Physical media offers a tangible collection experience with high-quality audio and video fidelity that digital formats may struggle to match. Digital media provides unparalleled convenience and instant access to vast libraries without the need for storage space. Entertainment enthusiasts often balance the reliability and collectible nature of physical media with the flexibility and portability of digital options.
Table of Comparison
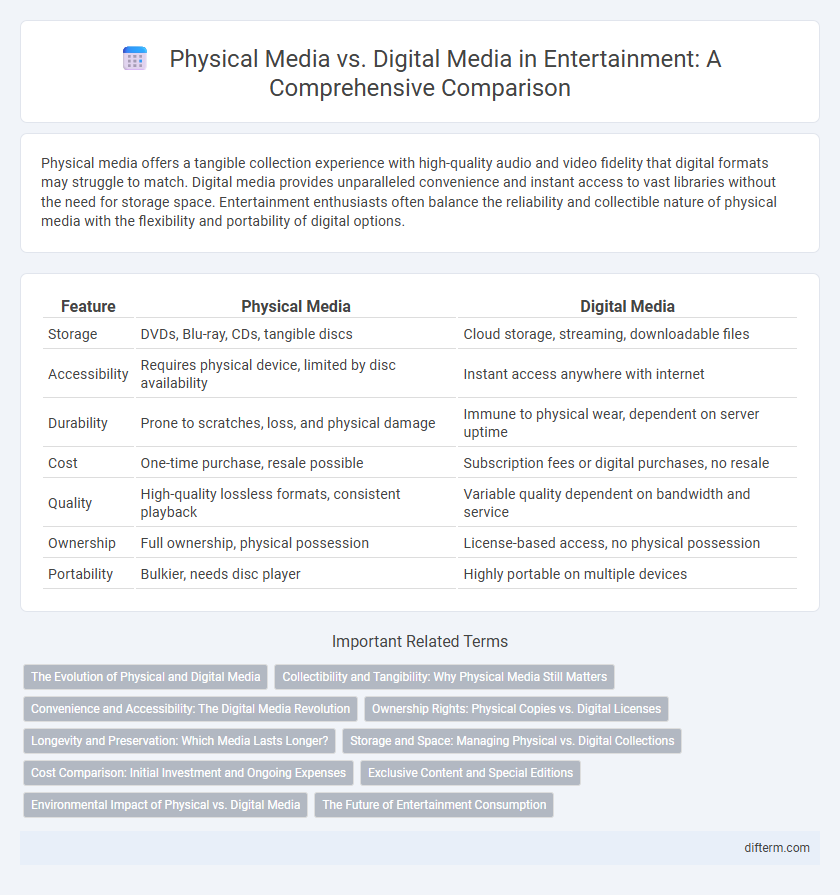
| Feature | Physical Media | Digital Media |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | DVDs, Blu-ray, CDs, tangible discs | Cloud storage, streaming, downloadable files |
| Accessibility | Requires physical device, limited by disc availability | Instant access anywhere with internet |
| Durability | Prone to scratches, loss, and physical damage | Immune to physical wear, dependent on server uptime |
| Cost | One-time purchase, resale possible | Subscription fees or digital purchases, no resale |
| Quality | High-quality lossless formats, consistent playback | Variable quality dependent on bandwidth and service |
| Ownership | Full ownership, physical possession | License-based access, no physical possession |
| Portability | Bulkier, needs disc player | Highly portable on multiple devices |
The Evolution of Physical and Digital Media
The evolution of physical and digital media in entertainment reflects a significant shift from tangible formats like DVDs, Blu-rays, and vinyl records to streaming platforms and downloadable content. Physical media offers collectible value and superior sound or video quality, while digital media provides unprecedented convenience, instant access, and extensive libraries through services such as Netflix, Spotify, and Apple Music. Advances in internet infrastructure and device compatibility continue to accelerate the dominance of digital media, reshaping consumer habits and content distribution models globally.
