A DJ specializes in selecting and mixing tracks to create a live, dynamic experience that energizes the crowd, emphasizing performance and crowd interaction. In contrast, a music producer crafts original sounds and compositions in the studio, focusing on sound design, arrangement, and recording techniques. Both roles contribute uniquely to the entertainment industry, shaping how audiences experience music through either live sets or recorded tracks.
Table of Comparison
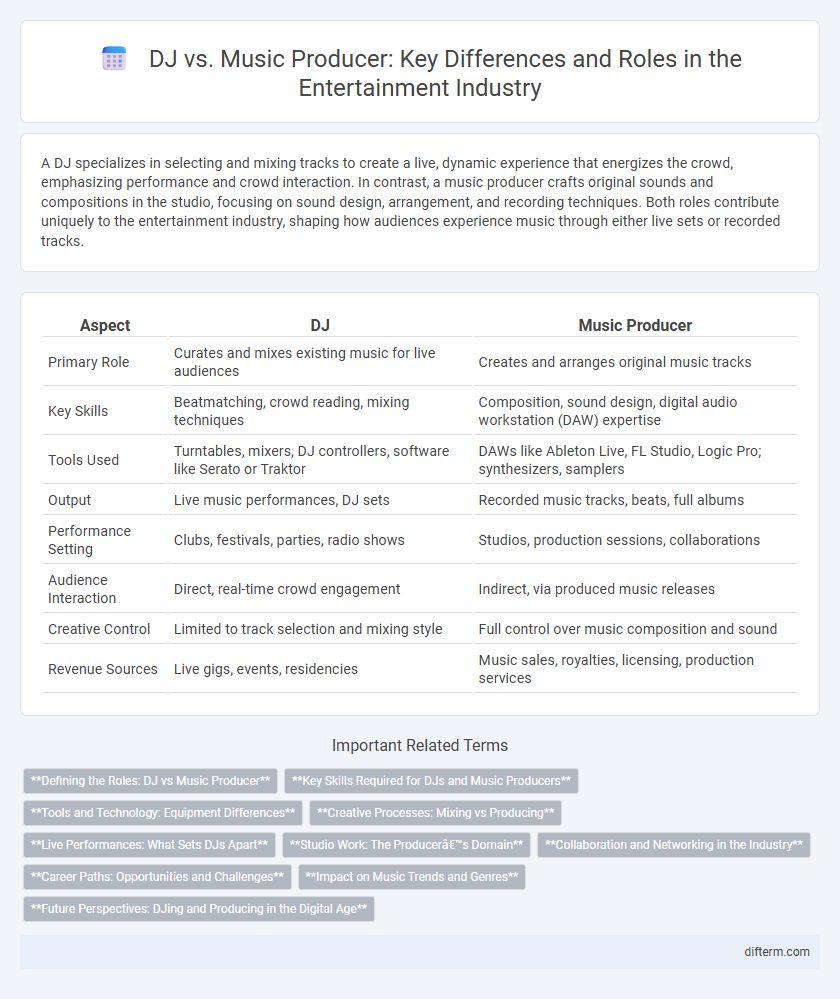
| Aspect | DJ | Music Producer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Curates and mixes existing music for live audiences | Creates and arranges original music tracks |
| Key Skills | Beatmatching, crowd reading, mixing techniques | Composition, sound design, digital audio workstation (DAW) expertise |
| Tools Used | Turntables, mixers, DJ controllers, software like Serato or Traktor | DAWs like Ableton Live, FL Studio, Logic Pro; synthesizers, samplers |
| Output | Live music performances, DJ sets | Recorded music tracks, beats, full albums |
| Performance Setting | Clubs, festivals, parties, radio shows | Studios, production sessions, collaborations |
| Audience Interaction | Direct, real-time crowd engagement | Indirect, via produced music releases |
| Creative Control | Limited to track selection and mixing style | Full control over music composition and sound |
| Revenue Sources | Live gigs, events, residencies | Music sales, royalties, licensing, production services |
Defining the Roles: DJ vs Music Producer
A DJ primarily selects, mixes, and manipulates pre-recorded tracks to create a live music experience tailored to their audience, often emphasizing crowd interaction and seamless transitions. In contrast, a music producer crafts original compositions or remixes, shaping the sound through technical skills like arranging, sound design, and audio engineering within a studio environment. Both roles demand creativity, but the DJ focuses on live performance dynamics while the producer centers on music creation and studio production.
