Synchronous learning offers real-time interaction between students and instructors, enhancing immediate feedback and collaborative experiences, which can boost engagement and motivation. Asynchronous learning provides flexibility, allowing students to access materials and complete assignments at their own pace, accommodating diverse schedules and learning styles. Both methods have unique advantages that educators can blend to optimize student understanding and participation.
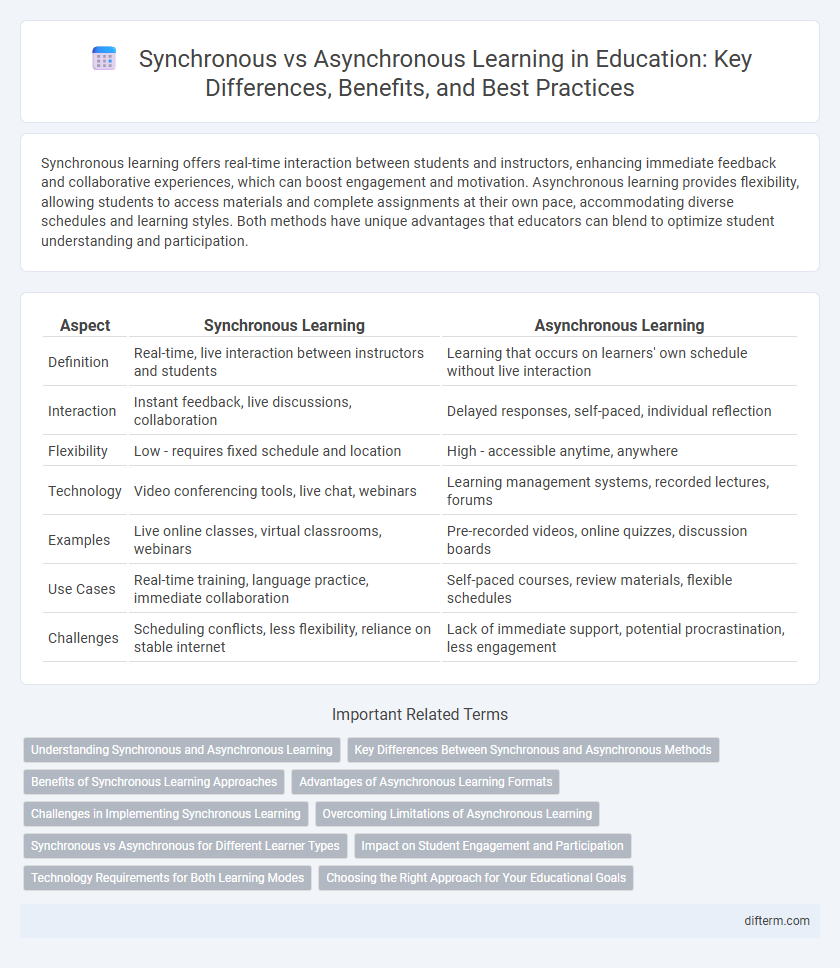
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Synchronous Learning | Asynchronous Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time, live interaction between instructors and students | Learning that occurs on learners' own schedule without live interaction |
| Interaction | Instant feedback, live discussions, collaboration | Delayed responses, self-paced, individual reflection |
| Flexibility | Low - requires fixed schedule and location | High - accessible anytime, anywhere |
| Technology | Video conferencing tools, live chat, webinars | Learning management systems, recorded lectures, forums |
| Examples | Live online classes, virtual classrooms, webinars | Pre-recorded videos, online quizzes, discussion boards |
| Use Cases | Real-time training, language practice, immediate collaboration | Self-paced courses, review materials, flexible schedules |
| Challenges | Scheduling conflicts, less flexibility, reliance on stable internet | Lack of immediate support, potential procrastination, less engagement |
Understanding Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning
Synchronous learning involves real-time interaction between instructors and students via live video sessions, enabling immediate feedback and collaboration. Asynchronous learning allows students to access materials, lectures, and assignments on their own schedule, promoting flexibility and self-paced study. Understanding these modes helps educators design effective curricula that balance engagement with accessibility.
Key Differences Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Methods
Synchronous learning involves real-time interaction between instructors and students through live lectures, video conferences, or chat sessions, enabling immediate feedback and collaboration. In contrast, asynchronous learning allows students to access course materials, lectures, and assignments at their convenience, promoting flexible pacing but reducing instant communication. Key differences include the timing of participation, level of direct engagement, and the adaptability of the learning schedule to individual needs.
Benefits of Synchronous Learning Approaches
Synchronous learning enables real-time interaction between instructors and students, fostering immediate feedback and active engagement that enhances comprehension and retention. This approach supports dynamic discussions, collaborative activities, and the development of communication skills vital for academic success. Institutions adopting synchronous methods often report higher student motivation and improved classroom community compared to asynchronous formats.
Advantages of Asynchronous Learning Formats
Asynchronous learning formats offer students flexibility to access course materials and complete assignments at their own pace, enhancing time management and accommodating diverse schedules. This method promotes deeper understanding by allowing learners to revisit content multiple times and engage in reflective thinking without the pressure of real-time participation. Furthermore, asynchronous learning supports a wider range of learning styles and provides accessibility for students across different time zones, making education more inclusive and adaptable.
Challenges in Implementing Synchronous Learning
Synchronous learning faces challenges including scheduling conflicts, limited flexibility for students across different time zones, and reliance on stable internet connectivity, which can disrupt real-time interactions. Educators also encounter difficulties in engaging all students simultaneously, managing classroom dynamics virtually, and providing immediate personalized feedback. These obstacles often result in decreased participation and increased dropout rates compared to asynchronous learning environments.
Overcoming Limitations of Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous learning often faces challenges like reduced real-time interaction and delayed feedback, which can hinder student engagement and comprehension. Utilizing strategies such as scheduled live discussions, timely instructor responses, and interactive multimedia content can mitigate these limitations. Enhancing the learning experience this way fosters better communication and ensures more effective knowledge retention, bridging the gap between asynchronous and synchronous education.
Synchronous vs Asynchronous for Different Learner Types
Synchronous learning benefits social and auditory learners by providing real-time interaction and immediate feedback, enhancing engagement and collaboration. Asynchronous learning suits reflective and independent learners who thrive on self-paced study, allowing flexibility and deeper content absorption. Both methods can be strategically combined to address diverse learner needs and maximize educational outcomes.
Impact on Student Engagement and Participation
Synchronous learning fosters immediate interaction and real-time feedback, increasing student engagement through live discussions and collaborative activities. Asynchronous learning allows flexible access to content, enabling students to participate at their own pace but often results in lower spontaneous interaction and delayed responses. Balancing both approaches can enhance participation by catering to diverse learning preferences and schedules.
Technology Requirements for Both Learning Modes
Synchronous learning requires robust technology such as high-speed internet, video conferencing platforms like Zoom or Microsoft Teams, and devices equipped with webcams and microphones for real-time interaction. Asynchronous learning depends on reliable learning management systems (LMS) like Canvas or Blackboard that support pre-recorded lectures, discussion boards, and assignment submissions accessible anytime. Both modes demand strong cybersecurity measures and user-friendly interfaces to ensure seamless access and protect student data.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Educational Goals
Synchronous learning offers real-time interaction and immediate feedback, ideal for collaborative projects and subjects requiring instant clarification. Asynchronous learning provides flexibility, allowing students to access materials and complete coursework at their own pace, which benefits diverse schedules and promotes self-directed study. Selecting the appropriate method depends on factors such as course objectives, learner autonomy, technological access, and the need for engagement or flexibility.
synchronous learning vs asynchronous learning Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com