Collectibility and Tangibility: Why Physical Media Still Matters
Physical media offers a unique tangibility that digital formats cannot replicate, providing collectors with a sense of ownership and nostalgia through tangible items like vinyl records, Blu-rays, and special edition box sets. Limited edition releases, exclusive artwork, and packaging enhance collectibility, making physical media prized possessions for enthusiasts and investors alike. Despite the convenience of streaming, the physicality and rarity of these items sustain their cultural and monetary value in the entertainment market.
Convenience and Accessibility: The Digital Media Revolution
Digital media offers unprecedented convenience, enabling instant access to vast entertainment libraries anytime on smartphones, tablets, and smart TVs. Physical media like DVDs and Blu-rays require storage space and hardware, limiting accessibility compared to streaming platforms such as Netflix, Spotify, and Apple Music. The digital media revolution enhances user experience through personalized recommendations and offline download options, transforming how consumers engage with entertainment content.
Ownership Rights: Physical Copies vs. Digital Licenses
Physical copies of entertainment media provide tangible ownership, allowing consumers to use, lend, or resell the content without restrictions. Digital licenses, while convenient, often limit usage to specific devices or platforms and restrict the transfer or resale of purchased content. This distinction significantly impacts consumer rights, influencing long-term access and control over entertainment assets.
Longevity and Preservation: Which Media Lasts Longer?
Physical media such as vinyl records, CDs, and DVDs offer superior longevity and preservation compared to digital files, which are vulnerable to data corruption, format obsolescence, and accidental deletion. Archival-quality physical formats can remain intact for decades or even centuries when stored properly, while digital media require ongoing file migrations and hardware compatibility updates. Collectors and archivists often prefer physical media for long-term preservation due to its tangible durability and independence from digital infrastructure.
Storage and Space: Managing Physical vs. Digital Collections
Physical media requires ample storage space to accommodate discs, cases, and shelving, often leading to clutter in living areas. Digital media minimizes physical footprint by storing vast collections on hard drives or cloud services, enabling quick access without occupying physical space. Efficient management of digital libraries allows users to categorize and retrieve entertainment content effortlessly, contrasting with the manual organization demanded by physical collections.
Cost Comparison: Initial Investment and Ongoing Expenses
Physical media such as DVDs and Blu-rays require a higher initial investment for purchasing discs and players, while digital media platforms often have lower upfront costs through subscription models or individual downloads. Ongoing expenses for physical media include maintenance, storage, and potential damage replacement, whereas digital media incurs continuous subscription fees and data usage costs. Consumers should weigh the one-time purchase advantage of physical formats against the flexible, but recurring, expenses associated with digital media streaming services.
Exclusive Content and Special Editions
Exclusive content and special editions thrive on physical media, offering collectors unique packaging, bonus discs, and tangible extras that digital formats often lack. Limited edition releases, including signed covers and embossed cases, create a sense of rarity and value unattainable in streaming platforms. Physical media's ability to host high-fidelity audio and video along with exclusive artwork enhances the entertainment experience beyond standard digital offerings.
Environmental Impact of Physical vs. Digital Media
Physical media production, such as CDs, DVDs, and Blu-rays, generates significant carbon emissions due to resource extraction, manufacturing, and distribution processes. Digital media, while reducing physical waste, relies heavily on data centers and network infrastructure that consume large amounts of electricity, often sourced from non-renewable energy. Lifecycle assessments show that digital streaming's environmental footprint varies widely depending on user behavior and energy efficiency of data centers, but physical media generally results in higher direct material waste and energy use.
The Future of Entertainment Consumption
Physical media, including Blu-rays and vinyl records, continue to serve niche markets valuing tangibility and collectible ownership, but digital media platforms dominate with instant access, vast libraries, and personalized recommendations. Streaming services like Netflix, Spotify, and Disney+ leverage AI algorithms to tailor content, enhancing user engagement and driving subscription growth. Emerging technologies such as cloud gaming and augmented reality promise to further transform entertainment consumption by offering immersive, on-demand experiences without the limitations of physical storage.
physical media vs digital media Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com