Overdubbing replaces the original audio with a new voice track, making content accessible without requiring reading skills, while subtitling preserves the original dialogue and provides written translations for viewers to read. Both techniques enhance entertainment experiences by bridging language barriers, but subtitling maintains the authenticity of the original performance. Choosing between overdubbing and subtitling depends on audience preferences, content type, and desired engagement levels.
Table of Comparison
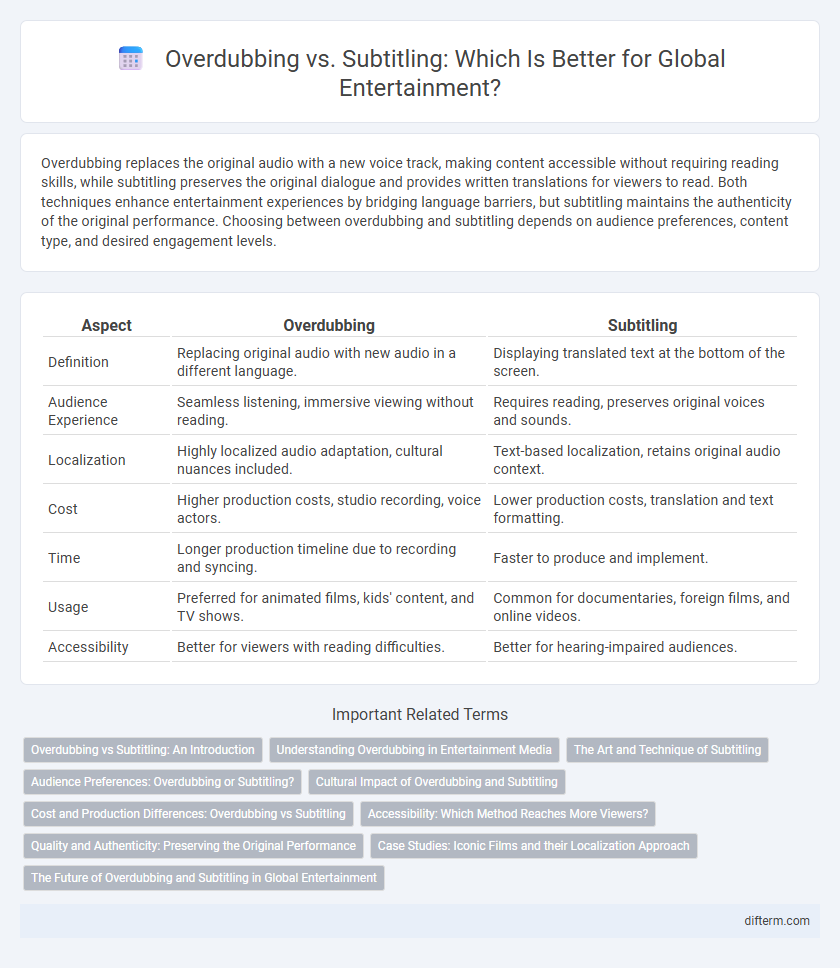
| Aspect | Overdubbing | Subtitling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Replacing original audio with new audio in a different language. | Displaying translated text at the bottom of the screen. |
| Audience Experience | Seamless listening, immersive viewing without reading. | Requires reading, preserves original voices and sounds. |
| Localization | Highly localized audio adaptation, cultural nuances included. | Text-based localization, retains original audio context. |
| Cost | Higher production costs, studio recording, voice actors. | Lower production costs, translation and text formatting. |
| Time | Longer production timeline due to recording and syncing. | Faster to produce and implement. |
| Usage | Preferred for animated films, kids' content, and TV shows. | Common for documentaries, foreign films, and online videos. |
| Accessibility | Better for viewers with reading difficulties. | Better for hearing-impaired audiences. |
Overdubbing vs Subtitling: An Introduction
Overdubbing replaces the original audio track with a new voice recording in the target language, enhancing viewer immersion by matching lip movements and emotional tone. Subtitling displays translated text at the bottom of the screen, preserving the original audio and allowing audiences to hear authentic dialogue while understanding the content. Both methods serve to localize films and TV shows but differ in audience preference, production cost, and cultural impact.
