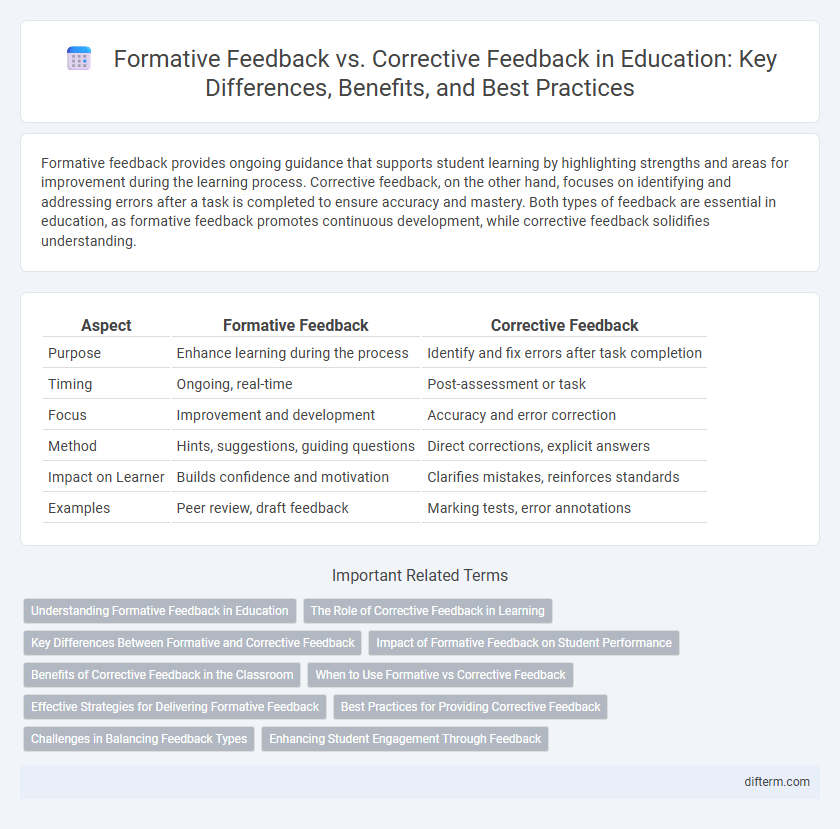
Formative feedback provides ongoing guidance that supports student learning by highlighting strengths and areas for improvement during the learning process. Corrective feedback, on the other hand, focuses on identifying and addressing errors after a task is completed to ensure accuracy and mastery. Both types of feedback are essential in education, as formative feedback promotes continuous development, while corrective feedback solidifies understanding.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Formative Feedback | Corrective Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhance learning during the process | Identify and fix errors after task completion |
| Timing | Ongoing, real-time | Post-assessment or task |
| Focus | Improvement and development | Accuracy and error correction |
| Method | Hints, suggestions, guiding questions | Direct corrections, explicit answers |
| Impact on Learner | Builds confidence and motivation | Clarifies mistakes, reinforces standards |
| Examples | Peer review, draft feedback | Marking tests, error annotations |
Understanding Formative Feedback in Education
Formative feedback in education is an ongoing process that provides students with constructive insights to enhance learning and improve performance before final evaluations. It emphasizes identifying strengths and areas for growth, promoting self-reflection and active engagement with the material. Unlike corrective feedback, which addresses errors post-assessment, formative feedback fosters continuous development and deeper understanding throughout the learning journey.
The Role of Corrective Feedback in Learning
Corrective feedback plays a crucial role in learning by identifying specific errors and guiding students toward accurate understanding and skill development. It helps learners recognize misconceptions, refine their knowledge, and improve performance through targeted interventions. Effective corrective feedback supports continuous progression and mastery within educational settings.
Key Differences Between Formative and Corrective Feedback
Formative feedback provides ongoing, constructive insights aimed at improving student learning processes while corrective feedback focuses on identifying and fixing specific errors or misconceptions. Formative feedback encourages self-reflection and skill development through timely, detailed comments, whereas corrective feedback often involves direct error correction to ensure accuracy. The key differences lie in their purposes: formative feedback promotes growth and understanding, and corrective feedback ensures correctness and mastery of content.
Impact of Formative Feedback on Student Performance
Formative feedback significantly enhances student performance by providing ongoing, specific insights that help learners identify strengths and areas for improvement during the learning process. Studies reveal that students receiving formative feedback show increased engagement, higher retention rates, and improved mastery of subject matter compared to those who only receive corrective feedback. This targeted feedback fosters a growth mindset, encouraging students to take active roles in their learning and achieve better academic outcomes.
Benefits of Corrective Feedback in the Classroom
Corrective feedback in the classroom enhances student learning by addressing errors immediately, which helps solidify correct understanding and knowledge retention. It promotes active engagement by encouraging students to analyze and reflect on their mistakes, leading to improved critical thinking skills. This type of feedback supports differentiated instruction, allowing teachers to tailor guidance according to individual student needs and learning paces.
When to Use Formative vs Corrective Feedback
Formative feedback is most effective during the learning process to guide students' understanding and skill development while tasks are ongoing. Corrective feedback should be applied after task completion to address specific errors and reinforce accurate knowledge. Using formative feedback early encourages self-reflection and continuous improvement, whereas corrective feedback ensures clarity and accuracy in final outcomes.
Effective Strategies for Delivering Formative Feedback
Effective strategies for delivering formative feedback include providing specific, actionable comments that guide students toward improvement without discouraging effort. Using timely, frequent feedback helps learners adjust their understanding and skills continuously, enhancing retention and motivation. Incorporating questions and prompts encourages self-reflection and deeper engagement in the learning process.
Best Practices for Providing Corrective Feedback
Effective corrective feedback in education should be clear, specific, and focused on the task rather than the learner, promoting a growth mindset and encouraging improvement. Best practices include timely delivery, actionable suggestions, and maintaining a positive tone to motivate students without discouragement. Using evidence-based strategies such as scaffolding and peer-assisted feedback enhances understanding and facilitates skill development.
Challenges in Balancing Feedback Types
Balancing formative and corrective feedback presents challenges such as ensuring timely and specific responses that support student learning without causing confusion or frustration. Educators must carefully gauge when to encourage growth-oriented feedback versus direct error correction to maintain motivation and promote deeper understanding. Limited class time and diverse student needs complicate the effective integration of both feedback types in instructional practices.
Enhancing Student Engagement Through Feedback
Formative feedback enhances student engagement by providing timely, specific insights that guide learners' ongoing progress, fostering motivation and self-regulation. Corrective feedback primarily addresses errors after task completion, often limiting opportunities for immediate improvement and reflection. Integrating formative feedback strategies cultivates active participation and deeper understanding, ultimately supporting sustained academic growth.
Formative feedback vs Corrective feedback Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com