Key Skills Required for DJs and Music Producers
DJs require skills in beatmatching, crowd reading, and live mixing to create seamless transitions and maintain energy on the dance floor, while music producers excel in sound design, digital audio workstation (DAW) proficiency, and arranging tracks to craft original compositions. Both roles demand a deep understanding of music theory, rhythm, and genre-specific trends to engage audiences effectively. Mastery of audio equipment and software enhances performance capabilities, with DJs focusing on turntables and controllers, and producers emphasizing synthesizers, samplers, and mixing consoles.
Tools and Technology: Equipment Differences
DJs primarily use mixers, turntables, CDJs, and software such as Serato or Rekordbox to blend and manipulate tracks live, emphasizing real-time control and crowd interaction. Music producers rely on digital audio workstations (DAWs) like Ableton Live, FL Studio, or Logic Pro, alongside MIDI controllers, synthesizers, and audio interfaces, focusing on creating, arranging, and refining original compositions. While DJs optimize hardware and software for performance, music producers prioritize production tools for sound design and mixing precision.
Creative Processes: Mixing vs Producing
DJs focus on the creative process of mixing by seamlessly blending tracks, manipulating sound effects, and reading the crowd to create a dynamic live experience. Music producers engage in producing by composing original melodies, arranging instrumentation, and meticulously crafting audio layers within a digital audio workstation (DAW). While DJs emphasize performance and real-time interaction, producers prioritize sound design and track development behind the scenes.
Live Performances: What Sets DJs Apart
DJs excel in live performances by skillfully blending tracks, reading the crowd, and creating seamless transitions that energize the audience in real time. Their ability to improvise and adapt sets based on the venue and crowd response distinguishes them from music producers, who primarily focus on studio creation. This dynamic interaction makes DJ performances unique and immersive experiences in the entertainment industry.
Studio Work: The Producer’s Domain
Music producers excel in studio work by crafting and manipulating sounds, arranging tracks, and applying advanced mixing techniques to create polished recordings. Their role involves extensive use of digital audio workstations (DAWs) like Ableton Live, Logic Pro, and FL Studio to shape the final sound. Unlike DJs, producers focus on original composition and sound design, laying the foundation for both recorded music and live performances.
Collaboration and Networking in the Industry
Collaboration and networking in the entertainment industry are crucial for both DJs and music producers to expand their creative reach and professional opportunities. DJs often connect with producers to remix tracks and create unique live sets, while producers rely on DJs to test and popularize their music in clubs and festivals. Building strong relationships within the industry enhances visibility, opens doors to joint projects, and fosters innovation across genres.
Career Paths: Opportunities and Challenges
DJ career paths emphasize live performance skills, crowd interaction, and playlist curation at clubs, festivals, and private events, offering immediate audience feedback but often requiring irregular schedules and travel. Music producers focus on music creation, sound engineering, and studio work, providing opportunities for songwriting royalties, collaborations with artists, and work in various genres, yet facing high competition and the need for continuous technical skill development. Both roles demand strong industry networking, adaptability to evolving music trends, and mastery of digital audio workstations (DAWs) to sustain long-term success.
Impact on Music Trends and Genres
DJs play a crucial role in shaping music trends by curating and popularizing tracks during live performances, directly influencing audience preferences and club culture. Music producers drive innovation by creating original sounds and experimenting with genre fusion, often setting new standards within the industry. Together, DJs and producers propel the evolution of music genres, blending creativity with audience engagement to shape the future of entertainment.
Future Perspectives: DJing and Producing in the Digital Age
DJing and music producing continue to evolve rapidly with advancements in digital technology, blending traditional skills with innovative software tools and AI-driven sound design. The future sees DJs integrating live remixing and immersive visuals while producers leverage cloud-based collaboration and algorithmic composition to create dynamic, genre-defying tracks. This digital transformation enhances creative possibilities, audience engagement, and the global reach of both disciplines in the entertainment industry.
DJ vs music producer Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com