Understanding Overdubbing in Entertainment Media
Overdubbing in entertainment media involves replacing the original audio track, often dialogue, with a new recording in a different language or enhanced audio quality to improve viewer experience. This technique enhances emotional engagement by preserving lip-sync and natural character expressions, making foreign content more accessible without reading subtitles. Overdubbing is widely used in film, television, and video games to localize content while maintaining narrative immersion.
The Art and Technique of Subtitling
Subtitling is a precise art that involves synchronizing translated text with spoken dialogue to enhance viewer comprehension without distracting from visual elements. Unlike overdubbing, which replaces the original audio track, subtitling preserves the authentic voice performances while making content accessible to a wider audience. Effective subtitling requires mastery of timing, linguistic accuracy, and cultural adaptation to maintain narrative flow and emotional impact.
Audience Preferences: Overdubbing or Subtitling?
Audience preferences for overdubbing versus subtitling vary significantly by region and viewing habits, with European countries like Germany and Spain favoring overdubbing due to ease of comprehension, while Nordic countries and the Netherlands prefer subtitling to preserve original audio and language authenticity. Younger audiences increasingly opt for subtitling to improve language skills and enjoy performances as intended, whereas older viewers often find overdubbing less distracting. Market research indicates that platforms offering multiple audio and subtitle options cater better to diverse preferences, enhancing global content accessibility and viewer satisfaction.
Cultural Impact of Overdubbing and Subtitling
Overdubbing allows audiences to experience foreign films in their native language, fostering broader accessibility but sometimes causing a loss of original cultural nuances. Subtitling preserves the original audio, enabling viewers to engage directly with the source language and cultural expressions, which supports language learning and cultural authenticity. Both methods influence cultural perception, with overdubbing promoting mainstream assimilation and subtitling encouraging cross-cultural understanding and preservation.
Cost and Production Differences: Overdubbing vs Subtitling
Overdubbing involves replacing the original audio track with a new voice recording in the target language, resulting in higher production costs due to the need for voice actors, studio time, and sound engineering. Subtitling requires translating and timing text to appear on-screen, which is generally more cost-effective and faster to produce, but may demand skilled translators and precise synchronization. Studios prioritize overdubbing for immersive viewing experiences despite its higher budget, while subtitling suits projects with tighter financial and time constraints.
Accessibility: Which Method Reaches More Viewers?
Overdubbing enhances accessibility by enabling viewers with reading difficulties or visual impairments to enjoy content in their native language, broadening reach beyond literate audiences. Subtitling, while cost-effective and preserving original audio, primarily serves viewers who can read and hear simultaneously, limiting accessibility for younger audiences or those with cognitive challenges. Overall, overdubbing typically reaches a wider and more diverse audience by removing language and literacy barriers in entertainment media.
Quality and Authenticity: Preserving the Original Performance
Overdubbing alters the original vocal performance by replacing actors' voices, which can compromise the authenticity and emotional nuances of the film or series. Subtitling preserves the original audio, allowing viewers to experience the true tone, intonation, and performance quality, maintaining artistic integrity. High-quality subtitles also enhance accessibility while respecting the creator's original vision.
Case Studies: Iconic Films and their Localization Approach
Iconic films like "Parasite" utilized subtitling to preserve original audio nuances while conveying cultural context, enhancing global accessibility without altering performances. In contrast, "The Lion King" remake opted for overdubbing to target younger audiences, emphasizing character voices matching regional languages for immersive experience. These case studies demonstrate how localization choices impact emotional resonance and audience reach in diverse markets.
The Future of Overdubbing and Subtitling in Global Entertainment
The future of overdubbing and subtitling in global entertainment hinges on advancements in AI-driven voice synthesis and real-time translation technologies, offering more natural and immersive viewing experiences. Streaming platforms increasingly prioritize localized content, driving demand for high-quality overdubbing that preserves actor nuances alongside accurate subtitling for accessibility. Emerging hybrid models combining dynamic subtitles with adaptive dubbing solutions are set to revolutionize content consumption across diverse linguistic markets.
Overdubbing vs Subtitling Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com