include managing protected properties, ensuring long-term stewardship, and enforcing restrictions that prevent development or degradation. Land trusts play a crucial role in preserving biodiversity, maintaining natural habitats, and supporting sustainable land use practices.
Conservation Easements vs Land Trusts: Core Differences
Conservation easements are legally binding agreements that restrict land use to protect environmental values on private properties, while land trusts are nonprofit organizations that actively acquire and manage land or easements for conservation purposes. Easements focus on specific property-level restrictions without requiring ownership, whereas land trusts hold title to or stewardship responsibilities for conserved lands. These distinctions highlight how conservation easements provide a flexible tool for landowners, whereas land trusts offer sustained land management and long-term environmental protection.
Legal Framework: How Conservation Easements and Land Trusts Operate
Conservation easements are legally binding agreements that restrict land use to protect its conservation values while allowing private ownership, typically recorded with the property deed to run with the land. Land trusts are nonprofit organizations that acquire and hold these easements or land outright, ensuring long-term stewardship and legal enforcement. The legal framework involves state-specific statutes governing the creation, monitoring, and enforcement of easements, with land trusts acting as fiduciaries committed to upholding the conservation terms indefinitely.
Benefits of Conservation Easements for Landowners
Conservation easements provide landowners with significant benefits such as tax incentives, estate planning advantages, and the ability to retain private property ownership while permanently protecting natural resources. These legally binding agreements allow landowners to restrict development rights, ensuring long-term environmental conservation and preservation of wildlife habitats. By partnering with land trusts, landowners enhance ecosystem resilience and promote sustainable land use without sacrificing their property rights.
Advantages of Donating Land to a Land Trust
Donating land to a land trust provides significant tax benefits, including potential federal income tax deductions and reduced estate taxes, making it a financially advantageous conservation method. Land trusts offer ongoing stewardship, ensuring that donated land remains protected under legally binding conservation easements that restrict harmful development and preserve natural habitats. This method enhances biodiversity by maintaining ecosystems and provides public access opportunities, promoting environmental education and community engagement.
Financial and Tax Implications: Comparing Both Options
Conservation easements offer significant federal income tax deductions based on the appraised value of the easement donation, while also potentially reducing estate taxes by lowering the property's taxable value. Land trusts manage and enforce these easements, often providing additional benefits such as property tax reductions and eligibility for state-level tax incentives or grants. Choosing between a conservation easement and direct land trust acquisition requires analyzing upfront tax benefits, ongoing financial responsibilities, and potential long-term savings.
Long-Term Stewardship: Ensuring Lasting Conservation
Conservation easements provide legally binding agreements that restrict land use to preserve its ecological value, ensuring lasting protection for habitats and natural resources. Land trusts actively manage these easements and other conservation projects, offering long-term stewardship through monitoring, enforcement, and restoration efforts. Together, they create a sustainable framework for protecting biodiversity and preserving open space over generations.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a conservation easement and a land trust involves evaluating property ownership goals, long-term land use intentions, and the level of control retained by the landowner. Conservation easements allow landowners to restrict development while maintaining private ownership, offering tax benefits and ecological protections tailored to specific parcels. Land trusts provide organizational stewardship, often acquiring land or easements to ensure permanent conservation, making them ideal for those seeking active management and community involvement in preservation efforts.
Impact on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Preservation
Conservation easements legally restrict land development, directly safeguarding habitats and promoting biodiversity by maintaining natural ecosystems and preventing fragmentation. Land trusts, organizations that acquire and manage easements or properties, play a crucial role in long-term ecosystem preservation through active stewardship and monitoring. Both tools significantly enhance biodiversity conservation by ensuring protection against habitat loss and supporting ecological resilience.
conservation easement vs land trust Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com